Tetrachlorvinphos
Synonym(s):Stirofox
- CAS NO.:22248-79-9
- Empirical Formula: C10H9Cl4O4P
- Molecular Weight: 365.96
- MDL number: MFCD00078729
- EINECS: 244-865-4
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:07:02
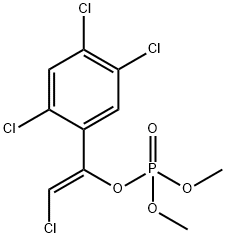
What is Tetrachlorvinphos?
Description
Tetrachlorvinphos was initially registered for use in the United States in 1966 for use on various food crops, livestock, and pet animals, and in around buildings. Its use on food crops were voluntarily canceled in the United States in 1987; however, it is used on food crops in developing countries. Tetrachlorvinphos is sold under the trade names Rabon and Gardona.
Chemical properties
Powder.Partially soluble in chloroform; slightly soluble in water.
Chemical properties
Technical tetrachlorvinphos is a tan-to-brown crystalline
solid. Tetrachlorvinphos is stable at ,100 C and slowly
hydrolyzed at 50°C. Aromatic odor.
Soluble in water at 24°C 15 ppm; limited
solubility in most aromatic hydrocarbons.
The Uses of Tetrachlorvinphos
Tetrachlorvinphos is used to control lepidopterous and dipterous larvae in fruit and lepidopterous larvae in cotton, maize, rice, tobacco and vegetables. It is also used against nuisance flies in animal houses, animal ectoparasites and stored product pests.
The Uses of Tetrachlorvinphos
Insecticide.
The Uses of Tetrachlorvinphos
Tetrachlorvinphos is commonly used as a feed additive to control flies in livestock and as dusts, sprays, dips, and collar ingredient to control ticks and fleas on domestic pets. It is extensively used in poultry. In horses, its formulations are commonly used as a feed additive (feed-through tetrachlorvinphos) larvicide. In addition, tetrachlorvinphos is also used in the control of public health pests, manure flies associated with livestock, and poultry as a feed additive.
Definition
ChEBI: Tetrachlorvinphos is an alkenyl phosphate, a dialkyl phosphate, an organophosphate insecticide, an organochlorine insecticide and a trichlorobenzene. It has a role as an EC 3.1.1.7 (acetylcholinesterase) inhibitor, an agrochemical, an EC 3.1.1.8 (cholinesterase) inhibitor and an acaricide. It is functionally related to a 1-phenylethenol.
Hazard
Cholinesterase inhibitor. Questionable carcinogen.
Carcinogenicity
When rats were given diets with 0, 4250, or 8500 ppm tetrachlorvinphos for 80 weeks, both males and females had a high incidence of thyroid C-cell hyperplasia, and females had increased incidences of adrenal cortical adenomas and thyroid C-cell adenomas .
Environmental Fate
Tetrachlorvinphos is nonpersistent in the environment. The primary route of dissipation is through biotic degradation. Based on its use pattern, risks of contamination of groundwater or surface water by tetrachlorvinphos are minimal.
Metabolic pathway
The chemical structure of tetrachlorvinphos is very close to that of chlorfenvinphos and the routes of metabolic breakdown have been shown to be very similar. Technical tetrachlorvinphos is usually >95% Z-isomer, unlike chlorfenvinphos which is an E/Z mixture. As with chlorfenvinphos, the major routes of detoxification are by dealkylation and hydrolysis to yield desmethyltetrachlorvinphos and 2,2’,4’,5’- tetrachloroacetophenone plus dimethyl phosphate, respectively. Further metabolism of the chloroacetophenone moiety then leads, via reduction or hydrolysis and glutathione-dependent displacement of the side chain chlorine substituent, to the formation of 1-(2,4,5-trichlophenyl) ethane-l,Z-diol and 1-(2,4,5-trichlorophenyl)ethan-l-owl hich are conjugated with glucose or glucuronic acid to afford the ultimate metabolites. Oxidation of the β carbon atom to give 2,4,5-trichloromandelic acid followed by decarboxylation leads to the formation of 2,4,5-trichlorobenzoic acid which is conjugated with glycine in some mammals as the final metabolite. The metabolic routes were summarised by Beynon et al. (1973).
Degradation
Tetrachlorvinphos is hydrolysed slowly in neutral, acidic and slightly alkaline aqueous solutions but hydrolysed rapidly in strongly alkaline solutions to metabolites 3 and 5 (PM). Dureja et al. (1987) reported the photochemical degradation of tetrachlorvinphos in water, ethanol, ether and hexane irradiated with a xenon lamp. In polar solvents, the main product was desmethyltetrachlorvinphos (2), whereas in non-polar solvents such as hexane the reaction yielded dimethyl phosphate (3), 2,4,5-trichloroacet ophenone (4) and 2,2’,4’,5’-tetrachloroacetophenone (5). Interconversion of the Z- and Ε-isomers has been observed on leaves (Beynon and Wright, 1969). These pathways are shown in Scheme 1.
Toxicity evaluation
Acute oral LD50 for rats: 4,000-5,000 mg/kg
Properties of Tetrachlorvinphos
| Melting point: | 97-98 °C(lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 399.5±42.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.520±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| vapor pressure | 6.0×10-6 Pa (20 °C) |
| storage temp. | 0-6°C |
| solubility | Acetonitrile (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly) |
| form | solid |
| Water Solubility | 11mg l-1(20°C) |
| Merck | 13,9267 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 22248-79-9(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Tetrachlorvinphos(22248-79-9) |
| IARC | 2B (Vol. 30, Sup 7, 112) 2017 |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Tetrachlorvinphos (22248-79-9) |
Safety information for Tetrachlorvinphos
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H410:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P270:Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P391:Collect spillage. Hazardous to the aquatic environment P301+P312:IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician IF you feel unwell. P501:Dispose of contents/container to..… |
Computed Descriptors for Tetrachlorvinphos
New Products
Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE DIETHYL AMINOMALONATE HYDROCHLORIDE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran



You may like
-
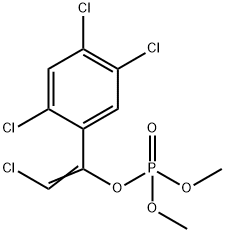
 Tetrachlorvinphos CAS 22248-79-9View Details
Tetrachlorvinphos CAS 22248-79-9View Details
22248-79-9 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 -
 733039-20-8 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 98+View Details
733039-20-8 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 98+View Details
733039-20-8