TOCOPHEROL
- CAS NO.:1406-66-2
- Empirical Formula: C28H48O2
- Molecular Weight: 416.67952
- MDL number: MFCD03001589
- EINECS: 604-195-9
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:15:32
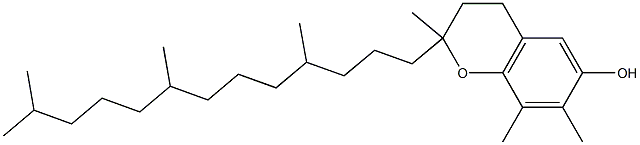
What is TOCOPHEROL?
Absorption
The absorption of tocopherol in the digestive tract requires the presence of fat. The bioavailability of tocopherols is highly dependent on the type of isomer that is administered where the alpha-tocopherol can present a bioavailability of 36%. This isomer specificity also determines the intestinal permeability in which the gamma-tocopherol presents a very low permeability. After oral administration, the Cmax was 1353.79 ng/ml for δ-tocopherol, 547.45 ng/ml for γ-tocopherol, 704.16 ng/ml for β-tocopherol, and 2754.36 ng/ml for α-tocopherol. The Tmax is three to four hours for δ-tocopherol, γ-tocopherol, and β-tocopherol and about six hours for α-tocopherol.
Toxicity
Tocopherols are considered as non-toxic but if very high doses are administered, there are reports of hemorrhagic activity. Reproductive and developmental toxicity tests are negative. These negative results were also observed in the analysis of mutagenicity and carcinogenicity.
The Uses of TOCOPHEROL
Tocopherols are a class or organic molecules. Many exhibit the activity of Vitamin E. They are commonly found in Olive and sunflower oils.
Background
Tocopherol exists in four different forms designated as α, β, δ, and γ. They present strong antioxidant activities, and it is determined as the major form of vitamin E. Tocopherol, as a group, is composed of soluble phenolic compounds that consist of a chromanol ring and a 16-carbon phytyl chain. The classification of the tocopherol molecules is designated depending on the number and position of the methyl substituent in the chromanol ring. The different types of tocopherol can be presented trimethylated, dimethylated or methylated in the positions 5-, 7- and 8-. When the carbons at position 5- and 7- are not methylated, they can function as electrophilic centers that can trap reactive oxygen and nitrogen species. Tocopherols can be found in the diet as part of vegetable oil such as corn, soybean, sesame, and cottonseed. It is currently under the list of substances generally recognized as safe (GRAS) in the FDA for the use of human consumption.
Indications
Tocopherol can be used as a dietary supplement for patients with a deficit of vitamin E; this is mainly prescribed in the alpha form. Vitamin E deficiency is rare, and it is primarily found in premature babies of very low birth weight, patients with fat malabsorption or patients with abetalipoproteinemia.
Tocopherol, due to its antioxidant properties, is studied for its use in prevention or treatment in different complex diseases such as cancer, atherosclerosis, cardiovascular diseases, and age-related macular degeneration.
General Description
Pale yellow, viscous liquid.
Air & Water Reactions
Insoluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
TOCOPHEROL is stable to heat and alkalis in the presence of oxygen, and is not affected by acids up to 212° F. TOCOPHEROL is slowly oxidized by atmospheric oxygen and rapidly oxidized by ferric and silver salts. TOCOPHEROL gradually darkens on exposure to light. .
Fire Hazard
Flash point data for TOCOPHEROL are unavailable, but TOCOPHEROL is probably combustible.
Contact allergens
Tocopherol and tocopheryl acetate are used mainly as antioxidants. Tocopheryl acetate, an ester of tocopherol (vitamin E), can induce allergic contact dermatitis.
Pharmacokinetics
The antioxidant effects of tocopherol can be translated into different changes at the pharmacodynamic level. In vitro studies have shown that this antioxidant activity can produce modification in protein kinase C (PKC) which will later be translated into an inhibition of cell death. Some other derivate effects are the anti-inflammatory properties of tocopherol which can be related to the modulation of cytokines or prostaglandins, prostanoids and thromboxanes.
