Urea hydrogen peroxide
Synonym(s):Urea hydrogen peroxide;Carbamide peroxide;Hydrogen peroxide urea;Percarbamide;Hydrogen peroxide–Urea adduct
- CAS NO.:124-43-6
- Empirical Formula: CH6N2O3
- Molecular Weight: 94.07
- MDL number: MFCD00013119
- EINECS: 204-701-4
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:08:57
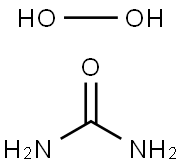
What is Urea hydrogen peroxide ?
Absorption
Upon treatment into the external auditory canal or the dental cavity, exposure to carbamide peroxide is limited to the intimate contact with the treated area without any systemic absorption.
Toxicity
Oral LD50 in rat is >2000 mg/kg .
Description
Carbamide peroxide is a combination of urea and hydrogen peroxide that is widely used at low concentrations (~10%) to whiten teeth. Upon contact with water, oxygen is released, providing the bleaching (oxidizing) power.
Description
Urea hydrogen peroxide (UHP) is a white crystalline solid that consists of 1:1 urea/hydrogen peroxide. As a solid, UHP serves as an easy to handle alternative to aqueous hydrogen peroxide. UHP dissolves in water to provide free hydrogen peroxide.
Chemical properties
White crystals or crystalline powder. Decomposed by moisture at temperatures around 40C. Soluble in water, alcohol, and ethylene glycol; solvents such as ether and acetone extract hydrogen peroxide and may form explosive solutions. Active oxygen (min) 16%
The Uses of Urea hydrogen peroxide
Urea hydrogen peroxide is an antiseptic, disinfectant and bleaching agent used in pharmaceuticals and cosmetics respectively. It is used in the whitening of teeth and relieves minor inflammation of gums, oral mucosal surfaces and lips. It finds application in the preparation of plastics, blue print development and starch modification. In addition to this, it is used as a source of hydrogen peroxide easily handled in the laboratory.
The Uses of Urea hydrogen peroxide

To a stirred solution of urea hydrogen peroxide (4.2 g, 43.8 mmol) in H2O (12 mL) was added NaOH (1.04 g, 25.5 mmol). The resulting mixture was cooled in an ice bath before a solution of the SM (1.00 g, 7.29 mmol) in EtOH (5 mL) was added. The reaction mixture was stirred vigorously at RT for 2 h. The mixture was diluted with H2O (100 mL) and EtOAc (100 mL) and was stirred 5 min, after which time 1M HCl was until pH 4. The layers were separated and the aq layer was further extracted with EtOAc (3 x 100 mL). The combined organics were dried (MgSO4) and concentrated to give a white solid. The solid was triturated with 2:1 ether/heptane (90 mL) for 1 h, before filtering to provide the product as a white solid. [1.05 g]
The Uses of Urea hydrogen peroxide
For extemporaneous preparation of H2O2.
Indications
Indicated as a dental bleaching agent.
Indicated as an oral wound healing agent in oral mucosal injuries.
Indicated as an aid in the removal of hardened ear wax.
What are the applications of Application
Hydrogen peroxide-Urea adduct is a chemical useful in many reactions
Background
Carbamide peroxide, also known as urea-hydrogen peroxide, is a water-soluble, white crystalline solid compound consisting of hydrogen peroxide and urea. As it is a source of hydrogen peroxide, it can be found in disinfecting and dental bleaching products. Some adverse effects of carbamide peroxide as a dental bleaching agent include dentin sensitivity and/or gingival irritation led by unstable and reactive H+ free radicals and low pH from prolonged use. It may also alter enamel surface morphology via enamel mineral loss and surface roughening . The FDA considers carbamide peroxide to be safe in oral mucosal injury drug products as an oral wound healing agent, although there is insufficient data to establish general recognition of the effectiveness of this ingredient as an oral wound healing agent . It is available in OTC otic drugs as non-water, non-oil-based solutions used to soften, loosen and remove excessive ear wax, or cerumen.
