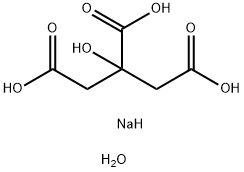
Trisodium citrate dihydrate
Synonym(s):Citric acid trisodium salt dihydrate;Natrii citras;Sodium citrate tribasic dihydrate;Trisodium citrate dihydrate;Trisodium Citrate, Sodium Citrate, Dihydrate
- CAS NO.:6132-04-3
- Empirical Formula: C6H9Na3O9
- Molecular Weight: 294.1
- MDL number: MFCD00150031
- EINECS: 612-118-5
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-04-28 21:36:36
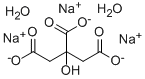
What is Trisodium citrate dihydrate?
Chemical properties
white powder or colourless crystals
Chemical properties
Sodium citrate dihydrate consists of odorless, colorless, monoclinic crystals, or a white crystalline powder with a cooling, saline taste. It is slightly deliquescent in moist air, and in warm dry air it is efflorescent. Although most pharmacopeias specify that sodium citrate is the dihydrate, the USP 32 states that sodium citrate may be either the dihydrate or anhydrous material.
The Uses of Trisodium citrate dihydrate
Trisodium citrate dihydrate, is widely applied in food, beverages and fillers as a buffering, sequestering or an emulsifying agent. It used as an anticoagulant in blood transfusions, osmotic laxative, functional fluids, solvents cleaning, furnishing care products, laundry dishwashing products and cleaning automobile radiators.
The Uses of Trisodium citrate dihydrate
An anticoagulant also used as a biological buffer
The Uses of Trisodium citrate dihydrate
Sodium citrate is chiefly used as a food additive, usually for flavor or as a preservative.
The Uses of Trisodium citrate dihydrate
Anticoagulant for collection of blood. In photography; as sequestering agent to remove trace metals; as emulsifier, acidulant and sequestrant in foods.
What are the applications of Application
Sodium Citrate, Dihydrate is an anticoagulant also used as a biological buffer
What are the applications of Application
Sodium Citrate Tribasic Dihydrate (Molecular Biology Grade) is for the preparation of total ribosomal RNA from E. coli
Definition
ChEBI: The dihydrate of trisodium citrate.
Production Methods
Sodium citrate is prepared by adding sodium carbonate to a solution of citric acid until effervescence ceases. The resulting solution is filtered and evaporated to dryness.
General Description
Sodium citrate tribasic dihydrate is the tribasic dihydrate sodium salt of citric acid.
Pharmaceutical Applications
Sodium citrate, as either the dihydrate or anhydrous material, is
widely used in pharmaceutical formulations.
It is used in food products, primarily to adjust the pH of
solutions. It is also used as a sequestering agent. The anhydrous
material is used in effervescent tablet formulations. Sodium citrate
is additionally used as a blood anticoagulant either alone or in
combination with other citrates such as disodium hydrogen citrate.
Therapeutically, sodium citrate is used to relieve the painful
irritation caused by cystitis, and also to treat dehydration and
acidosis due to diarrhea.
Biological Activity
Commonly used laboratory reagent
Biochem/physiol Actions
Sodium citrate can act as a buffering agent, resisting changes in pH. Used in blood collection tubes, the citrate chelates calcium ions in blood and thereby disrupts blood clotting. Citrate is a intermediate in the TCA cycle and fatty acid synthesis. Citrate is an allosteric modulator of acetyl-CoA carboxylase, the enzyme that regulates the conversion of acetyl-CoA to malonyl-CoA.
Safety
After ingestion, sodium citrate is absorbed and metabolized to
bicarbonate. Although it is generally regarded as a nontoxic and
nonirritant excipient, excessive consumption may cause gastrointestinal
discomfort or diarrhea. Therapeutically, in adults, up to
15 g daily of sodium citrate dihydrate may be administered orally, in
divided doses, as an aqueous solution to relieve the painful irritation
caused by cystitis.
Citrates and citric acid enhance intestinal aluminum absorption
in renal patients, which may lead to increased, harmful serum
aluminum levels. It has therefore been suggested that patients with
renal failure taking aluminum compounds to control phosphate
absorption should not be prescribed citrate- or citric acid-containing
products.
storage
Sodium citrate dihydrate is a stable material. Aqueous solutions
may be sterilized by autoclaving. On storage, aqueous solutions may cause the separation of small, solid particles from glass
containers.
The bulk material should be stored in an airtight container in a
cool, dry place.
