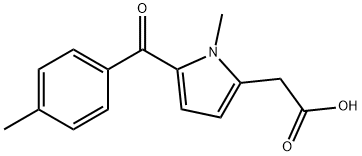
Tolmetin
- CAS NO.:26171-23-3
- Empirical Formula: C15H15NO3
- Molecular Weight: 257.28
- MDL number: MFCD00599595
- EINECS: 247-497-2
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:08:52
What is Tolmetin?
Absorption
Rapidly and almost completely absorbed with peak plasma levels being reached within 30-60 minutes after an oral therapeutic dose.
Toxicity
Symptoms of overdose include lethargy, drowsiness, nausea, vomiting, and epigastric pain.
Description
An antiinflammatory, analgesic, and antipyretic that is as efficacious as moderate doses of aspirin and better tolerated. Tolmetin produces a number of adverse effects including epigastric pain, dyspepsia, nausea, and vomiting. Tolmetin is approximately 99% plasma protein bound, yet does not interfere with concurrent treatment with oral hypoglycemics. Tolmetin has been found to be effective in the treatment of osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis.
Originator
Tolectin,McNeil,US,1976
The Uses of Tolmetin
Tolmetine is an NSAID.
The Uses of Tolmetin
inhibits synthesis of prostaglandins and exhibits expressed analgesic, anti-inflammatory, and fever-reducing properties. It is used for relieving weak to moderate pain in rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis.
Background
A non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agent (anti-inflammatory agents, NON-steroidal) similar in mode of action to indomethacin.
Indications
For the relief of signs and symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis, including the treatment of acute flares long-term management. Also for treatment of juvenile rheumatoid arthritis.
Definition
ChEBI: A monocarboxylic acid that is (1-methylpyrrol-2-yl)acetic acid substituted at position 5 on the pyrrole ring by a 4-methylbenzoyl group. Used in the form of its sodium salt dihydrate as a nonselective nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug.
Indications
Tolmetin (Tolectin) is indicated for the relief of osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, and moderate pain. It is ineffective in gouty arthritis for unknown reasons.Tolmetin can inhibit both COX-1 and COX-2 but has a moderate selectivity for COX-1. The most frequently reported side effects are GI disturbance and CNS reactions (e.g., headache, asthenia, and dizziness). These effects are less frequently observed than after aspirin or indomethacin use. Blood pressure elevation, edema, and weight gain or loss have been associated with tolmetin administration. Tolmetin metabolites in urine have been found to produce pseudoproteinuria in some laboratory tests.
Manufacturing Process
5-(p-Toluoyl)-1-methylpyrrole-2-acetonitrile - To a cooled suspension of 26.6 g
(0.2 mol) aluminum chloride in 80 ml dichloroethane is added dropwise 30.8 g
(0.2 mol) p-toluoyl chloride. The resulting solution is added dropwise to a
solution of 1-methylpyrrole-2-acetonitrile in 80 ml dichloroethane cooled
externally with an ice bath. After the addition, the resulting solution is stirred
at room temperature for 20 minutes and then refluxed for 3 minutes. The
solution is poured into ice acidified with dilute hydrochloric acid. The organic
and aqueous fractions are separated. The aqueous fraction is extracted once
with chloroform.
The organic fractions are combined and washed successively with N,N_x0002_dimethyl-1,3-propanediamine, dilute hydrochloric acid, saturated sodium
bicarbonate solution and saturated sodium chloride solution. The organic
fraction is dried over anhydrous magnesium sulfate. The solvent is then
evaporated off. Upon trituration of the residue with methanol, a solid
crystallizes, 5-(p-toluoyl)-1-methylpyrrole-2-acetonitrile, which is removed by
filtration and purified by recrystallization from benzene.
Additional product is isolated from the mother liquors which are combined,
concentrated in vacuo and the resulting oily residue column chromatographed
on neutral alumina using hexane, benzene and ether as successive solvents.
The product is isolated by concentrating in vacuo the first few major
compound-bearing fractions (10% ether in benzene). The solids are combined
and recrystallized from methanol and then from benzene-hexane, melting
point 102°C to 105°C.
5-(p-Toluoyl)-1-methylpyrrole-2-acetic acid - A solution of 3.67 g (0.015 mol)
of 5-(p-toluoyl)-1-methylpyrrole-2-acetonitrile, 24 ml of 1 N sodium hydroxide
and 50 ml of 95% ethanol is stirred and refluxed for 24 hours.
The resulting solution is poured into ice acidified with dilute hydrochloric acid.
A white solid precipitates which is extracted into ether. The ether phase is
washed with a saturated solution of sodium chloride and dried over anhydrous
magnesium sulfate. The solvent is evaporated and a white solid, 5-(p-toluoyl)-
1-methylpyrrole-2-acetic acid is obtained which is recrystallized twice from
isopropanol, melting point 155°C to 157°C.
