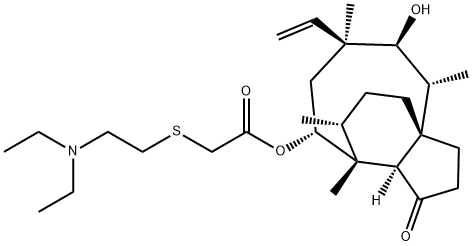
Tylosin
Synonym(s):Tylosin A
- CAS NO.:1401-69-0
- Empirical Formula: C46H77NO17
- Molecular Weight: 916.1
- MDL number: MFCD09881413
- EINECS: 215-754-8
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:08:57
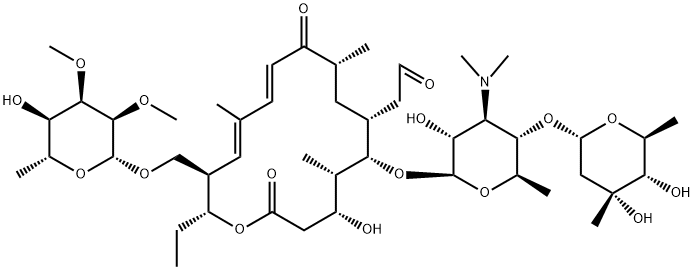
What is Tylosin?
Description
Tylosin is a macrolide antibiotic produced by S. fradiae that has bacteriostatic activity against Gram-positive bacteria. It is a mixture of tylosin A, B, C, and D, with tylosin A contributing 80% of its bacteriostatic activity. Tylosin has MIC values of 9.6, 16.4, 0.1, 1, and 0.5 μg/ml for F. necrophorum, A. pyogenes, M. gallisepticum, S. aureus, and S. uberis, respectively.,, Formulations containing tylosin have been used for the prevention of liver abscesses in cattle. Tylosin is an environmental contaminant because it is not fully metabolized by treated livestock and enters the environment through manure-based fertilizers.
Description
Occupational exposure concerns farmers, breeders, animal-feed workers and veterinarians.
Chemical properties
Off-White to Pale Yellow Solid.
Tylosin is a macrolide antibiotic which is active against certain Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria and Gram-positive mycoplasmas. It consists predominantly of tylosin(factor A), but varying amounts of desmycosin (factor B), macrocin (factor C) and relomycin(factor D) may also be present, depending on the manufacturing source. Most of themicrobiological activity resides with tylosin factor A.

Tylosin is a weak organic base with a high degree of lipid solubility, thus it is well distributed to the organs and tissues of animals (Burrows, 1980).
Tylosin is used in pigs, cattle and poultryfor the treatment of conditions caused by sensitive organisms. It may be administered by oral orparenteral routes. Tylosin is not used in human medicine.
The Uses of Tylosin
paramagnetic agent
The Uses of Tylosin
Macrolide antibiotic isolated from a strain of Streptomycetes fradiae found in soil from Thailand. Antibacterial.
The Uses of Tylosin
Tylosin is a 16-membered macrocyclic lactone isolated from Streptomyces fradiae in 1961. Tylosin has broad spectrum antibacterial activity and was developed as a veterinary pharmaceutical for treatment of bacterial infections in a range of domestic animals . Tylosin acts by binding to the 50S ribosomal subunit resulting in the inhibition of protein synthesis in bacteria.
Indications
In cattle, tylosin is used for treatment of BRD caused by Mannheimia, Pasteurella multocida, and Histophilus somni (formerly Haemophilus somnus). It is used for interdigital necrobacillosis (foot rot) in cattle caused by Fusobacterium necrophorum or Bacteroides melaninogenicus. In pigs, it is used for treatment of swine arthritis caused by Mycoplasma hyosynoviae, swine pneumonia caused by Pasteurella spp., swine erysipelas caused by Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae, swine dysentery associated with Serpulina (Treponema) hyodysenteriae, and proliferative enteropathy caused by L. intracellularis. For treatment in pigs, it is also added to feed (Type A–medicated feed article) or drinking water. In small animals, it is used for gram-positive soft tissue and skin infections. However, the most common use in dogs is for treatment of diarrhea, referred to as antibiotic-responsive diarrhea, that has not responded to other treatments. The etiology of the diarrhea is not known but may be caused by Clostridium or Camphylobacter. For this use, the powdered formulation (swine formulation) is most often added to food daily for maintenance.