Definition
ChEBI: A mixture obtained by combining equimolar amounts of hydrogen peroxide and urea.
brand name
Murine Ear Drops (Ross).
General Description
A solid or paste-like semisolid. Used to make plastics.
Air & Water Reactions
Decomposed by moisture at about 40°C to yield a solution of hydrogen peroxide (nonhazardous reaction). Water soluble.
Reactivity Profile
Urea hydrogen peroxide is an oxidizing agent. Liable to spontaneous combustion when heated or in contact with organic materials. The contents of a screw-capped brown glass bottle spontaneously erupted after four years storage at ambient temperature. [MCA Case History No. 719]. Combustion may release Irritating ammonia gas.
Health Hazard
Inhalation of dust causes irritation of nose from hydrogen peroxide formed when heated. Contact with eyes causes severe damage. Contact with moist skin causes temporary itching or burning sensation. Ingestion causes irritation of mouth and stomach.
Flammability and Explosibility
Not classified
Pharmacokinetics
Carbamide peroxide releases hydrogen peroxide and free radicals upon contact with water or outer surfaces of ear and tooth. Hydrogen peroxide exerts cerumenolytic, enamel-bleaching and antiseptic actions. In vitro, the chemical stability of ceramics against bleaching agents was observed after treatment with 15% carbamide peroxide for 56 h, 16% carbamide peroxide for 126 h, 10% or 15% carbamide peroxide and 38% hydrogen peroxide for 30 minutes or 45 minutes, respectively . According to in vitro studies, high (37%) or low (10 or 16%) concentrated carbamide peroxide agents were similarly effective as oral bleaching agents . Treatment with carbamide peroxide may lead to demineralization which involves decreased mineral content of enamel calcium, phosphate, and fluoride, and alteration of the chemical, structural, and mechanical properties . Carbamide peroxide may affect the organic components of the enamel and lead to increased susceptibility to erosion, fracture stability or decreased abrasion resistance of the treated area .
Clinical Use
Carbamide peroxide (Gly-Oxide) is a stable complex of ureaand hydrogen peroxide. It has the molecular formulaH2NCONH2 H2O2. The commercial preparation is a solutionof 12.6% carbamide peroxide in anhydrous glycerin.When mixed with water, hydrogen peroxide is liberated.Carbamide peroxide is used as both an antiseptic and disinfectant.The preparation is especially effective in the treatmentof oral ulcerations or in dental care. The oxygen bubblesthat are liberated remove debris.
Metabolism
No established pharmacokinetic data.
Purification Methods
It is a safe alternative to H2O2 in various oxidation reactions. It is commercially available in tablets (“rapidly soluble”, equivalent to ~30% H2O2) or as a white powder (with 15-17% active oxygen). It is usually used without purification after assaying for active oxygen. This is done by titration with potassium permanganate or by iodometry, i.e. titration of liberated iodine when glacial acetic acid containing Fe3+ and NaI are added. It can be recrystallised from 30% H2O2 in a molar ratio of ~2:3 by heating in a pyrex dish for a few minutes at ~60o, cooling and allowed to crystallise slowly by evaporation in a crystallising dish. It forms elongated white needles, but if the solution is seeded just before crystallisation and shaken gently for as few seconds, then small plates are formed. Perferably collect the crystals by centrifugation at low temperature and dry them at 0o in vacuo. When dry, it is stable at room temperature and it has been reported that the available oxygen content had not decreased noticeably after 12 months. However, it is best to store it dry at low temperature. It is soluble in organic solvents e.g. EtOH, Et2O, CHCl3, CH2Cl2 and Me2CO with slow decomposition, and its solubility in H2O is 40% where it also decomposes slowly. It decomposes slowly at 40-60o/20mm and at 55-70o/760mm in air, but decomposition appears to accelerate above 80o. It is very useful (and in many cases superior to p-chloroperbenzoic acid) in the oxidation of alkenes, (epoxides), aromatic hydrocarbons (to phenols), ketones (Baeyer-Villiger), sulfides (to sulfones) and N-heterocycles (to N-oxides) when using 5 to 10 molar ratios of oxidant in the presence of acetic or trifluoroacetic anhydrides. Care should be used with this reagent as it is potentially explosive. [Lu et al. J Am Chem Soc 63 1508 1941, Cooper et al. Synlett 533 1990, Beilstein 3 H 54, 3 I 25, 3 II 45, 3 III 105, 3 IV 102.]
