Tiopronin
Synonym(s):Tiopronin
- CAS NO.:1953-02-2
- Empirical Formula: C5H9NO3S
- Molecular Weight: 163.19
- MDL number: MFCD00004861
- EINECS: 217-778-4
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-19 20:33:22
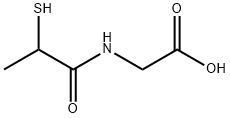
What is Tiopronin?
Absorption
Tiopronin undergoes slow absorption, reaching peak plasma concentration 3-6 hours after ingestion. In a study of healthy subjects, the bioavailability of total and unbound tiopronin was found to be 63% and 40%, respectively.
Toxicity
Long-term carcinogenicity and mutagenicity studies have not been performed with tiopronin. In experimental animal studies, high doses of tiopronin were shown to interfere with the maintenance of pregnancy and viability of a fetus. No neural tube defects were detected when tiopronin was given to mice and rats in doses up to 10 times the highest recommended human dose. However, the manufacturer does not rule out the possibility of teratogenicity, as it has been seen with the drug d-penicillamine, which acts with a similar mechanism to tiopronin. Tiopronin is not recommended for use in breastfeeding mothers and has no established safety in children 9 years old or younger. There have been case reports of tiopronin-related nephropathy.
Description
Tiopronin is a sulfiydryl derivative of N-propylglycine useful in the treatment of cystine urolithiasis in children. It is also reportedly effective in the management of rheumatoid polyarthritis, possibly due to its inhibitory effect on the free oxygen radicals produced by inflammatory macrophages and granulocytes.
Description
Tiopronin is an antioxidant that has diverse biological activities. It reduces free radical production by murine macrophages and granulocytes in vitro in a dose-dependent manner. Tiopronin induces expression of hypoxia-inducible factor 1α (HIF-1α) and increases VEGF secretion in human colon carcinoma cells. Rectal administration (500 μL of a 10 mM solution) reduces myeloperoxidase activity and reduces pro-inflammatory cytokine production in the colon in a rat model of colitis. Tiopronin (80-320 mg/kg per day) reduces the incidence of cleft palate in fetuses born to female mice orally exposed to teratogenic methylmercury chloride. Tiopronin (100 mg/kg) reduces heme oxygenase 1 mRNA expression, lipid peroxidation, and transverse aortic constriction in a mouse model of cardiac hypertrophy. Tiopronin (20 mg/kg) is hepatoprotective, increasing activity of the antioxidant enzymes superoxide dismutase and glutathione peroxidase and reversing hepatocyte degeneration in a rat model of high-fat diet-induced non-alcoholic steatohepatitis.
Chemical properties
White Solid
Originator
Roussel-Uclaf (Japan)
The Uses of Tiopronin
N-(2-Mercaptopropionyl)glycine or Tiopronin has been used:
- in the preparation of polyethylenimine (PEI)-coated gold microparticles (PEI-gold) for biolistic delivery of nucleic acids
- to study the role of reactive oxygen species (ROS) at the reperfusion stage in in vivo isoflurane preconditioning-induced neuroprotection
- as a ROS inhibitor to study its effect on lysophosphatidylcholine (LPC)-induced inflammasome activation
The Uses of Tiopronin
It is used as antidote against heavy metal poisoning; hepatoprotectant; mucolytic.
Indications
Tiopronin is indicated for the prevention of kidney stone formation in patients with severe homozygous cystinuria consisting of a urinary cystine concentration greater than 500 mg/day, and who have failed treatment with non-pharmacological measures of increased fluid intake, decreased sodium and protein intake, and urine alkalinization.
Background
Tiopronin is a prescription thiol drug used primarily in the treatment of severe homozygous cystinuria. Patients with cystinuria excrete high levels of cystine in their urine and are at risk for kidney stone formation. Tiopronin is used as a second-line therapy to control the rate of cystine precipitation and excretion, and prevent kidney stone formation. It is used after a failure of the non-pharmacological first line treatment consisting of increased fluid intake, restriction of sodium and protein, and urinary alkalinization. As cystinuria is a relatively rare disease, tiopronin is classified as an orphan drug and is not patented in the United States. It is similar to d-penicillamine in use and efficacy, but offers the advantage of far less adverse effects. Tiopronin is dosed on an individual basis using close monitoring of urinary cystine concentrations and urinary output.
