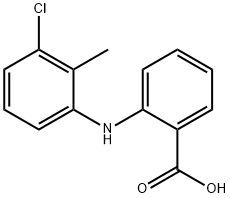
Tolfenamic acid
Synonym(s):2 (3-Chloro-2-methylanilino)benzoic acid;2-([3-Chloro-2-methylphenyl]amino)benzoic acid;Tolfenamic acid
- CAS NO.:13710-19-5
- Empirical Formula: C14H12ClNO2
- Molecular Weight: 261.7
- MDL number: MFCD00133865
- EINECS: 237-264-3
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:08:57
What is Tolfenamic acid?
Absorption
Tolfenamic acid pharmacokinetic is marked by a short tmax of 0.94-2.04 h. It also presented a linear pharmacokinetic profile with an AUC from 13-50 mcg/ml.h if administered in a dose of 2-8 mg/kg respectively. The oral absorption is delayed and it gives a mean lag-time to absorption of 32 min. The peak plasma concentration of 11.1 mcg/ml. The bioavailability of tolfenamic acid is around 75%.
Toxicity
Tolfenamic acid has a relatively low acute toxicity with LD50 values in 200-1000 mg/kg. The metabolites of tolfenamic acid are reported to have an even less important toxicity. Some of the expected toxicity is related to the presence of gastrointestinal effects such as gut ulceration and renal papillitis.
Chemical properties
White Solid
The Uses of Tolfenamic acid
Tolfenamic acid is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agent. It interferes with synthesis of β-amyloid precursor protein, and thus Aβ peptides, by promoting degradation of an essential transcription factor. It inhibits fMLP- and A23187-induced Ca2+ influx in human PMNL with an IC50 value of approximately 20 μM.
The Uses of Tolfenamic acid
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
The Uses of Tolfenamic acid
antiinflammatory, analgesia
The Uses of Tolfenamic acid
Amidated GRF fragment equipotent to GRF in release of somatotropin from anterior pituitary
The Uses of Tolfenamic acid
A non steroidal anti-inflammatory agent found to inhibit COX-2 isoenzymes
What are the applications of Application
Tolfenamic Acid is a non steroidal anti-inflammatory agent found to inhibit COX-2 isoenzymes
Indications
In the information for tolfenamic acid, it is stated that this drug, being an NSAID, is effective in treating the pain associated with the acute attack of migraines in adults.
Background
Tolfenamic acid, with the formula N-(2-methyl-3-chlorphenyl)-anthranilic acid, is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agent. It was discovered by scientists at Medica Pharmaceutical Company in Finland. It is used in the UK as a treatment for migraine under the name of Clotam. In the US, it presents a Status class I by the FDA. By the European Medicine Agency, it was granted in 2016 with the status of orphan for the treatment of supranuclear palsy.
Definition
ChEBI: An aminobenzoic acid that is anthranilic acid in which one of the hydrogens attached to the nitrogen is replaced by a 3-chloro-2-methylphenyl group. Tolfenamic acid is used specifically for relieving the pain of migraine. It also shows anticancer activity.
General Description
Tolfenamic Acid is an anthranilic acid derivative and a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID). Its applications in treating pancreatic, esophageal, colorectal and lung cancer is being investigated.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agent. Interferes with synthesis of β-amyloid precursor protein, and thus Aβ peptides, by promoting degradation of an essential transcription factor.
Pharmacokinetics
Studies have shown that tolfenamic acid presents a non-dose dependent partial inhibition of irritant-induced temperature rise as well as a dose-dependent inhibition of skin edema. By studying its NSAID properties more closely, it was noted a dose-related inhibition of serum thromboxane which indicated the inhibition of COX-1. In the same line, there was noted a inhibition of prostaglandin E2 synthesis which marks a related COX-2 inhibition. The maximal inhibition of thromboxane was greater than 80% as well as is proven to be a potent prostaglandin E inhibitor.
Clinical Use
NSAID:
Treatment of migraine
Synthesis
Tolfenamic acid is obtained by
condensation of 2-chlorobenzoic acid with 3-
chloro-2-methyl-phenylamine using CuBr2 in
diethylenglycol dimethyl ether .
Veterinary Drugs and Treatments
Tolfenamic acid may be useful for the treatment of acute or chronic pain and/or inflammation in dogs and acute pain/inflammation in cats. In Europe, it is also approved for use in cattle.
Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
ACE inhibitors and angiotensin-II antagonists:
antagonism of hypotensive effect; increased risk of
nephrotoxicity and hyperkalaemia.
