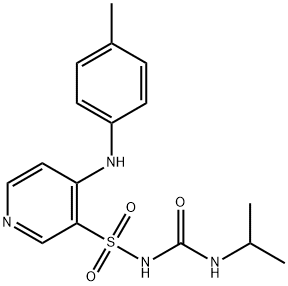
Torasemide
Synonym(s):Demadex;N-[[(1-Methylethyl)amino]carbonyl]-4-[(3-methylphenyl)amino]-3-pyridinesulfonamide
- CAS NO.:56211-40-6
- Empirical Formula: C16H20N4O3S
- Molecular Weight: 348.42
- MDL number: MFCD00866166
- EINECS: 637-197-3
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-07-04 15:10:57

What is Torasemide?
Absorption
Torasemide is the diuretic with the highest oral bioavailability even in advanced stages of chronic kidney disease. This bioavailability tends to be higher than 80% regardless of the patient condition. The maximal serum concentration is reported to be of 1 hour and the absorption parameters are not affected by its use concomitantly with food.
Toxicity
The oral LD50 of torasemide in the rat is 5 g/kg. When overdose occurs, there is a marked diuresis with the danger of loss of fluid and electrolytes which has been seen to lead to somnolence, confusion, hypotension, hyponatremia, hypokalemia, hypochloremic alkalosis, hemoconcentration dehydration and circulatory collapse. This effects can include some gastrointestinal disturbances.
There is no increase in tumor incidence with torasemide and it is proven to not be mutagenic, not fetotoxic or teratogenic.
Description
Torasemide is a novel loop diuretic launched in 1993 after a 12-year gap from the last diuretic introduction. It is indicated for the treatment of hypertension and edema associated with chronic congestive heart failure, renal disease and hepatic cirrhosis. Torasemide exerts its major diuretic activity on the thick ascending limb of the Henle's loop to promote rapid and marked excretion of water, Na+, Cl-, and to a lesser extent,K+ and Ca2+. Compared with other loop diuretics such as furosemide, torasemide has a stronger antihypertensive action, a higher bioavailability, a longer duration of action that is independent of the renal function, and has no side effects such as paradoxical antidiuresis. The mechanism of its vasodilating effect has been suggested to result from, at least in part, the competitive antagonism of the thromboxane A2 receptor.
Chemical properties
Crystalline Solid
Originator
Hafslund Nycomed Germany; Italy (Norway)
The Uses of Torasemide
Used as a diuretic
The Uses of Torasemide
Torasemide is a loop diuretic. Diuretics have been abused as performance-enhancing drugs and masking agents in doping in sports. Use of torsemide is effective for the treatment of edema associated with chronic renal failure. The pharmacology of torasemide is similar to that of frusemide,though torasemide has a longer duration of action with a plasma half-life of approximately 3.5 hours. It also causes a less marked loss of potassiumand calcium.
Background
Torasemide is a high-ceiling loop diuretic. Structurally, it is a pyridine-sulfonylurea used as an antihypertensive agent. Torasemide was first approved for clinical use by the FDA in 1993.
Indications
Torasemide is indicated for the treatment of edema associated with congestive heart failure, renal or hepatic diseases. From this condition, it has been observed that torasemide is very effective in cases of kidney failure.
As well, torasemide is approved to be used as an antihypertensive agent either alone or in combination with other antihypertensives.
What are the applications of Application
Torsemide is an inhibitor of NKCC
Definition
ChEBI: Torasemide is an N-sulfonylurea obtained by formal condensation of [(3-methylphenyl)amino]pyridine-3-sulfonic acid with the free amino group of N-isopropylurea. It is a potent loop diuretic used for the treatment of hypertension and edema in patients with congestive heart failure. It has a role as a loop diuretic and an antihypertensive agent. It is a N-sulfonylurea, an aminopyridine and a secondary amino compound. It is functionally related to a 4-aminopyridine.
Manufacturing Process
In a 100 ml three-necked flask equipped with magnetic stirrer, condenser,
thermometer and dropping funnel 3-sulfonylchloride-4-chloropyridine (10 g, 1
eq., 46.7 mmoles) was suspended in t-butyl-methyl ether (MTBE) (30 ml) at
room temperature. Ammonium hydroxide, 25% solution (13.5 ml, 2.13 eq.)
was dropped into the suspension in a rate such that the temperature is
allowed to increase to 22°-26°C, this temperature was maintained until all the
ammonium hydroxide was added. The suspension was then to cooled to room
temperature and was stirred for 1 h. The pH of the suspension was adjusted
to 80.1 by the addition of a few drops of ammonium hydroxide, 25% solution.
