Trimetrexate
- CAS NO.:52128-35-5
- Empirical Formula: C19H23N5O3
- Molecular Weight: 369.42
- MDL number: MFCD00866404
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-10-23 13:36:13
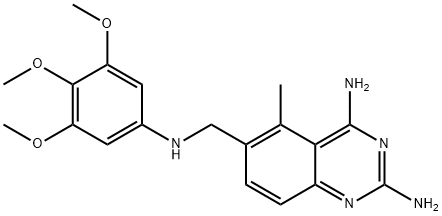
What is Trimetrexate?
Toxicity
The LD50 of intravenous trimetrexate in mice is 62 mg/kg (186 mg/m2). Myelosuppression is a dose-limiting toxic effect.
Description
Trimetrexate (TMQ) has been approved for the treatment of Pneumocystis carinii in patients with AIDS and also exhibits antiprotozoal activity against Trypanosoma cruzi . The drug is available as a single-ingredient medication, but it can be administered along with folinic acid in much the same way that methotrexate is administered with calcium leucovorin in cancer chemotherapy. Trimetrexate is a derivative of methotrexate.
The Uses of Trimetrexate
Trimetrexate is an FDA-approved drug which selectively inhibits Streptococcus mutans through targeting dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR).
The Uses of Trimetrexate
Antineoplastic.
Indications
For use, with concurrent leucovorin administration (leucovorin protection), as an alternative therapy for the treatment of moderate-to-severe Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia (PCP) in immunocompromised patients, including patients with the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS). Also used to treat several types of cancer including colon cancer.
Background
A nonclassical folic acid inhibitor through its inhibition of the enzyme dihydrofolate reductase. It is being tested for efficacy as an antineoplastic agent and as an antiparasitic agent against pneumocystis pneumonia in AIDS patients. Myelosuppression is its dose-limiting toxic effect.
Definition
ChEBI: Trimetrexate is a member of quinazolines. It has a role as an antifungal drug.
General Description
The drug is available as a lyophilized powder in 5- or 30-mgvials for IV use. The drug is used to treat colorectal cancer,head and neck cancer as well as NSCLC. The mechanism ofaction of trimetrexate involves folate antagonism and inhibitionof thymidylate synthesis. Trimetrexate does not formintracellular polyglutamate adducts as does methotrexateand other related compounds. Resistance can occur by increasedexpression of the target enzyme, decreased bindingaffinity for the target enzyme, or decreased intracellulardrug transport. Trimetrexate is administered only by the IVroute and distributed throughout the body with extensivebinding to plasma proteins. The major catabolic pathwaysinvolve O-demethylation followed by glucuronide conjugation.The drug interaction and toxicity profiles are similar tothose for methotrexate.
Mechanism of action
Trimetrexate is considered to be a nonclassical folate antagonist, whereas methotrexate, the structurally similar analogue of TMQ, is a classical folate antagonist. The difference between these two drugs is that methotrexate, with its polar glutamate side chain, is transported into the cell via a carrier-mediated transport system, whereas TMQ, without the glutamate moiety, is absorbed by the cell via a passive diffusion. Once in the cell, TMQ inhibits DHFR. Trimetrexate binds to Pneumocystis cari nii DHFR 1,500 times more strongly than trimethoprim and somewhat more strongly than methotrexate. It also has been reported that TMQ readily enters the P. carinii cell because of the lipophilic nature of this drug. Methotrexate and leucovorin are not able to enter the cell, however, because the cell membrane of P. carinii does not possess the transporter protein.
Pharmacokinetics
Trimetrexate, a non-classical folate antagonist, is a synthetic inhibitor of the enzyme dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR). During DNA synthesis and cellular reproduction, folic acid is reduced to tetrahydrofolic acid by the enzyme folic acid reductase. By interfering with the reduction of folic acid, trimetrexate interferes with tissue cell reproduction. Generally, the most sensitive cells to the antimetabolite effect of trimetrexate are those cells which are most actively proliferating such as malignant cells, dermal epithelium, buccal and intestinal mucosa, bone marrow, fetal cells, and cells of the urinary bladder. Because the proliferation of cells in malignant tissues is greater than in most normal tissues, trimetrexate may impair the growth of the malignant tissues without causing irreversible damage to normal tissues. Due to very serious and potentially life-threatening side-effects of this drug, leucovorin must be co-administered for at least 72 hours after the last dose.
Clinical Use
Trimetrexate, when combined with the cytoprotective agent leucovorin, is more effective and better tolerated than pentamidine in the treatment of PCP. Because the first- and second-line agents are successful in only 50 to 75% of these cases, and because adverse reactions severely limit the use of some of the older agents, TMQ may offer some advantages in treatment. Trimetrexate is administered by IV infusion over 60 to 90 minutes and should be combined with the cytoprotective drug leucovorin. The leucovorin protects against bone marrow suppression and against renal and hepatic dysfunction. Leucovorin administration should continue for 72 hours after the last dose of TMQ. Additionally, TMQ has been reported to be effective in the treatment of Chagas' disease.
Metabolism
Hepatic. Preclinical data strongly suggest that the major metabolic pathway is oxidative O-demethylation, followed by conjugation to either glucuronide or the sulfate.
Properties of Trimetrexate
| Melting point: | 215-217 °C |
| Boiling point: | 647.0±65.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.305±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C(protect from light) |
| solubility | DMSO : ≥ 61.5 mg/mL (166.48 mM) |
| form | Solid |
| pka | 8.09±0.30(Predicted) |
| color | Light yellow to green yellow |
Safety information for Trimetrexate
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Trimetrexate
New Products
Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid DIETHYL AMINOMALONATE HYDROCHLORIDE 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 -
 733039-20-8 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 98+View Details
733039-20-8 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 98+View Details
733039-20-8