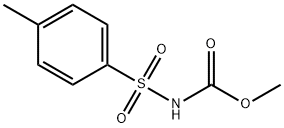
Gliclazide
Synonym(s):N-[[(hexahydrocylopenta[c]pyrrol-2(1H)-yl)amino]carbony]-4-methylbenzene sulfonamide;1-(3-Azabicyclo[3.3.0]oct-3-yl)-3-p-tolylsulphonylurea;Gliclazide
- CAS NO.:21187-98-4
- Empirical Formula: C15H21N3O3S
- Molecular Weight: 323.41
- MDL number: MFCD00409893
- EINECS: 244-260-5
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-22 18:23:36
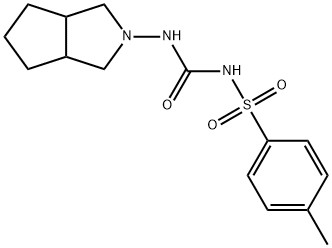
What is Gliclazide?
Chemical properties
White Cyrstalline Solid
Originator
Diamicron,Servier,France,1972
The Uses of Gliclazide
Gliclazide is an oral hypoglycemic agent used to treat non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus.Treatment of diabetes associated with obesity or vascular disease, for adults with type 2 diabetes.Diabetes is a chronic (long-lasting) health condition that affects how your body turns food into energy. Gliclazide reduces blood glucose levels by stimulating insulin secretion from the β-cells of the islets of Langerhans.
Background
Gliclazide is an oral antihyperglycemic agent used for the treatment of non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (NIDDM). It has been classified differently according to its drug properties in which based on its chemical structure, gliclazide is considered a first-generation sulfonylurea due to the structural presence of a sulfonamide group able to release a proton and the presence of one aromatic group. On the other hand, based on the pharmacological efficacy, gliclazide is considered a second-generation sulfonylurea which presents a higher potency and a shorter half-life.
Indications
For the treatment of NIDDM in conjunction with diet and exercise.
Definition
ChEBI: Gliclazide is a N-sulfonylurea. It has a role as a hypoglycemic agent, a radical scavenger and an insulin secretagogue.
Manufacturing Process
To a suspension containing 4.86 parts of 4-methylbenzenesulfonyl urethane (MP 80° to 82°C) and 36 parts of anhydrous toluene there are rapidly added 2.5 parts of N-amino-3-azabicyclo(3.3.0)octane (BP/18 mm = 86°C). The reaction mixture is heated under reflux for 1 hour. The resulting clear solution crystallizes on cooling. The crystals are filtered, washed with 2 parts of toluene, then recrystallized from anhydrous ethanol. There are obtained 3.8 parts of the desired product, MP 180° to 182°C.
Therapeutic Function
Oral hypoglycemic
Mechanism of action
Gliclazide belongs to the sulfonylurea class of insulin secretagogues, which act by stimulating β cells of the pancreas to release insulin. Sulfonylureas increase both basal insulin secretion and meal-stimulated insulin release.
General Description
Chemically, gliclazide, 1-(3-azabicyclo[3.3.0]oct-3-yl)-3-p-tolylsulphonylurea (Diamicron), isvery similar to tolbutamide, with the exception of the bicyclicheterocyclic ring found in gliclazide. The pyrrolidineincreases its lipophilicity over that of tolbutamide,which increases its half-life. Even so, the p-methyl is susceptibleto the same oxidative metabolic fate as observedfor tolbutamide, namely, it will be metabolized to a carboxylicacid.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Oxidative modification of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) plays an important role in vascular dysfunction associated with diabetes mellitus. Gliclazide is a second-generation sulfonylurea with free-radical-scavenging activity. Incubation of human aortic smooth muscle cell (HASMC) with native human LDL (100 μg/mL) in the presence of increasing concentrations of gliclazide (1 to 10 μg/mL) resulted in a dose-dependent decrease in HASMC-mediated LDL oxidation. Exposure of HASMCs to gliclazide (1 to 10 μg/mL) and native LDL (100 μg/mL) also led to a dose-dependent decrease in oxidized LDL-induced human monocyte adhesion to HASMCs. In addition, incubation of HASMCs with gliclazide dramatically reduced the ability of oxidized LDL to stimulate the proliferation of these cells. Finally, treatment of HASMCs with gliclazide resulted in a marked decrease in oxidatively modified LDL-induced monocyte chemoattractant protein (MCP)-1 and human heat shock protein 70 (HSP 70) expression, both at the gene and protein levels. These results show that gliclazide, at concentrations in the therapeutic range (5 to 10 μg/mL), is effective in vitro in reducing vascular smooth muscle cell (VSMC) dysfunction induced by oxidatively modified LDL. Administration of gliclazide to type 2 diabetic patients could form part of the strategy for the prevention and management of diabetic cardiovascular diseases
Pharmacokinetics
Based on the pharmacological properties, gliclazide is a second generation sulphonylurea which acts as a hypoglycemic agent. It stimulates β cells of the islet of Langerhans in the pancreas to release insulin. It also enhances peripheral insulin sensitivity. Overall, it potentiates insulin release and improves insulin dynamics.
