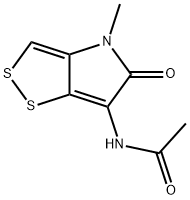
THIOLUTIN
Synonym(s):Farcinicin;N-(4,5-Dihydro-4-methyl-5-oxo-1,2-dithiolo[4,3-b]pyrrol-6-yl);Propiopyvothine
- CAS NO.:87-11-6
- Empirical Formula: C8H8N2O2S2
- Molecular Weight: 228.29
- MDL number: MFCD01076610
- EINECS: 635-840-2
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-19 20:33:22
What is THIOLUTIN?
Description
Thiolutin is a natural dithiol that reversibly inhibits bacterial and yeast RNA polymerases (IC50 = 3 μg/ml). Because of this, it can be used for the analysis of mRNA stability. Thiolutin also inhibits endothelial cell adhesion (IC50 < 1 μM) and S180 tumor-
Chemical properties
Yellow solid
The Uses of THIOLUTIN
Thiolutin is an antibiotic isolated from several strains of Streptomyces albus. Thiolutin is a natural dithiol that reversibly inhibits bacterial and yeast RNA polymerases.
The Uses of THIOLUTIN
Thiolutin is an antibiotic first described by Tanner and co-workers in 1950. Resurgent interest in this class of microbial metabolites was stimulated by the discovery of their selective antitumour activity. Thiolutin is a potent inhibitor of bacterial and yeast RNA polymerases, and also inhibits mannan and glucan formation in fungi. Thiolutin suppresses tumour cell-induced angiogenesis in vivo.
The Uses of THIOLUTIN
Thiolutin has been used as a polymerase II inhibitor:
- to study its effects on yeast cells to calculate transcript half-life
- to study its effects on transcription during germination in budding yeast
- to study its effects on cell adhesion in zebrafish
What are the applications of Application
Thiolutin is an RNA polymerase inhibitor and suppressor of tumor cell-induced angiogenesis
Definition
ChEBI: Thiolutin is a dithiolopyrrolone antibiotic that is 4,5-dihydro[1,2]dithiolo[4,3-b]pyrrole in which the hydrogens at positions 4,5 and 6 have been replaced by methyl, oxo and acetamido groups, respectively. It is a potent inhibitor of RNA polymerases, inhibits the angiogenesis of human umbilical vein endothelial cells, and also inhibits JAMM metalloproteases. It has a role as an angiogenesis inhibitor, a chelator, a protein synthesis inhibitor, an EC 2.7.7.6 (RNA polymerase) inhibitor, an antibacterial agent, a toxin, a marine metabolite, a bacterial metabolite, an antifungal agent and an antineoplastic agent. It is a dithiolopyrrolone antibiotic and a member of acetamides. It is functionally related to a holomycin.
Biological Activity
Antibiotic; inhibits bacterial RNA polymerase. Inhibits adhesion of HUVEC cells to vitronectin (IC 50 = 0.83 mM) and subsequently reduces paxillin levels. Suppresses tumor cell-induced angiogenesis.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Sulfur-containing antibiotic, which is a potent inhibitor of bacterial and yeast RNA polymerases. It was found to inhibit in vitro RNA synthesis directed by all three yeast RNA polymerases (I, II, and III). Thiolutin is also an inhibitor of mannan and glucan formation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and used for the analysis of mRNA stability. Studies have shown that thiolutin inhibits adhesion of human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs) to vitronectin and thus suppresses tumor cell-induced angiogenesis in vivo.
Safety Profile
Poison by ingestion andsubcutaneous routes. When heated to decomposition itemits very toxic fumes of NOx and SOx.
References
Jing et al. (2021), Blockade of deubiquitinating enzyme PSMD14 overcomes chemoresistance in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma by antagonizing E2F1/Akt/SOX2-mediated stemness; Theranostics, 11 2655 Jia et al. (2010), Thiolutin inhibits endothelial cell adhesion by perturbing Hsp27 interactions with components of the actin and intermediate filament cytoskeleton; Cell Stress Chaperones 15 165 Minamiguchi et al. (2001), Thiolutin, an inhibitor of HUVEC adhesion to vitronectin, reduces paxillin in HUVECs and suppresses tumor cell-induced angiogenesis; Int. J. Cancer, 93 307
Properties of THIOLUTIN
| Melting point: | 273-276℃ |
| Boiling point: | 200°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 1.4614 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.5690 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | −20°C |
| solubility | DMSO: 5 mg/mL |
| pka | 10.54±0.20(Predicted) |
| form | Yellow crystalline solid. |
| color | Brilliant-yellow needles from 1-butanol |
| Stability: | Stable for 3 years as supplied. Solutions in DMSO may be stored at -20°C for up to 3 months. |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Thiolutin (87-11-6) |
Safety information for THIOLUTIN
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H300:Acute toxicity,oral |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P270:Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. P301+P310:IF SWALLOWED: Immediately call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician. P405:Store locked up. P501:Dispose of contents/container to..… |
Computed Descriptors for THIOLUTIN
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE 4-Bromopyrazole 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran



You may like
-
 Thiolutin CAS 87-11-6View Details
Thiolutin CAS 87-11-6View Details
87-11-6 -
 2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1