Vortioxetine
- CAS NO.:508233-74-7
- Empirical Formula: C18H22N2S
- Molecular Weight: 298.45
- MDL number: MFCD22380814
- EINECS: 823-919-6
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-02-23 21:28:46
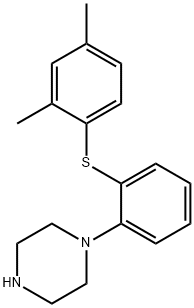
What is Vortioxetine?
Absorption
The maximal plasma vortioxetine concentration (Cmax) after dosing is reached within 7 to 11 hours postdose. Absolute bioavailability is 75%. No effect of food on the pharmacokinetics was observed.
Toxicity
The most commonly reported adverse effects during clinical trials were nausea, diarrhea, and dry mouth. The FDA label includes a blackbox warning for the following risks and complications: serotonin syndrome, especially when combined with other serotonergic agents; increased risk of abnormal bleeding, especially when combined with NSAIDs, aspirin, or other drugs that affect coagulation; activation of mania/hypomania; hyponatremia; and suicidal thoughts and behaviour in children, adolescents, and young adults.
Description
In September 2013, vortioxetine (also known as Lu AA21004) was approved in the United States for the treatment of major depressive disorder (MDD). Vortioxetine was discovered from a designed multiple ligand approach to identifying an antidepressant agent that combined SERT inhibition with 5-HT1A agonism to more rapidly desensitize 5-HT1A receptors and 5-HT3A antagonism to improve mood and cognitive function. Vortioxetine has a human SERT IC50=5.4 nM, an EC50=200 nM as a human 5-HT1A receptor agonist (efficacy=96%; Ki=39 nM), and an IC50=12 nM as a human 5-HT3A receptor antagonist (Ki=3.7 nM). It has weak inhibition of the dopamine and norepinephrine transporters, but high affinity for the human β1-noradrenergic receptor (Ki=46 nM), human 5-HT1B receptor (Ki=33 nM, partial agonist), and the human 5-HT-7 receptor (Ki=19 nM, antagonist).
Originator
Lundbeck (Denmark)
The Uses of Vortioxetine
Vortioxetine can be used in biological study of effectiveness of long term vortioxetine treatment of patients with major depressive disorder.
Indications
Vortioxetine is indicated for the treatment of major depressive disorder (MDD).
Background
Vortioxetine is an antidepressant medication indicated for the treatment of major depressive disorder (MDD). It is classified as a serotonin modulator and stimulator (SMS) as it has a multimodal mechanism of action towards the serotonin neurotransmitter system whereby it simultaneously modulates one or more serotonin receptors and inhibits the reuptake of serotonin. More specifically, vortioxetine acts via the following biological mechanisms: as a serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SRI) through inhibition of the serotonin transporter, as a partial agonist of the 5-HT1B receptor, an agonist of 5-HT1A, and an antagonist of the 5-HT3, 5-HT1D, and 5-HT7 receptors. SMSs were developed because there are many different subtypes of serotonin receptors, however, not all of these receptors appear to be involved in the antidepressant effects of SRIs. Some serotonin receptors seem to play a relatively neutral or insignificant role in the regulation of mood, but others, such as 5-HT1A autoreceptors and 5-HT7 receptors, appear to play an oppositional role in the efficacy of SRIs in treating depression.
Definition
ChEBI: An N-arylpiperazine in which the aryl group is specified as 2-[(2,4-dimethylphenyl)sulfanyl]phenyl. Used (as its hydrobromide salt) for treatment of major depressive disorder.
brand name
Brintellix
Pharmacokinetics
Vortioxetine binds with high affinity to the human serotonin transporter (Ki=1.6 nM), but not to the norepinephrine (Ki=113 nM) or dopamine (Ki>1000 nM) transporters. Vortioxetine potently and selectively inhibits reuptake of serotonin by inhibition of the serotonin transporter (IC50=5.4 nM). Specifically, vortioxetine binds to 5-HT3 (Ki=3.7 nM), 5-HT1A (Ki=15 nM), 5-HT7 (Ki=19 nM), 5-HT1D (Ki=54 nM), and 5-HT1B (Ki=33 nM), receptors and is a 5-HT3, 5-HT1D, and 5-HT7 receptor antagonist, 5-HT1B receptor partial agonist, and 5-HT1A receptor agonist.
Clinical Use
Antidepressant
Synthesis
The sequence involves iterative palladium-catalyzed carbon¨C heteroatom bond formations, the first establishing the thioethereal bond between commercially available thiol (213) and o-iodobromobenzene (214) employing conditions described by Schopfer and Schlapbach. Next, Buchwald¨CHartwig conditions were employed to establish the piperazine linkage, and this was followed by subjection to warm hydrobromic acid to furnish vortioxetine hydrobromide (XXVI) in 75% yield across the entire three-step sequence.

in vitro
vortioxetine (lu aa21004) was the lead compound, displaying high affinity for recombinant human 5-ht1a (ki = 15 nm), 5-ht1b (ki = 33 nm), 5-ht3a (ki = 3.7 nm), 5-ht7 (ki = 19 nm), and noradrenergic β1 (ki = 46 nm) receptors, and sert (ki = 1.6 nm). vortioxetine displayed antagonistic properties at 5-ht3a and 5-ht7 receptors, partial agonist properties at 5-ht1b receptors, agonistic properties at 5-ht1a receptors, and potent inhibition of sert [1].
in vivo
in conscious rats, vortioxetine significantly increased extracellular 5-ht levels in the brain after acute and 3 days of treatment. following the 3-day treatment (5 or 10 mg/kg/day) sert occupancies were only 43% and 57%, respectively [1].
Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Antibacterials: avoid with linezolid; concentration
reduced by rifampicin - consider increasing
vortioxetine dose.
Antidepressants: possible increased risk of
convulsions with SSRIs and, tricyclics; avoid with
moclobemide; increased risk of hypertension and
CNS excitation with MAOIs - avoid.
Antiepileptics: concentration possibly reduced by
carbamazepine, fosphenytoin and phenytoin -
consider increasing vortioxetine dose.
Antimalarials: possible increased risk of convulsions
with mefloquine; avoid with artemether with
lumefantrine and artenimol with piperaquine.
Antipsychotics: possible increased risk of convulsions
with butyrophenones, phenothiazines and
thioxanthenes.
Dopaminergics: risk of CNS excitation and
hypertension with rasagiline and selegiline.
Metabolism
Vortioxetine is extensively metabolized primarily through oxidation via cytochrome P450 isozymes CYP2D6, CYP3A4/5, CYP2C19, CYP2C9, CYP2A6, CYP2C8 and CYP2B6 and subsequent glucuronic acid conjugation. CYP2D6 is the primary enzyme catalyzing the metabolism of vortioxetine to its major, pharmacologically inactive, carboxylic acid metabolite, and poor metabolizers of CYP2D6 have approximately twice the vortioxetine plasma concentration of extensive metabolizers.
Metabolism
Vortioxetine is extensively metabolised in the liver, mainly
by oxidation catalysed by CYP2D6 and to a minor extent
CYP3A4/5 and CYP2C9, and subsequent glucuronic
acid conjugation. The major metabolite of vortioxetine is
pharmacologically inactive.
Approximately two thirds of the inactive vortioxetine
metabolites are excreted in the urine and approximately
one third in the faeces. Only negligible amounts of
vortioxetine are excreted in the faeces.
References
[1] bang-andersen b, ruhland t, jørgensen m, smith g, frederiksen k, jensen kg, zhong h, nielsen sm, hogg s, mørk a, stensbøl tb. discovery of 1-[2-(2,4-dimethylphenylsulfanyl)phenyl]piperazine (lu aa21004): a novel multimodal compound for the treatment of major depressive disorder. j med chem. 2011;54(9):3206-21.
[2] theunissen el, street d, højer am, vermeeren a, van oers a, ramaekers jg. a randomized trial on the acute and steady-state effects of a new antidepressant, vortioxetine (lu aa21004), on actual driving and cognition. clin pharmacol ther. 2013;93(6):493-501.
Properties of Vortioxetine
| Melting point: | 115-117°C |
| Boiling point: | 424.8±45.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.16 |
| storage temp. | -20°C Freezer |
| solubility | DMSO (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly) |
| form | Solid |
| pka | 8.85±0.10(Predicted) |
| color | White to Off-White |
| InChI | InChI=1S/C18H22N2S/c1-14-7-8-17(15(2)13-14)21-18-6-4-3-5-16(18)20-11-9-19-10-12-20/h3-8,13,19H,9-12H2,1-2H3 |
Safety information for Vortioxetine
Computed Descriptors for Vortioxetine
| InChIKey | YQNWZWMKLDQSAC-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | N1(C2=CC=CC=C2SC2=CC=C(C)C=C2C)CCNCC1 |
New Products
3-Iodophenylacetic acid 3-Pyridineacetonitrile, α-hydroxy- 2-Propanamine, 1-chloro-, hydrochloride (9CI) 3-(hexyloxy)-4-(pyridin-3-yl)-1,2,5-thiadiazole 2-Hexyn-1-ol Dibenzo-18-crown-6 Nickel(II) perchlorate hexahydrate, 98% 4-Bromophenylacetonitrile, 95% 3-Bromo-4-fluoroaniline, 97% Sodium tetraborate decahydrate, 98% Palladium(II) acetate, trimer, Pd 99% 4-Bromo-2-chlorotoluene, 97% N N Dimethylformamide Dimethyl Acetal (Dmf Dma) 2,3-Dichloro Benzoyl Cyanide [Side Chain] Bis(2-Chloroethyl) Amine Hydrochloride L-Glutamic Acid Diethyl Ester Hydrochloride 5-(Difluoromethoxy)-2-Mercaptobenzimidazole 1-Ethyl-3-(3-Dimethylaminopropyl)-Carbodiimide Hydrochloride [EDC Hcl] 1,4-Napthoquinone Bromoiodomethane Sodium Bicarbonate Methylene Dichloride (MDC) Ethyl Acetate Indole-3-Carbinol (I3C)Related products of tetrahydrofuran



You may like
-
 508233-74-7 98%View Details
508233-74-7 98%View Details
508233-74-7 -
 Vortioxetine 99%View Details
Vortioxetine 99%View Details
508233-74-7 -
 Vortioxetine 508233-74-7 98%View Details
Vortioxetine 508233-74-7 98%View Details
508233-74-7 -
 508233-74-7 Vortioxetine 98%View Details
508233-74-7 Vortioxetine 98%View Details
508233-74-7 -
 Vortioxetine 508233-74-7 98%View Details
Vortioxetine 508233-74-7 98%View Details
508233-74-7 -
 508233-74-7 Vortioxetine 98%View Details
508233-74-7 Vortioxetine 98%View Details
508233-74-7 -
 Vortioxetine 95% CAS 508233-74-7View Details
Vortioxetine 95% CAS 508233-74-7View Details
508233-74-7 -
 132945-75-6 (S)-1-Boc-3-methanesulfonyloxy-pyrrolidine 98+View Details
132945-75-6 (S)-1-Boc-3-methanesulfonyloxy-pyrrolidine 98+View Details
132945-75-6