Analgesics: avoid concomitant use of 2 or more
NSAIDs, including aspirin (increased side effects);
avoid with ketorolac (increased risk of side effects
and haemorrhage).
Antibacterials: possibly increased risk of convulsions
with quinolones.
Anticoagulants: effects of coumarins and
phenindione enhanced; possibly increased risk of
bleeding with heparins, dabigatran and edoxaban.
Antidepressants: increased risk of bleeding with
SSRIs and venlafaxine.
Antidiabetic agents: effects of sulphonylureas enhanced.
Antiepileptics: possibly increased phenytoin
concentration.
Antivirals: increased risk of haematological toxicity
with zidovudine; concentration possibly increased by
ritonavir.
Ciclosporin: may potentiate nephrotoxicity.
Cytotoxics: reduced excretion of methotrexate;
increased risk of bleeding with erlotinib.
Diuretics: increased risk of nephrotoxicity;
antagonism of diuretic effect; hyperkalaemia with
potassium-sparing diuretics.
Lithium: excretion decreased.
Pentoxifylline: increased risk of bleeding.
Tacrolimus: increased risk of nephrotoxicity
Metabolism
The first pass metabolism accounts for 20% of the administered dose of tolfenamic acid. Urine metabolite studies have demonstrated the identification of five metabolites from which three of them are monohydroxylated, one is monohydroxylated and hydroxylated and one last metabolite that presented and oxidized methyl group to form a carboxyl group. Two of these hydroxylated metabolites are N-(2-hydroxymethyl-3-chlorophenyl)-anthranilic acid and N-(2-hydroxymethyl-3-chloro-4-hydroxyphenyl)-anthranilic acid.
Metabolism
Tolfenamic acid is metabolised in the liver; the metabolites and unchanged drug are conjugated with glucuronic acid. About 90
% of an ingested dose is excreted in the urine and the remainder in the faeces.
Properties of Tolfenamic acid
| Melting point: | 210-214°C |
| Boiling point: | 405.4±40.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.2037 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.5270 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | Practically insoluble in water, soluble in dimethylformamide, sparingly soluble in ethanol and in methylene chloride. It dissolves in dilute solutions of alkali hydroxides. |
| form | neat |
| pka | 3.66±0.36(Predicted) |
| form | Solid |
| color | White to Off-White |
| Water Solubility | Soluble in water (slightly), acetone (~10 mg/ml), DMSO (52 mg/ml at 25°C), methanol (~10 mg/ml) and ethanol (50 mg/ml). |
| Merck | 14,9513 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 13710-19-5(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Benzoic acid, 2-[(3-chloro-2-methylphenyl)amino]- (13710-19-5) |
Safety information for Tolfenamic acid
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H301:Acute toxicity,oral |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P270:Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. P301+P310:IF SWALLOWED: Immediately call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician. P405:Store locked up. P501:Dispose of contents/container to..… |
Computed Descriptors for Tolfenamic acid
| InChIKey | YEZNLOUZAIOMLT-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
Tolfenamic acid manufacturer
Anlon Healthcare Pvt Ltd
Nira Life Sciences Pvt Ltd
Sindhu Organics Pvt Ltd
Diligent Life Care
Parmax Pharma Limited
New Products
Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate (S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL N-octanoyl benzotriazole 3,4-Dibenzyloxybenzaldehyde 4-Hydrazinobenzoic acid 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 4-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 4-(3-chloropropyl)morpholine phenylhydrazine hydrochloride (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 Tolfenamic Acid 99%View Details
Tolfenamic Acid 99%View Details -
 TOLEFNAMIC ACID 99%View Details
TOLEFNAMIC ACID 99%View Details
13710-19-5 -
 Tolfenamic acid 98% CAS 13710-19-5View Details
Tolfenamic acid 98% CAS 13710-19-5View Details
13710-19-5 -
 Tolfenamic Acid CAS 13710-19-5View Details
Tolfenamic Acid CAS 13710-19-5View Details
13710-19-5 -
 13710-19-5 99%View Details
13710-19-5 99%View Details
13710-19-5 -
 Tolfenamic acid 13710-19-5 99%View Details
Tolfenamic acid 13710-19-5 99%View Details
13710-19-5 -
 Tolfenamic acid 98.00% CAS 13710-19-5View Details
Tolfenamic acid 98.00% CAS 13710-19-5View Details
13710-19-5 -
 Tolfenamic acid CAS 13710-19-5View Details
Tolfenamic acid CAS 13710-19-5View Details
13710-19-5