Definition
ChEBI: A macrolide antibiotic that is tylonolide having mono- and diglycosyl moieties attached to two of its hydroxy groups. It is found naturally as a fermentation product of Streptomyces fradiae.
brand name
Tylan (Lilly).
Contact allergens
Tylosin is a macrolid antibiotic used in veterinary medicine. Occupational exposure concerns farmers, breeders, animal feed workers, and veterinarians.
Mechanism of action
Tylosin is a 16-membered macrolide approved for therapy of a variety of infections in pigs, cattle, dogs, and poultry (see indications below). It is formulated as tylosin tartrate or tylosin phosphate. Like other macrolide antibiotics, tylosin inhibits bacteria by binding to the 50S ribosome and inhibiting protein synthesis. Spectrum of activity is limited primarily to gram-positive aerobic bacteria. Clostridium and Campylobacter are usually sensitive. The spectrum also includes the bacteria that cause BRD. Escherichia coli and Salmonella are resistant. In pigs, Lawsonia intracellularis is sensitive.
Side Effects
Tylosin may cause diarrhea in some animals. However, oral treatment for colitis in dogs has been administered for several months with safety. Skin reactions have been observed in pigs. Oral administration to horses has been fatal.
Safety Profile
Poison by intravenous route. Moderately toxic by ingestion and intraperitoneal routes. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of NOx. See also TnOSIN HYDROCHLORIDE.
Veterinary Drugs and Treatments
Although the injectable form of tylosin is approved for use in dogs
and cats, it is rarely used parenterally in those species. Oral tylosin
is sometimes recommended for the treatment of chronic colitis in
small animals (see Doses), but controlled studies documenting its
efficacy have not been performed.
Tylosin is also used clinically in cattle and swine for infections
caused by susceptible organisms.
Solubility in organics
soluble in lower alcohols, esters, ketones,chlorinated hydrocarbons, benzene, ether, chloroform.
Properties of Tylosin
| Melting point: | 135-137°C |
| Boiling point: | 796.05°C (rough estimate) |
| alpha | D25 -46° (c = 2 in methanol) |
| Density | 1.1424 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.5280 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | Sealed in dry,2-8°C |
| solubility | DMF: 30 mg/ml; DMSO: 25 mg/ml; Ethanol: 30 mg/ml |
| form | A crystalline solid |
| pka | pKa 7.73(H2O
t = 25
I = 0.167) (Uncertain) |
| color | White to light yellow |
| Water Solubility | H2O: soluble 50 mg/mL |
| Stability: | Solutions are stable at pH 4-9 (most stable at pH 7); Below pH 4 tylosin B (desmycosin) is formed as a result of acid hydrolysis; In neutral and alkaline pH – tylosin aldol (TAD) is formed together with polar degradation products of unknown identity; When tylosin solution is exposed to daylight, a photodegradation product - isotylosin A (isoTA) is formed. |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Tylosin (1401-69-0) |
Safety information for Tylosin
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H317:Sensitisation, Skin H334:Sensitisation, respiratory |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P272:Contaminated work clothing should not be allowed out of the workplace. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P284:Wear respiratory protection. P302+P352:IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of soap and water. P333+P313:IF SKIN irritation or rash occurs: Get medical advice/attention. |
Computed Descriptors for Tylosin
| InChIKey | WBPYTXDJUQJLPQ-VMXQISHHSA-N |
New Products
Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate (S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL N-octanoyl benzotriazole 4-Hydrazinobenzoic acid 3,4-Dibenzyloxybenzaldehyde 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) 4-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran




You may like
-
 1401-69-0 Tylosin 98%View Details
1401-69-0 Tylosin 98%View Details
1401-69-0 -
 Tylosin CAS 1401-69-0View Details
Tylosin CAS 1401-69-0View Details
1401-69-0 -
 Tylosin CAS 1401-69-0View Details
Tylosin CAS 1401-69-0View Details
1401-69-0 -
 55441-95-7 99%View Details
55441-95-7 99%View Details
55441-95-7 -
 N-Vinylformamide 99%View Details
N-Vinylformamide 99%View Details
13162-05-5 -
 Chloro Uracil 1820-81-1 99%View Details
Chloro Uracil 1820-81-1 99%View Details
1820-81-1 -
 2-ethyl-6-methyl-3-hydroxypyridine succinate 99%View Details
2-ethyl-6-methyl-3-hydroxypyridine succinate 99%View Details
127464-43-1 -
 2-ETHYLPYRIDINE 100-71-0 99%View Details
2-ETHYLPYRIDINE 100-71-0 99%View Details
100-71-0