Tiopronin may also be used to bind metal nanoparticles in Wilson's disease, which is an overload of copper in the body. It has been investigated for use in the treatment of arthritis and as a neuroprotective agent in aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage.
What are the applications of Application
Tiopronin is controls the rate of cystine precipitation and excretion
Definition
ChEBI: Tiopronin is a N-acyl-amino acid.
Manufacturing Process
α-Benzylmercaptopropionic acid (melting point 76°C to 78°C; 100 g) prepared
by condensation of α-mercaptopropionic acid with benzyl chloride is allowed to
stand overnight with 80 g of thionyl chloride. After removal of excess thionyl
chloride distillation in vacuo gives 70 g of α-benzylmercaptopropionic acid
chloride of boiling point 138°C to 139°C/7 to 8 mm Hg.
Then, 25 g of glycine is dissolved in 165 ml of 2 N sodium hydroxide solution
and 70 g of α-benzylmercaptopropionic acid chloride and 100 ml of 2 N
sodium hydroxide solution are dropped thereinto simultaneously at 3°C to
5°C. The solution is then stirred at room temperature for 3 to 4 hours to
complete the reaction, the reaction solution is washed with ether, the aqueous
layer is acidified with hydrochloric acid, and the resulting crystals are collected
by filtration. These are recrystallized from a mixture of methanol and ethyl
acetate to give 60 g of α-benzylmercaptopropionylglycine of melting point
133°C to 134°C.
This α-benzylmercaptopropionylglycine (60 g) is dissolved in 400 ml of liquid
ammonia, kept at about -50°C, and 12 g of sodium metal is gradually added
thereto. After the reaction, excess ammonia is removed therefrom, the
residue is dissolved in water, washed with ether and the residual aqueous
layer is adjusted to pH 1 with hydrochloric acid and concentrated in vacuo in a
stream of hydrogen sulfide. The crystalline residue is dried and recrystallized
from ethyl acetate to give 25 g of α-mercaptopropionylglycine of melting point
95°C to 97°C.
brand name
Thiola
Therapeutic Function
Antidote (heavy metal)
Biochem/physiol Actions
N-(2-Mercaptopropionyl)glycine (NMPG) is a thiol compound associated with autoimmune hypoglycemia. It is a diffusible antioxidant and reduces the severity of colonic injury. NMPG also relieves myeloperoxidase activity and stimulates hypoxia-inducible factor-1 (HIF-1) - vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) pathway for ulcer healing.
Veterinary Drugs and Treatments
Tiopronin is indicated for the prevention of cystine urolithiasis in patients where dietary therapy combined with urinary alkalinization is not completely effective. It may also be useful in combination with urine alkalinization to dissolve stones.
Metabolism
The principle metabolite of tiopronin is 2-mercaptopropionic acid (2-MPA). Between 10-15% of the drug is metabolized to 2-MPA via hydrolysis.
Properties of Tiopronin
| Melting point: | 93-98 °C |
| Boiling point: | 418.3±30.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.249 (estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.5216 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | Inert atmosphere,2-8°C |
| solubility | DMSO (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly) |
| form | solid |
| pka | 3.36±0.10(Predicted) |
| color | White |
| Merck | 14,9453 |
| BRN | 1859822 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 1953-02-2(CAS DataBase Reference) |
Safety information for Tiopronin
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P270:Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. P301+P312:IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician IF you feel unwell. P501:Dispose of contents/container to..… |
Computed Descriptors for Tiopronin
Tiopronin manufacturer
Biophore India Pharmaceuticals Pvt Ltd
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 1953-02-2 / 953-02-2 Tiopronin 98%View Details
1953-02-2 / 953-02-2 Tiopronin 98%View Details
1953-02-2 / 953-02-2 -
 1953-02-2 / 953-02-2 98%View Details
1953-02-2 / 953-02-2 98%View Details
1953-02-2 / 953-02-2 -
 Tiopronin 96% CAS 1953-02-2View Details
Tiopronin 96% CAS 1953-02-2View Details
1953-02-2 -
 Tiopronin CAS 1953-02-2View Details
Tiopronin CAS 1953-02-2View Details
1953-02-2 -
 N-(2-Mercaptopropionyl)glycine CAS 1953-02-2View Details
N-(2-Mercaptopropionyl)glycine CAS 1953-02-2View Details
1953-02-2 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1