The suspension was filtered and washed with water (2 times 10 ml) and the
wet product (8 g) dried at 40°C, under the 1 mm Hg vacuum. 3-Sulfonamide-
4-chloropyridine was isolated in 74.4% yield, 6.7 g.
A mixture of 0.01 moles of 3-sulfonamido-4-chloropyridine, 0.02 mole of 3-
methylbenzylamine and 50 ml of dry ethanol was heated to reflux
temperature for 9 h. After distillation of the ethanol the residue was taken up
in an excess of diluted NaOH and the excess of amine was extracted by
means of ether.
The aqueous solution was then decolourized with charcoal and filtered, and
the filtrate was neutralized with acetic acid. The precipitated product was
separated and purified by crystallization from a mixture of water and acetone.The 3-sulfonamido-4-(3-methylbenzyl)amino-pyridine crystallized in the form
of beige coloured cristals having a melting point of 184°-186°C.
0.01 mole of 3-sulfonamido-4-(3-methylbenzyl)amino-pyridine was reacted
with 0.015 mole of isopropylisocyanate in the presence of 0.02 mole of
triethylamine and of 20 ml of dichloromethane, at room temperature for 20 h.
After evaporation under vacuum, the residue was taken up in an excess of
diluted Na2CO3, filtered off and acidified by means of acetic acid. After
precipitation of the product it was filtered and washed several times with ice
cold water. The 3-isopropylcarbamoylsulfonamido-4-(3-methylbenzyl)amino_x0002_pyridine (Torsemide) showing as a white powder, has a melting point of 147°-
149°C.
brand name
Torasemide is INN and BAN;Unat;Toradiur.
Therapeutic Function
Diuretic
Biochem/physiol Actions
Torsemide is a loop diuretic of the pyridine-sulfonylurea class with antialdosteronergic properties and inhibitor of the Na+/K+/2Cl- carrier system.
Pharmacokinetics
It is widely known that administration of torasemide can attenuate renal injury and reduce the severity of acute renal failure. This effect is obtained by increasing urine output and hence, facilitating fluid, acid-base and potassium control. This effect is obtained by the increase in the excretion of urinary sodium and chloride.
Several reports have indicated that torasemide presents a long-lasting diuresis and less potassium excretion which can be explained by the effect that torasemide has on the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system. This effect is very similar to the effect observed with the administration of combination therapy with furosemide and spironolactone and it is characterized by a decrease in plasma brain natriuretic peptide and improved measurements of left ventricular function.
Above the aforementioned effect, torasemide presents a dual effect .in which the inhibition of aldosterone which donates torasemide with a potassium-sparing action.
Torasemide has been shown to reduce extracellular fluid volume and blood pressure in hypertensive patients suffering from chronic kidney disease. As well, some reports have indicated that torasemide can reduce myocardial fibrosis by reducing the collagen accumulation. This effect is suggested to be related to the decrease in aldosterone which in order has been shown to reduce the production of the enzyme procollagen type I carboxy-terminal proteinase which is known to be overexpressed in heart failure patients.
Clinical Use
Loop diuretic:
Hypertension
Oedema
Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Analgesics: increased risk of nephrotoxicity with
NSAIDs; antagonism of diuretic effect with
NSAIDs.
Anti-arrhythmics: risk of cardiac toxicity with
anti-arrhythmics if hypokalaemia occurs; effects of
lidocaine and mexiletine antagonised.
Antibacterials: increased risk of ototoxicity with
aminoglycosides, polymyxins and vancomycin; avoid
concomitant use with lymecycline.
Antidepressants: increased risk of hypokalaemia with
reboxetine; enhanced hypotensive effect with MAOIs;
increased risk of postural hypotension with tricyclics.
Antiepileptics: increased risk of hyponatraemia with
carbamazepine.
Antifungals: increased risk of hypokalaemia with
amphotericin.