Toxicity
LD50=3000 mg/kg (orally in mice). Gliclazide and its metabolites may accumulate in those with severe hepatic and/or renal dysfunction. Symptoms of hypoglycemia include: dizziness, lack of energy, drowsiness, headache and sweating.
Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Analgesics: effects enhanced by NSAIDs.
Antibacterials: effects enhanced by chloramphenicol,
sulphonamides, tetracyclines and trimethoprim;
effect reduced by rifamycins.
Anticoagulants: effect possibly enhanced by
coumarins; also possibly changes to INR.
Antifungals: concentration increased by fluconazole
and miconazole and possibly voriconazole - avoid
with miconazole.
Lipid-regulating drugs: possibly additive
hypoglycaemic effect with fibrates.
Sulfinpyrazone: enhanced effect of sulphonylureas.
When gliclazide is used with nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (especially salicylates), sulfa antibiotic, double coumarin anticoagulants, monoamine oxidase inhibitors, β-blockers, tetracycline, chloramphenicol, dicyclohexyl B piperidine, clofibrate, ethanol and other drugs, its dosage should be reduced to avoid hypoglycemia reaction.
Absorption
Rapidly and well absorbed but may have wide inter- and intra-individual variability. Peak plasma concentrations occur within 4-6 hours of oral administration.
Metabolism
Extensively metabolized in the liver. Less than 1% of the orally administered dose appears unchanged in the urine. Metabolites include oxidized and hydroxylated derivates, as well as glucuronic acid conjugates.
Metabolism
Gliclazide is extensively metabolised in the liver to
metabolites that have no significant hypoglycaemic
activity.
Metabolites and a small amount of unchanged drug are
excreted in the urine.
Properties of Gliclazide
| Melting point: | 163-169 °C (lit.) |
| Density | 1.2205 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.6740 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | methylene chloride: soluble |
| form | powder |
| pka | 6.07±0.10(Predicted) |
| color | white |
| Merck | 14,4439 |
| InChI | InChI=1S/C15H21N3O3S/c1-11-5-7-14(8-6-11)22(20,21)17-15(19)16-18-9-12-3-2-4-13(12)10-18/h5-8,12-13H,2-4,9-10H2,1H3,(H2,16,17,19) |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 21187-98-4(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Benzenesulfonamide, N-[[(hexahydrocyclopenta[c]pyrrol-2(1H)-yl)amino]carbonyl]-4-methyl (21187-98-4) |
Safety information for Gliclazide
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral |
Computed Descriptors for Gliclazide
| InChIKey | BOVGTQGAOIONJV-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | C1(S(NC(NN2CC3CCCC3C2)=O)(=O)=O)=CC=C(C)C=C1 |
Gliclazide manufacturer
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
![octahydro-2-nitrosocyclopenta[c]pyrrole](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/GIF/54786-86-6.gif)
![N-[[(HEXAHYDROCYCLOPENTA [C]PYRROL-2(1H)-YL)AMINO]CARBONYL]-2-METHYL BENZENESULFONAMIDE](https://img.chemicalbook.in/StructureFile/ChemBookStructure9/GIF/CB1271199.gif)


You may like
-
 Gliclazide 99%View Details
Gliclazide 99%View Details -
 Gliclazide 99%View Details
Gliclazide 99%View Details -
 Gliclazide 21187-98-4 98%View Details
Gliclazide 21187-98-4 98%View Details
21187-98-4 -
 Gliclazide 99%View Details
Gliclazide 99%View Details
21187-98-4 -
 Gliclazide 99%View Details
Gliclazide 99%View Details -
 Gliclazide 97% CAS 21187-98-4View Details
Gliclazide 97% CAS 21187-98-4View Details
21187-98-4 -
 Gliclazide CAS 21187-98-4View Details
Gliclazide CAS 21187-98-4View Details
21187-98-4 -
 Gliclazide 40MG, Packaging Size: 5x2x15View Details
Gliclazide 40MG, Packaging Size: 5x2x15View Details
21187-98-4
