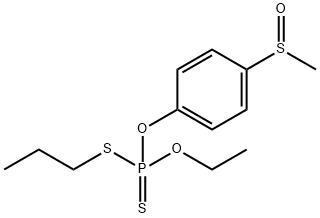
SULPROFOS
Synonym(s):Sulprophos
- CAS NO.:35400-43-2
- Empirical Formula: C12H19O2PS3
- Molecular Weight: 322.45
- MDL number: MFCD00078721
- EINECS: 252-545-0
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2023-05-04 17:34:38
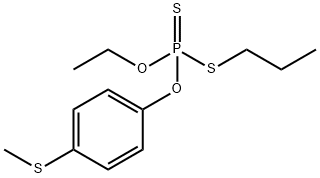
What is SULPROFOS?
Chemical properties
Tan colored liquid; sulfide odor. Soluble in organic solvents; insoluble in water.
Chemical properties
Sulprofos is a tan colored liquid.
The Uses of SULPROFOS
Sulprofos is used to control Lepidoptera, thrips and other insects in cotton, soya, tobacco, vegetables and tomatoes.
The Uses of SULPROFOS
Insecticide.
The Uses of SULPROFOS
Sulprofos is a component of an inventive pesticide water dispersible granule used for preventing and controlling scale insect of tobacco and has advantages of obvious synergistic effect, environmental protection, good pest control effect, less usage amount and low insecticide resistance.
Definition
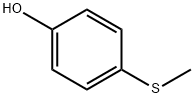
ChEBI: Sulprofos is an organic thiophosphate, an organothiophosphate insecticide and an organosulfur compound. It has a role as an EC 3.1.1.7 (acetylcholinesterase) inhibitor and an agrochemical. It is functionally related to a 4-(methylsulfanyl)phenol.
General Description
Tan-colored liquid with a sulfide-like odor.
Reactivity Profile
Organothiophosphates are susceptible to formation of highly toxic and flammable phosphine gas in the presence of strong reducing agents such as hydrides. Partial oxidation by oxidizing agents may result in the release of toxic phosphorus oxides.
Hazard
Cholinesterase inhibitor. Questionable carcinogen.
Safety Profile
Poison by ingestion. Moderately toxic by skin contact. When heated to decomposition it emits very toxic fumes of POx and SOx.
Potential Exposure
A potential danger to those involved in the manufacture, formulation, and application of this insecticide that is used for control of certain lepidopterous, dipterous, and hemipterous insects on cotton, etc.
Environmental Fate
Biological. From the first-order biotic and abiotic rate constants of sulprofos in estu-
arine water and sediment/water systems, the estimated biodegradation half-lives were
19.5–61.6 and 3.5–19 days, respectively (Walker et al., 1988).
Photolytic. When sulprofos was exposed to sunlight as deposits on cotton foliage, glass
surfaces and in aqueous solution, the insecticide degraded rapidly (half-life <2 days).
Irradiation of sulprofos in aqueous solution using UV light (λ >290
Chemical/Physical. Emits toxic oxides of sulfur and phosphorus when heated to
decomposition (Lewis, 1990).
Metabolic pathway
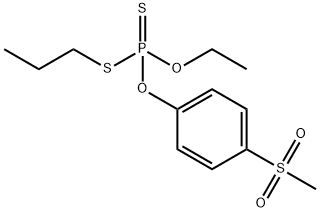
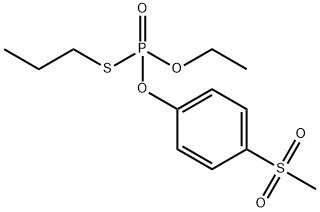
Sulprofos is an organophosphorus insecticide possessing a 4-(methylthio) phenyl group and as such its metabolic fate has much in common with fenthion with which it also has the phosphorothioate (P=S) group in common. The major route of sulprofos metabolism is by oxidation to the sulfoxide and more slowly to the sulfone. The additional route of bioactivation is through oxidative desulfuration to form the sulprofos oxon and all five oxidative metabolites (sulprofos sulfoxide, sulprofos sulfone, sulprofos oxon, sulprofos oxon sulfoxide and sulprofos oxon sulfone) have been detected in rats. Degradative metabolism by hydrolysis or oxidative dearylation to the phenols occurs rapidly. Stage II metabolism in mammals involves the rapid conjugation of the phenolic dearylation products. The fate of the S-propyl phosphorodithioate group has not apparently been reported.
Metabolism
Major metabolic routes are by oxidation to the sulfoxide and sulfone and oxidative desulfuration to the oxons. Detoxification by dearylation to the phenols occurs rapidly. Sulprofos is degraded in soil with a half-life ranging from a few days to several weeks, depending on the soil type.
Shipping
UN3018 Organophosphorus pesticides, liquid, toxic, Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials.