Antihypertensives: enhanced hypotensive effect;
increased risk of first dose hypotensive effect
with alpha-blockers; increased risk of ventricular
arrhythmias with sotalol if hypokalaemia occurs.
Antipsychotics: increased risk of ventricular
arrhythmias with amisulpride or pimozide (avoid
with pimozide) if hypokalaemia occurs; enhanced
hypotensive effect with phenothiazines.
Atomoxetine: hypokalaemia increases risk of
ventricular arrhythmias.
Cardiac glycosides: increased toxicity if hypokalaemia
occurs.
Cytotoxics: increased risk of ventricular arrhythmias
due to hypokalaemia with arsenic trioxide; increased
risk of nephrotoxicity and ototoxicity with platinum
compounds.
Lithium: risk of toxicity.
Metabolism
Torasemide is extensively metabolized in the liver and only 20% of the dose remains unchanged and it is recovered in the urine. Metabolized via the hepatic CYP2C8 and CYP2C9 mainly by reactions of hydroxylation, oxidation and reduction to 5 metabolites. The major metabolite, M5, is pharmacologically inactive. There are 2 minor metabolites, M1, possessing one-tenth the activity of torasemide, and M3, equal in activity to torasemide. Overall, torasemide appears to account for 80% of the total diuretic activity, while metabolites M1 and M3 account for 9% and 11%, respectively.
Metabolism
Torasemide is metabolised by the cytochrome P450 isoenzyme CYP2C9 to three inactive metabolites, M1, M3 and M5 by stepwise oxidation, hydroxylation or ring hydroxylation. The inactive metabolites are excreted in the urine.
Properties of Torasemide
| Melting point: | 163-164°C |
| Density | 1.283±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | Keep in dark place,Inert atmosphere,Room temperature |
| solubility | DMSO: soluble18mg/mL |
| pka | 6.44(at 25℃) |
| form | solid |
| color | White |
| Water Solubility | Soluble |
| Merck | 14,9552 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 56211-40-6(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | 3-Pyridinesulfonamide, N-[[(1-methylethyl)amino]carbonyl]-4-[(3-methylphenyl)amino]- (56211-40-6) |
Safety information for Torasemide
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P201:Obtain special instructions before use. P202:Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood. P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. P308+P313:IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention. |
Computed Descriptors for Torasemide
| InChIKey | NGBFQHCMQULJNZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
Torasemide manufacturer
Jai Radhe Sales
New Products
Indole Methyl Resin tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Boc-His(Boc)-OH 2-CTC Resin 4-Chloro-7-tosy1-7Hpyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine 5,7-Dibromo-1H-indole 2,5-dichloro-N-hydroxy-4,6-dimethylpyridine-3-carboximidamide 2,2-Dimethoxy-7-azaspiro[3.5]nonane hydrochloride 4-chloromethyl-5-methyl-1,3-dioxol-2-one (DMDO-Cl) R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-((2-hydroxyethyl)thio)benzoic acid 1-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-2-PYRROLIDINONE Methyl 6-methylnicotinate 3-Pyridineacrylic acid tert-Butyl carbazate TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 1,3-Diethyl-1,3-Diphenylurea Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 TORSEMIDE 99%View Details
TORSEMIDE 99%View Details -
 Torasemide 99%View Details
Torasemide 99%View Details -
 Torasemide 98% CAS 56211-40-6View Details
Torasemide 98% CAS 56211-40-6View Details
56211-40-6 -
 Torsemide CAS 56211-40-6View Details
Torsemide CAS 56211-40-6View Details
56211-40-6 -
 Torsemide CAS 56211-40-6View Details
Torsemide CAS 56211-40-6View Details
56211-40-6 -
 Torsemide API Manufacturer India, Capacity: 5000kg, Packaging Size: 5KgView Details
Torsemide API Manufacturer India, Capacity: 5000kg, Packaging Size: 5KgView Details
56211-40-6 -
 Dytor Tablet (Torasemide), Cipla Ltd, 5 mg,10 mg,20 mg,40 mg,100 mgView Details
Dytor Tablet (Torasemide), Cipla Ltd, 5 mg,10 mg,20 mg,40 mg,100 mgView Details
56211-40-6 -
 99.99 Powder Torsemide Api Price, 56211-40-6View Details
99.99 Powder Torsemide Api Price, 56211-40-6View Details
56211-40-6