Purification Methods
Crystallise the salt from warm water by cooling to 0o. [Beilstein 3 III 1100, 3 IV 1274.]
Incompatibilities
Aqueous solutions are slightly alkaline and will react with acidic substances. Alkaloidal salts may be precipitated from their aqueous or hydro-alcohol solutions. Calcium and strontium salts will cause precipitation of the corresponding citrates. Other incompatibilities include bases, reducing agents, and oxidizing agents.
Regulatory Status
GRAS listed. Accepted for use as a food additive in Europe. Included in the FDA Inactive Ingredients Database (inhalations; injections; ophthalmic products; oral solutions, suspensions, syrups and tablets; nasal, otic, rectal, topical, transdermal, and vaginal preparations). Included in nonparenteral and parenteral medicines licensed in the UK. Included in the Canadian List of Acceptable Non-medicinal Ingredients.
Properties of Trisodium citrate dihydrate
| Melting point: | >300 °C(lit.) |
| Density | 1.76 |
| FEMA | 3026 | SODIUM CITRATE |
| Flash point: | 173.9 °C |
| storage temp. | Store at +5°C to +30°C. |
| solubility | H2O: 100 mg/mL |
| form | powder |
| color | white |
| PH | 7.0-9.0 (25℃, 50mg/mL in H2O) |
| Odor | Odorless |
| PH Range | 7.5 - 9 at 29.4 g/l at 25 °C |
| Water Solubility | 720 g/L (25 ºC) |
| λmax | λ: 260 nm Amax: 0.01 λ: 280 nm Amax: 0.01 |
| Merck | 14,8602 |
| BRN | 6104939 |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with bases, reducing agents, oxidizing agents. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 6132-04-3(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | 1,2,3-Propanetricarboxylic acid, 2-hydroxy-, trisodium salt, dihydrate (6132-04-3) |
Safety information for Trisodium citrate dihydrate
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Corrosion Corrosives GHS05  Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H318:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. P337+P313:IF eye irritation persists: Get medical advice/attention. |
Computed Descriptors for Trisodium citrate dihydrate
| InChIKey | NLJMYIDDQXHKNR-UHFFFAOYSA-K |
Trisodium citrate dihydrate manufacturer
JSK Chemicals
ASM Organics
New Products
Ethyl 3,3- diethoxypropionate 7-Bromo-2-chloroquinoxaline N-Benzyl-3-hydroxypiperidine 2-(4-bromophenyl)-2-methylpropanoic acid Benzylacetoacetate Radiator Flux Zinc Chloride Solution (All Grades) Phenylazomalononitrile 2-Fluoro-6-iodobenzoic acid 3-(4-bromo-3-methyl-2-oxo-2,3-dihydro-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-1-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 2,3-Difluoro-6-methoxybenzyl Chloride 2-(6-(benzyloxy)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-2-yl)-4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolane Ethyl2-oxo-2,3,9,10-tetrahydro-1H-pyrido[3',4':4,5]pyrrolo[1,2,3-de]quinoxaline-8(7H)-carboxylate Acetyl-meldrum's acid 3-(hexyloxy)-4-(pyridin-3-yl)-1,2,5-thiadiazole 2-Hexyn-1-ol Dibenzo-18-crown-6 2-Propanamine, 1-chloro-, hydrochloride (9CI) 3-Pyridineacetonitrile, α-hydroxy- 3-Iodophenylacetic acid N Ethylmethylamine Ethyl Methanesulfonate N N' DimethylEthylenediamine Lead II BromideRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 Trisodium citrate dihydrate 98%View Details
Trisodium citrate dihydrate 98%View Details -
 Trisodium citrate dihydrate 99%View Details
Trisodium citrate dihydrate 99%View Details -
 Sodium citrate dihydrate 99% CASView Details
Sodium citrate dihydrate 99% CASView Details -
 Sodium citrate dihydrate CASView Details
Sodium citrate dihydrate CASView Details -
 tri-SODIUM CITRATE DIHYDRATE AR/ACS CASView Details
tri-SODIUM CITRATE DIHYDRATE AR/ACS CASView Details -
 Sodium citrate dihydrate, 99% 99%View Details
Sodium citrate dihydrate, 99% 99%View Details -
 tri-SODIUM CITRATE DIHYDRATE Molecular Biology CASView Details
tri-SODIUM CITRATE DIHYDRATE Molecular Biology CASView Details -
 tri-SODIUM CITRATE DIHYDRATE Extra Pure CASView Details
tri-SODIUM CITRATE DIHYDRATE Extra Pure CASView Details