Properties of Urea hydrogen peroxide
| Melting point: | 90-93 °C (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 175.5°C (rough estimate) |
| vapor pressure | 23.3 mm Hg ( 30 °C) |
| RTECS | T4860000 |
| refractive index | 1.4616 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | Store at +15°C to +25°C. |
| solubility | H2O: 0.5 g/mL, clear to very faintly hazy |
| form | tablets |
| appearance | White solid |
| color | White |
| PH | 6.3 (H2O, 20℃) |
| Water Solubility | 500 g/L (20 ºC) |
| Sensitive | Hygroscopic |
| Merck | 14,1782 |
| BRN | 3680414 |
| Exposure limits | NIOSH: TWA 5 mg/m3 |
| Stability: | Unstable. Oxidizer. Severe explosion hazard on exposure to shock or heat. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents, organic materials, reducing agents, finely powdered metals. May form explosive solutions with ether or propanone. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 124-43-6(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Carbamide peroxide (124-43-6) |
Safety information for Urea hydrogen peroxide
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Flame Over Circle Oxidizers GHS03  Corrosion Corrosives GHS05 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H272:Oxidising liquids;Oxidising solids H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H318:Serious eye damage/eye irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P210:Keep away from heat/sparks/open flames/hot surfaces. — No smoking. P220:Keep/Store away from clothing/…/combustible materials. P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P302+P352:IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of soap and water. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Urea hydrogen peroxide
New Products
Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate (S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL 3-(2,4-Dimethoxybenzyl)dihydropyrimidine-2,4(1H,3H)-dione 7-Bromo-1H-indazole N-octanoyl benzotriazole 3,4-Dibenzyloxybenzaldehyde 4-Hydrazinobenzoic acid Electrolytic Iron Powder Fmoc-Val-Cit-PAB 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 4-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 1-(4-Methylphenylsulfonyl)-1H-1,2,3-benzotriazole 1-(2-Chlorobenzyl)-4-nitro-1H-pyrazole 1-(2-Nitrophenyl)-4-phenylpiperazineRelated products of tetrahydrofuran




You may like
-
 Urea hydrogen peroxide adduct CAS 124-43-6View Details
Urea hydrogen peroxide adduct CAS 124-43-6View Details
124-43-6 -
 Hydrogen peroxide–Urea adduct CAS 124-43-6View Details
Hydrogen peroxide–Urea adduct CAS 124-43-6View Details
124-43-6 -
 Hydrogen Peroxide Urea 96% CAS 124-43-6View Details
Hydrogen Peroxide Urea 96% CAS 124-43-6View Details
124-43-6 -
 Ste-Glu-AEEA-AEEA-OSUView Details
Ste-Glu-AEEA-AEEA-OSUView Details
1169630-40-3 -
 1446013-08-6 Fmoc-His-Aib-OH TFA 98%View Details
1446013-08-6 Fmoc-His-Aib-OH TFA 98%View Details
1446013-08-6 -
 127464-43-1 99%View Details
127464-43-1 99%View Details
127464-43-1 -
 2-ETHYLPYRIDINE 100-71-0 99%View Details
2-ETHYLPYRIDINE 100-71-0 99%View Details
100-71-0 -
 13162-05-5 99%View Details
13162-05-5 99%View Details
13162-05-5