Therapeutic Function
Antiinflammatory
Biological Functions
Tolmetin (Tolectin) is an antiinflammatory, analgesic, and antipyretic agent that produces the usual gastric distress and ulceration observed with NSAIDs. However, tolmetin is better tolerated than aspirin and produces less tinnitus and vertigo. Tolmetin is a substitute for indomethacin in indomethacin-sensitive patients and is unique among such drugs in that it can be used to treat juvenile arthritis.
General Description
Tolmetin sodium (Tolectin), is an arylacetic acid derivativewith a pyrrole as the aryl group. This drug is well absorbed and has a relatively short plasma half-life (1 hour). It is recommendedfor use in the management of acute and chronicRA. Its efficacy is similar to aspirin and indomethacin, butwith less frequency of the adverse effects and tinnitus associatedwith aspirin. It does not potentiate coumarin-likedrugs nor alter the blood levels of sulfonylureas or insulin.However, tolmetin, and especially its closely related drug,zomepirac (i.e., with a p-chlorobenzoyl group and an additionalmethyl group on the pyrrole ring), can produce a rarebut fatal anaphylactic reaction because of irreversible bindingof their unstable acyl glucuronides. Zomepirac waswithdrawn from market because it is eliminated only via theester-type, acyl glucuronide. It is possible that tolmetin isless toxic in this regard because it undergoes additional hepaticbenzylic hydroxylation via its p-methyl group and isexcreted as its stable ether glucuronide.
Trade name
Artrocaptin (Estedi, Spain), Tolectin (Cilag, Belgium; Janssen-Cilag, Austria; McNeil, USA).
Mechanism of action
Tolmetin inhibits both isoforms of cyclooxygenase with some preference for COX-1 .
Pharmacokinetics
Tolmetin is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agent. Studies in animals have shown tolmetin to possess anti-inflammatory, analgesic and antipyretic activity. In the rat, tolmetin prevents the development of experimentally induced polyarthritis and also decreases established inflammation. In patients with either rheumatoid arthritis or osteaoarthritis, tolmetin is as effective as aspirin and indomethacin in controlling disease activity, but the frequency of the milder gastrointestinal adverse effects and tinnitus was less than in aspirin-treated patients, and the incidence of central nervous system adverse effects was less than in indomethacin-treated patients. In patients with juvenile rheumatoid arthritis, tolmetin is as effective as aspirin in controlling disease activity, with a similar incidence of adverse reactions. tolmetin has produced additional therapeutic benefit when added to a regimen of gold salts and, to a lesser extent, with corticosteroids. Tolmetin should not be used in conjunction with salicylates since greater benefit from the combination is not likely, but the potential for adverse reactions is increased.
Pharmacology
Tolmetin is administered orally, rectally, or topically (600–1800 mg/d). The peak plasma concentrations are reached within 30 to 60 min. Tolmetin shows a high plasma protein binding of 99% and a biphasic plasma half-life of 1 to 2 and 5h, respectively.
Clinical Use
Tolmetin is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug used for the treatment of mild to moderate pain states in musculoskeletal, soft-tissue, and joint disorders like rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, and gout as well as juvenile rheumatoid arthritis.
Synthesis
Tolmetin, 1-methyl-5-n-tolylpyrrol-2-acetic acid (3.2.61) is synthesized from 1- methylindole, which is aminomethylated using formaldehyde and dimethylamine, forming 2-dimethylaminomethyl-1-methylindol (3.2.57). The product is methylated by methyl iodide, giving the corresponding quaternary salt (3.2.58). Reaction of the product with sodium cyanide gives 1-methylpyrrole-2-acetonitrile (3.2.59), which is acylated at the free |á-position of the pyrrole ring by 4-methylbenzoylchloride in the presence of aluminum chloride. The resulting 1-methyl-5-n-toluylpyrrol-2-acetonitrile (3.2.60) undergoes further alkaline hydrolysis, giving corresponding acid, tolmetin (3.2.61) [116¨C118].

Metabolism
Essentially all of the administered dose is recovered in the urine in 24 hours either as an inactive oxidative metabolite or as conjugates of tolmetin.
Properties of Tolmetin
| Melting point: | 156 °C |
| Boiling point: | 400.53°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 1.1391 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.5200 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | Chloroform (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly) |
| form | Solid |
| pka | pKa 3.5(H2O
t undefined
I undefined) (Uncertain) |
| color | Off-White to Pale Yellow |
| Water Solubility | 222 mg/L |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Tolmetin(26171-23-3) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | 1H-Pyrrole-2-acetic acid, 1-methyl-5-(4-methylbenzoyl)- (26171-23-3) |
Safety information for Tolmetin
Computed Descriptors for Tolmetin
Tolmetin manufacturer
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 26171-23-3 Tolmetin 98%View Details
26171-23-3 Tolmetin 98%View Details
26171-23-3 -
 26171-23-3 98%View Details
26171-23-3 98%View Details
26171-23-3 -
 Tolmetin 98% CAS 26171-23-3View Details
Tolmetin 98% CAS 26171-23-3View Details
26171-23-3 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1