Thioglycolic acid
Synonym(s):Mercaptoacetic acid;Mercaptoacetic acid, 2-Mercaptoethanoic acid;Thioglycolic acid
- CAS NO.:68-11-1
- Empirical Formula: C2H4O2S
- Molecular Weight: 92.12
- MDL number: MFCD00004876
- EINECS: 200-677-4
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-03-20 19:16:41
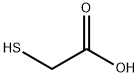
What is Thioglycolic acid?
Description
Thio glycolic acid (TGA) is the organic compound HSCH2CO2H . It contains both a thiol (mercaptan) and a carboxylic acid. It is a clear liquid with a strong unpleasant odor. It is readily oxidized by air to the corresponding disulfide [SCH2CO2H]2.
TGA was developed in the 1940s for use as a chemical depilatory and is still used as such, especially in salt forms, including calcium thioglycolate and sodium thioglycolate. TGA is the precursor to ammonium thioglycolate that is used for permanents. TGA and its derivatives break the disulfide bonds in the cortex of hair. One reforms these broken bonds in giving hair a "perm." Alternatively and more commonly, the process leads to depilation as is done commonly in leather processing. It is also used as an acidity indicator, manufacturing of thioglycolates, and in bacteriology for preparation of thioglycolate media.
TGA is also used in the making of tin stabilizers often used in certain polyvinyl chloride products (such as vinyl siding).
TGA, usually as its dianion, forms complexes with metal ions. Such complexes have been used for the detection of iron, molybdenum, silver, and tin.
Thioglycolic acid is used as nucleophile in thioglycolysis reactions used on condensed tannins to study their structure.
Chemical properties
Also known as mercaptoacetic acid, HSCH2COOH is a colorless liquid with a strong unpleasant odor. Used as a reagent for metals such as iron, molybdenum, silver, and tin,and in bacteriology.
Chemical properties
Thioglycolic acid is a colorless liquid with a strong unpleasant odor like rotten eggs.
The Uses of Thioglycolic acid
Mercaptoacetic acid is used as a reagent formetals analysis; in the manufacture of thioglycolates, pharmaceuticals, and permanentwave solutions; and as a vinyl stabilizer.
The Uses of Thioglycolic acid
Thioglycolic Acid is an organic compound containing both a thiol and a carboxylic acid. Thioglycolic Acid is a precursor to ammonium thioglycolate, a chemical used for permanents. Thioglycolic Acid is used in organic synthesis as a nucleophile in thioglycolysis reactions and is used as a S transfer agent for sulfonyl chloride synthesis.
The Uses of Thioglycolic acid
Sensitive reagent for iron, molybdenum, silver, tin. With ferric iron a blue color appears, and when an alkali hydroxide is added to a solution contg ferrous salts and thioglycolic acid, a yellow precipitate forms. Used in the manufacture of thioglycolates. The ammonium and sodium salts are commonly used for cold waving and the calcium salt is a depilatory. The sodium salt also is used in bacteriology in the preparation of thioglycolate media.
What are the applications of Application
Thioglycolic acid is an organic acid used in the preparation of thioglycolate media
What are the applications of Application
Thioglycolic acid is an intermediate in the production of thiomethoprol (caputril), biotin, thiozinc acid, sodium dithiosuccinate and other pharmaceuticals, and is also an intermediate in the synthesis of cysteine, hormonal agent, and industrial disinfectant. And an important raw material for the synthesis of sulfuric acid. Thioglycolic acid is used as antioxidant and stabilizer in pharmaceuticals to enhance the stability of the main drug and prolong the validity period of pharmaceutical preparations. Ammonium and sodium salts of thioglycolic acid are mainly used as curling agents, calcium salts can be used as depilatory agents, polymerization initiators, accelerators and chain transfer agents, and can be used for hair removal before cosmetic surgery and animal experiments. Thioglycolic acid is used to make epoxy resin, catalyst of bisphenol A, and it can also be used as the basic raw material for synthesizing PVC transparent plastic and organic antimony and organic tin heat stabilizer.
