Sulfanilamide
Synonym(s):Sulfanilamide;4-Aminobenzenesulfonamide;CHGC;Chromogranin-C;p-Aminobenzenesulfonamide
- CAS NO.:63-74-1
- Empirical Formula: C6H8N2O2S
- Molecular Weight: 172.2
- MDL number: MFCD00007939
- EINECS: 200-563-4
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-15 16:34:10
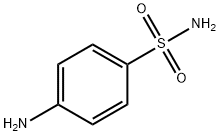
What is Sulfanilamide?
Absorption
Sulfonamides are absorbed through the vaginal mucosa. There are no pharmacokinetic data available describing how much of an intravaginal dose reaches the systemic circulation.
Toxicity
Oral, mouse LD50 = 3700 mg/kg; Intravenous, mouse LD50 = 621 mg/kg; Oral, rabbit LD50 = 1300 mg/kg. Side effects include itching, burning, skin rash, redness, swelling, or other sign of irritation not present before use of this medicine and long-term use of sulfonamides may cause cancer of the thyroid gland.
Description
Sulfanilamide was one of the earliest sulfonamide antimicrobials. It was first synthesized in 1908 by P. Gelmo and first used as a chemotherapeutic agent in 1935 by G. Domagk, J. Trefouel, and T. Trefouel. They thought that the drug was a complex sulfonamide; but it was later shown that its metabolite, sulfanilamide, was the true active substance.
Indications
For the treatment of vulvovaginitis caused by Candida albicans.
Background
Sulfanilamide is a molecule containing the sulfonamide functional group attached to an aniline.
Preparation
Sulfonamide is synthesized from acetanilide by chlorosulfonation, amination, hydrolysis, and neutralization:
Acetanilide is reacted with chlorosulfonic acid at 40~50℃, then cooled, slowly added to water for acid decomposition, precipitated at the same time, dried and filtered to obtain p-acetamidobenzenesulfonyl chloride, and then subjected to ammoniation, and the amination temperature is controlled at 40~ 45 ℃, and then hydrolyzed, acidified to obtain sulfonamide.
Antimicrobial activity
Sulfanilamide is a sulfonamide antibiotic. It is bacteriostatic against Streptococci in vitro at a concentration of 20 μg/ml and inhibits the growth of 106 clinically isolated strains of Gonococcus. Sulfanilamide reduces the concentration of Streptococcus in rabbit plasma ex vivo following four doses of 20 ml of a 2% sulfanilamide solution. Sulfonamide class antibiotics, of which sulfanilamide is a member, are bacteriostatic and inhibit bacterial synthesis of dihydrofolic acid by competing with 4-aminobenzoic acid for binding to dihydropteroate synthase. Formulations containing sulfanilamide have been used to treat T. vaginalis infections.
Pharmacokinetics
Sulfanilamide is a sulfonamide antibiotic. The sulfonamides are synthetic bacteriostatic antibiotics with a wide spectrum against most gram-positive and many gram-negative organisms. However, many strains of an individual species may be resistant. Sulfonamides inhibit multiplication of bacteria by acting as competitive inhibitors of p-aminobenzoic acid in the folic acid metabolism cycle. Bacterial sensitivity is the same for the various sulfonamides, and resistance to one sulfonamide indicates resistance to all. Most sulfonamides are readily absorbed orally. However, parenteral administration is difficult, since the soluble sulfonamide salts are highly alkaline and irritating to the tissues. The sulfonamides are widely distributed throughout all tissues. High levels are achieved in pleural, peritoneal, synovial, and ocular fluids. Although these drugs are no longer used to treat meningitis, CSF levels are high in meningeal infections. Their antibacterial action is inhibited by pus.
The Uses of Sulfanilamide
Sulfanilamide was one of the earliest sulfonamide antimicrobials. It was first synthesized in 1908 by P. Gelmo and first used as a chemotherapeutic agent in 1935 by G. Domagk, J. Trefouel, and T. Trefouel. They thought that the drug was a complex sulfonamide; but it was later shown that its metabolite, sulfanilamide, was the true active substance.
Overdose
There are no reports of sulfanilamide overdose. Vaginal sulfanilamide is systemically absorbed through the vaginal mucous membranes. Excessive use of sulfanilamide vaginal cream may intensify its side effects, which should resolve with discontinuation of the drug. Long term use of sulfanilamide can cause cancer of the thyroid gland.
Properties of Sulfanilamide
| Melting point: | 164-166 °C(lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 400.5±47.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.08 |
| vapor pressure | 0.00001 hPa (70 °C) |
| refractive index | 1.6490 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | 5.37g/l |
| form | powder |
| pka | pKa 10.65(H2O
t = 25.0±0.5
I = 0.2) (Uncertain) |
| color | white to faintly beige |
| Odor | Odorless |
| PH | 5.8-6.1 (5g/l, H2O, 20℃) |
| PH Range | 5.8 - 6.1 (0.5% aq.sol.) |
| Water Solubility | 7.5 g/L at 25 ºC |
| λmax | 257nm(H2O)(lit.) |
| Merck | 14,8925 |
| BRN | 511852 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 63-74-1(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Benzenesulfonamide, 4-amino-(63-74-1) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Sulfanilamide (63-74-1) |
Safety information for Sulfanilamide
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Corrosion Corrosives GHS05  Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H303:Acute toxicity,oral H314:Skin corrosion/irritation H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P301+P330+P331:IF SWALLOWED: Rinse mouth. Do NOT induce vomiting. P303+P361+P353:IF ON SKIN (or hair): Remove/Take off Immediately all contaminated clothing. Rinse SKIN with water/shower. P304+P340:IF INHALED: Remove victim to fresh air and Keep at rest in a position comfortable for breathing. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. P405:Store locked up. |
Computed Descriptors for Sulfanilamide
| InChIKey | FDDDEECHVMSUSB-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
Sulfanilamide manufacturer
JSK Chemicals
CEFA CILINAS BIOTICS PVT LTD
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 Sulfanilamide 98%View Details
Sulfanilamide 98%View Details -
 Sulphanilamide extrapure AR CAS 63-74-1View Details
Sulphanilamide extrapure AR CAS 63-74-1View Details
63-74-1 -
 Sulphanilamide pure CAS 63-74-1View Details
Sulphanilamide pure CAS 63-74-1View Details
63-74-1 -
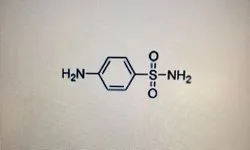 Sulfanilamide (CAS 63-74-1) Industrial grade- 98%minView Details
Sulfanilamide (CAS 63-74-1) Industrial grade- 98%minView Details
63-74-1 -
 99 % Sulfanilamide Chemical Powder, 63-74-1View Details
99 % Sulfanilamide Chemical Powder, 63-74-1View Details
63-74-1 -
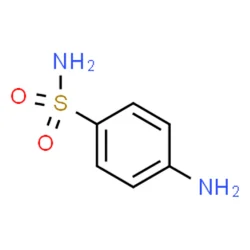 SulfanilamideView Details
SulfanilamideView Details
63-74-1 -
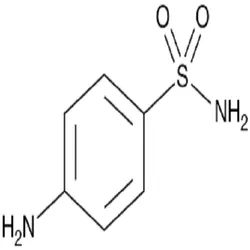 Reagent Grade Sulfanilamide PowderView Details
Reagent Grade Sulfanilamide PowderView Details
63-74-1 -
 SulphanilamideView Details
SulphanilamideView Details
63-74-1