Degradation
The half-lives in aqueous solution at pH values 4,7 and 9 were 26,151 and 51 days, respectively. Its DT50 was less than two days when a thin film was exposed to sunlight. Ivie and Bull (1976), examined the photodecomposition in sunlight of sulprofos on cotton leaves, glass surfaces and aqueous solutions. The major metabolites were sulprofos sulfoxide (2) and sulfone (3), with minor amounts of sulprofos oxon sulfoxide (4) and the three possible phenolic hydrolysis products (5, 6 and 7). Photodecomposition is thus via thiooxidation, oxidative desulfuration and cleavage of the P-O-aryl group as shown in Scheme 1. A large number of minor photolysis products which could not be identified were also formed.
Toxicity evaluation
The acute oral LD50 for rats is 176–304 mg/kg. Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for rats is >4.1 mg/L air. NOEL (2 yr) for rats is 6 mg/kg diet (0.3 mg/kg/d). ADI is 3 μg/kg b.w. Sulprofos administered to rats is rapidly metabolized, and 92% of the dose is excreted within 24 h.
Incompatibilities
Incompatible with oxidizers (chlorates, nitrates, peroxides, permanganates, perchlorates, chlorine, bromine, fluorine, etc.); contact may cause fires or explosions. Keep away from alkaline materials, strong bases, strong acids, oxoacids, epoxides. Strong oxidizers may cause release of toxic phosphorus oxides. Organophosphates, in the presence of strong reducing agents such as hydrides, may form highly toxic and flammable phosphine gas. Keep away from alkaline materials.
Waste Disposal
In accordance with 40CFR165, follow recommendations for the disposal of pesticides and pesticide containers. Must be disposed properly by following package label directions or by contacting your local or federal environmental control agency, or by contacting your regional EPA office.
Properties of SULPROFOS
| Melting point: | -15℃ |
| Boiling point: | bp0.1 155-158° |
| Density | 1.20 g/cm3 |
| vapor pressure | 8.4×10-5Pa (20 °C) |
| refractive index | nD20 1.5859 |
| storage temp. | APPROX 4°C
|
| form | Liquid |
| Water Solubility | 0.31 mg 1l-1(20 °C) |
| Specific Gravity | 1.20 (20℃) |
| Merck | 13,9081 |
| BRN | 1990231 |
| Exposure limits | NIOSH PEL: TWA 1 mg/m3; ACGIH TLV: TWA 1 mg/m3. |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Sulprofos (35400-43-2) |
Safety information for SULPROFOS
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H330:Acute toxicity,inhalation H410:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P260:Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. |
Computed Descriptors for SULPROFOS
New Products
4-AMINO-TETRAHYDRO-PYRAN-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID HCL 4-(Dimethylamino)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-4-carbonitrile 4-Aminotetrahydropyran-4-carbonitrile Hydrochloride (R)-3-Aminobutanenitrile Hydrochloride 3-((Dimethylamino)methyl)-5-methylhexan-2-one oxalate 1,4-Dioxa-8-azaspiro[4.5]decane 5-Bromo-2-nitropyridine Nimesulide BP Aceclofenac IP/BP/EP Diclofenac Sodium IP/BP/EP/USP Mefenamic Acid IP/BP/EP/USP Ornidazole IP Diclofenac Potassium THOMAIND PAPER PH 2.0 TO 4.5 1 BOX BUFFER CAPSULE PH 9.2 - 10 CAP SODIUM CHLORIDE 0.1N CVS ALLOXAN MONOHYDRATE 98% PLATINUM 0.5% ON 3 MM ALUMINA PELLETS (TYPE 73) LITHIUM AAS SOLUTION 2-Bromo-1-(bromomethyl)-3-chloro-5-nitrobenzene 2-Bromo-3-nitroaniline N-(3-Hydroxypropyl)-N-methylacetamide 3-Bromo-6-chloropyridazine 4-ethyl-3-nitrobenzoic acidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 Sulprofos CAS 35400-43-2View Details
Sulprofos CAS 35400-43-2View Details
35400-43-2 -
 1-Methyl-6-oxo-1,6-dihydropyridazine-3-carbonitrile 98%View Details
1-Methyl-6-oxo-1,6-dihydropyridazine-3-carbonitrile 98%View Details
99903-60-3 -
 1823368-42-8 98%View Details
1823368-42-8 98%View Details
1823368-42-8 -
 2-(3-(tert-butyl)phenoxy)-2-methylpropanoic acid 1307449-08-6 98%View Details
2-(3-(tert-butyl)phenoxy)-2-methylpropanoic acid 1307449-08-6 98%View Details
1307449-08-6 -
 Ethyl 3-(furan-2-yl)-3-hydroxypropanoate 25408-95-1 98%View Details
Ethyl 3-(furan-2-yl)-3-hydroxypropanoate 25408-95-1 98%View Details
25408-95-1 -
 2-Chloro-5-fluoro-1-methoxy-3-methylbenzene 98%View Details
2-Chloro-5-fluoro-1-methoxy-3-methylbenzene 98%View Details
1805639-70-6 -
 1784294-80-9 98%View Details
1784294-80-9 98%View Details
1784294-80-9 -
 Lithium ClavulanateView Details
Lithium ClavulanateView Details
61177-44-4