Thioglycolic acid is a sensitive reagent for the determination of iron, molybdenum, aluminum, tin, etc., and is an inhibitor of copper sulfide and iron sulfide minerals in beneficiation. In the petrochemical industry and the railway sector, it is used for cleaning and derusting of equipment and rails. It can be used as a crystallization nucleating agent in polypropylene processing and molding, as a modifier for coatings and fibers, as a blanket quickening agent, as a stabilizer raw material for polyvinyl chloride and rubber, as a cold perm agent, and as a pharmaceutical intermediate. Thioglycolic acid is used as a color developer for the photometric determination of molybdenum, rhenium and iron, and as a compounding masking agent.
Definition
ChEBI: Thioglycolic acid is a sulfur-containing carboxylic acid. It is a conjugate acid of a thioglycolate(1-).
Preparation
Thioglycolic acid is prepared from Sodium sulfide plus Sodium monochloride acetate to yield Dithioglycollic acid. Electrolysis of the latter acid yields the title material.
General Description
A colorless liquid with an unpleasant odor. Density 1.325 g / cm3. Used to make permanent wave solutions and depilatories. Corrosive to metals and tissue.
Air & Water Reactions
Readily oxidized by air. Water soluble.
Reactivity Profile
Mercaptoacetic acid is readily oxidized by air . Reacts readily with other oxidizing agents as well in reactions that may generate toxic gases. Incompatible with diazo and azo compounds, halocarbons, isocyanates, aldehydes, alkali metals, nitrides, hydrides, and other strong reducing agents. Reactions with these materials may generate heat and toxic and flammable gases. May react with acids to liberate hydrogen sulfide. Neutralizes bases in exothermic reactions. Reacts with cyanides, sulfites, nitrites, thiosulfates to generate flammable and toxic gases and heat. Reacts with carbonates and bicarbonates.
Hazard
Toxic by ingestion and inhalation, strong irritant to tissue, eyes, and skin.
Health Hazard
TOXIC; inhalation, ingestion or skin contact with material may cause severe injury or death. Contact with molten substance may cause severe burns to skin and eyes. Avoid any skin contact. Effects of contact or inhalation may be delayed. Fire may produce irritating, corrosive and/or toxic gases. Runoff from fire control or dilution water may be corrosive and/or toxic and cause pollution.
Health Hazard
Mercaptoacetic acid is a highly toxic and ablistering compound. Even a 10% solutionwas lethal to most experimental animals by dermal absorption. The oral LD50 value ofundiluted acid is less than 50 mg/kg (Patty1963). The lethal dose in rabbits by skinabsorption is 300 mg/kg. The acute toxicsymptoms in test animals include weakness,respiratory distress, convulsions, irritation ofthe gastrointestinal tract, and liver damage.
Mercaptoacetic acid is a severe irritant.Contact with eyes can cause conjunctivalinflammation and corneal opacity. Skin contact can result in burns and necrosis.
Fire Hazard
Combustible material: may burn but does not ignite readily. When heated, vapors may form explosive mixtures with air: indoors, outdoors and sewers explosion hazards. Contact with metals may evolve flammable hydrogen gas. Containers may explode when heated. Runoff may pollute waterways. Substance may be transported in a molten form.
Safety Profile
Poison by ingestion, skin contact, intraperitoneal, and intravenous routes. Moderately toxic by subcutaneous route. A corrosive irritant to skin, eyes, and mucous membranes. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of SOx. See also MERCAPTANS and HYDROGEN SULFIDE.
Potential Exposure
Thioglycolic acid is used to make thioglycolates; in sensitivity tests for iron; in formulations of permanent wave solutions and depilatories; in pharmaceutical manufacture; as a stabilizer in vinyl plastics.
Carcinogenicity
Thioglycolic acid was not mutagenic in a number of Salmonella typhimurium strains with or without metabolic activation.
Shipping
UN1940 Thyoglycolic acid, Hazard class: 8; Labels: 8-Corrosive material.
Purification Methods
Mix the acid with an equal volume of *benzene; the *benzene is then distilled off to dehydrate the acid. After heating to 100o to remove most of the *benzene, the residue is distilled under vacuum and stored in sealed ampoules at 3o. [Eshelman et al. Anal Chem 22 844 1960, Beilstein 3 IV 1130.]
Incompatibilities
Compounds of the carboxyl group react with all bases, both inorganic and organic (i.e., amines) releasing substantial heat, water and a salt that may be harmful. Incompatible with arsenic compounds (releases hydrogen cyanide gas), diazo compounds, dithiocarbamates, isocyanates, mercaptans, nitrides, and sulfides (releasing heat, toxic and possibly flammable gases), thiosulfates and dithionites (releasing hydrogen sulfate and oxides of sulfur). Air, strong oxidizers; bases, active metals, for example, sodium potassium, magnesium, and calcium. Readily oxidized by air. Thermal decomposition causes release of hydrogen sulfide. May attack various metals.