Metabolism
Excess tocopherol is converted into their corresponding carboxyethylhydroxychroman (CEHC), based on the isomer of tocopherol. More deeply, the metabolism of tocopherol begins with the hepatic metabolism which is led by a CYP4F2/CYP3A4-dependent ω-hydroxylation of the side chains which leads to the formation of 13'-carboxychromanol. The metabolic pathway is followed by five cycles of β-oxidation. The β-oxidation cycles function by shortening the side chains, the first cycle results in the formation of carboxydimethyldecylhydroxychromanol followed by carboxymethyloctylhydroxychromanol. These two metabolites are categorized as long-chain metabolites and they are not excreted in the urine. Some intermediate-chain metabolites that are products of two rounds of β-oxidation are carboxymethylhexylhydroxychromanol and carboxymethylbutylhydroxychromanol. These intermediate-chain metabolites can be found in human feces and urine. The catabolic end-product of tocopherols, as stated before, is CEHC which can be largely found in urine and feces.
Two new metabolites have been detected in human and mice feces. These new metabolites are 12'-hydroxychromanol and 11'-hydroxychromanol. Because of their chemistry, it is thought that these metabolites can be the evidence for a ω-1 and ω-2 hydroxylation which leads to an impaired oxidation of 12'-OH followed side-chain truncation.
Properties of TOCOPHEROL
| Density | 0.930 g/mL at 25 °C |
| refractive index | n20/D1.501 |
| Flash point: | >200℃ |
| form | Viscous |
| Boiling point: | >200°C |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Tocopherols (1406-66-2) |
Safety information for TOCOPHEROL
Computed Descriptors for TOCOPHEROL
TOCOPHEROL manufacturer
Prakash Chemicals Agencies
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
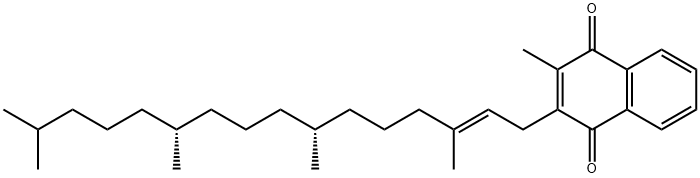
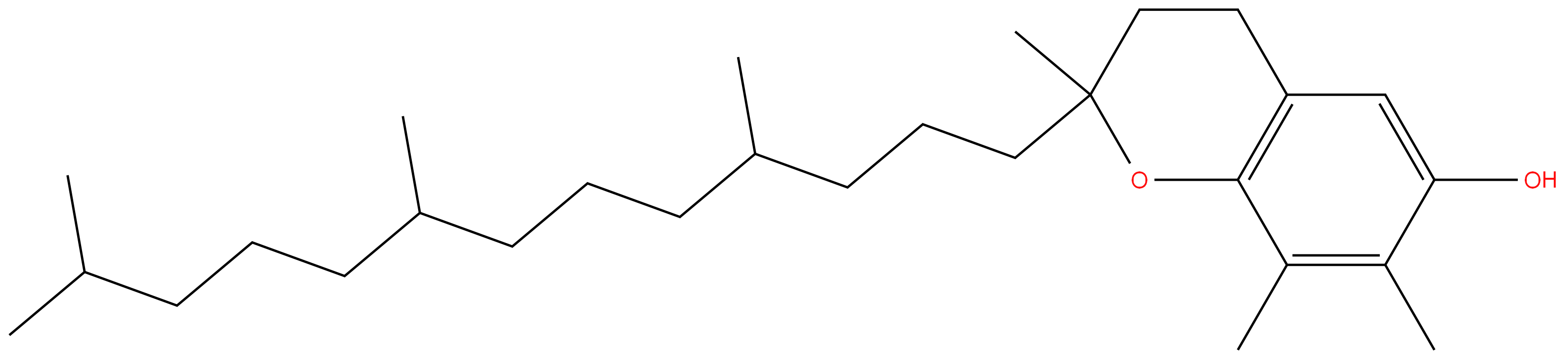 1406-66-2 Tocopherol 99%View Details
1406-66-2 Tocopherol 99%View Details
1406-66-2 -
 Tocopherols CAS 1406-66-2View Details
Tocopherols CAS 1406-66-2View Details
1406-66-2 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1