Waste Disposal
Dissolve in flammable solvent and burn in furnace equipped with afterburner and alkaline scrubber.
Properties of Thioglycolic acid
| Melting point: | −16 °C(lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 96 °C5 mm Hg(lit.) |
| Density | 1.326 g/mL at 20 °C(lit.) |
| vapor density | 3.2 (vs air) |
| vapor pressure | 0.4 mm Hg ( 25 °C) |
| refractive index | n |
| Flash point: | 126 °C |
| storage temp. | Store at +2°C to +8°C. |
| solubility | Chloroform (Sparingly), Methanol (Sparingly) |
| form | Liquid |
| pka | 3.68(at 25℃) |
| color | clear clear, colorless |
| PH | 1 (H2O, 20℃) |
| Odor | strong unpleasant odor |
| Water Solubility | soluble |
| Sensitive | Air Sensitive |
| Merck | 14,9336 |
| BRN | 506166 |
| Exposure limits | TLV-TWA 1 ppm (~3.8 mg/m3) (ACGIH). |
| Stability: | Air Sensitive |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 68-11-1(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Acetic acid, mercapto-(68-11-1) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Thioglycolic acid (68-11-1) |
Safety information for Thioglycolic acid
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Corrosion Corrosives GHS05  Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H314:Skin corrosion/irritation H317:Sensitisation, Skin |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P270:Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P303+P361+P353:IF ON SKIN (or hair): Remove/Take off Immediately all contaminated clothing. Rinse SKIN with water/shower. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Thioglycolic acid
| InChIKey | CWERGRDVMFNCDR-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
Thioglycolic acid manufacturer
New Products
Methyl (R)-1-Boc-4,4-difluoropyrrolidine-2-carboxylate 2,2-Difluoropropylamine hydrochloride tert-butyl 3-bromoazetidine-1-carboxylate (R)-1-Boc-3-hydroxypyrrolidine DIFLUOROACETIC ANHYDRIDE 2,2-Difluoropropionic acid Diallylamine, 99% Calcium hydroxide, 95% Aluminum oxide, basic 2-Bromophenylacetonitrile, 97% L-tert-Leucine,97% N-Hydroxy-2-methylpropanimidamide 4-(3,4-Dichlorophenyl)-3,4-Dihydro-N-Methyl-1-(2H)-Naphthalenimine (Schiff Base) 2-AMINO-3,5-DIBROMO BENZALDEHYDE [ADBA] L-Glutamic Acid Dimethyl Ester Hcl 10-Methoxy-5H-dibenz[b,f]azepine 5-Cyanophthalide N, N-Carbonyldiimidazole (CDI) Dibenzoyl Peroxide Titanium Dioxide 2-(Methylthio) Benzonitrile Sodium Acetate Anhydrous Allopurinol 1,5-DibromopentaneRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

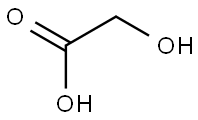
You may like
-
 THIOGLYCOLIC ACID 99%View Details
THIOGLYCOLIC ACID 99%View Details -
 Thioglycolic Acid ExiPlus CAS 68-11-1View Details
Thioglycolic Acid ExiPlus CAS 68-11-1View Details
68-11-1 -
 Thioglycollic Acid (SQ) CAS 68-11-1View Details
Thioglycollic Acid (SQ) CAS 68-11-1View Details
68-11-1 -
 Mercaptoacetic acid 95% CAS 68-11-1View Details
Mercaptoacetic acid 95% CAS 68-11-1View Details
68-11-1 -
 Thioglycollic acid, puriss CAS 68-11-1View Details
Thioglycollic acid, puriss CAS 68-11-1View Details
68-11-1 -
 Thioglycollic acid CAS 68-11-1View Details
Thioglycollic acid CAS 68-11-1View Details
68-11-1 -
 Thioglycolic Acid CAS 68-11-1View Details
Thioglycolic Acid CAS 68-11-1View Details
68-11-1 -
 Thioglycolicacid CAS 68-11-1View Details
Thioglycolicacid CAS 68-11-1View Details
68-11-1
