Sulfadiazine
Synonym(s):N1-(Pyrimidin-2-yl)sulfanilamide;4-Amino-N-(2-pyrimidinyl)benzenesulfonamide;Sulfadiazine
- CAS NO.:68-35-9
- Empirical Formula: C10H10N4O2S
- Molecular Weight: 250.28
- MDL number: MFCD00006065
- EINECS: 200-685-8
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-01-27 09:38:02
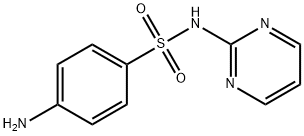
What is Sulfadiazine?
Toxicity
Oral LD50 in mouse is 1500 mg/kg.
Chemical properties
White to slightly yellow crystalline pow
Originator
Sulfadiazine,Lederle,US ,1941
The Uses of Sulfadiazine
It is used in the form of silver salts (sulfadiazine silver) as an external antibacterial agent, primarily for treating burns. It is believed that the presence of the silver ion in the molecule facilitates increased antimicrobial and wound-healing action.
The Uses of Sulfadiazine
Sulfonamide antibacterial.
The Uses of Sulfadiazine
DMSO soluble potent immunosuppressant, neuroprotective neuroregenerative, in vitro T cell proliferation blocker. disrupts calcineurin-mediated signal transduction in T lymphocytes
Background
One of the short-acting sulfonamides used in combination with pyrimethamine to treat toxoplasmosis in patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome and in newborns with congenital infections.
Indications
For the treatment of rheumatic fever and meningococcal meningitis
What are the applications of Application
Sulfadiazine is An antibacterial
Definition
ChEBI: A sulfonamide consisting of pyrimidine with a 4-aminobenzenesulfonamido group at the 2-position.
Manufacturing Process
5.4 parts of 2-amino-pyrimidine were covered with 15 parts of anhydrous
pyridine. The reaction mixture was treated with 14 parts of pnitrobenzenesulfonyl
chloride and the whole heated briefly on the steam bath
and let stand 45 minutes at room temperature. To the reaction mixture were
added 80 parts of hot alcohol and the precipitate was filtered off and washed
with water. The solid was dissolved in dilute caustic solution and the solution
was filtered, cooled and acidified. The 2-(p-nitrobenzenesulfonamido)-
pyrimidine precipitated and was collected.
The crude 2-(p-nitrobenzenesulfonamido)-pyrimidine from the preceding step
was suspended in 130 parts alcohol and 1.5 parts of concentrated hydrochloric
acid were added. The suspension was then heated to reflux and 30 parts of
iron powder were added with mechanical stirring. The mixture was refluxed
and stirred for 24 hours with occasional addition of concentrated hydrochloric
acid. The reaction mixture was then made slightly basic and filtered hot and
the residues were extracted with several portions of boiling alcohol. The filtrate and wash solutions were combined and evaporated. The 2-
(sulfanilamido)-pyrimidine was recrystallized from boiling water with
decolorizing charcoal added, according to US Patent 2,410,793.
brand name
Coco-Diazine (Lilly); Eskadiazine (SmithKline Beecham).
Therapeutic Function
Antibacterial
Antimicrobial activity
Sulfadiazine is somewhat more active than other sulphonamides.
General Description
Sulfadiazine’s plasma half-life is 17 hours. It is a white,odorless crystalline powder soluble in water to the extentof 1:8,100 at 37°C and 1:13,000 at 25°C, in human serumto the extent of 1:620 at 37°C, and sparingly soluble in alcoholand acetone. It is readily soluble in dilute mineralacids and bases. Its pKa is 6.3.
Pharmaceutical Applications
Sulfadiazine is almost insoluble in water and unstable on exposure to light. It is administered orally or, as the sodium salt, by intravenous injection. It is a component of several multi-ingredient preparations. Its low solubility in urine led to its general replacement by other compounds. The intravenous solution is highly alkaline and should not be given by any other route.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Sulfadiazine is a sulfonamide antibiotic that blocks the synthesis of dihydrofolic acid by inhibiting the enzyme dihydropteroate synthase. Sulfadiazine is a competitive inhibitor of bacterial para-aminobenzoic acid (PABA), which is required for bacterial synthesis of folic acid. It is active against Gram positive bacteria, Gram negative bacteria and Chlamydia. Mode of resistance is via the alteration of dihydropteroate synthase or alternative pathway for folic acid synthesis.
Pharmacokinetics
Sulfadiazine is a sulfonamide antibiotic. The sulfonamides are synthetic bacteriostatic antibiotics with a wide spectrum against most gram-positive and many gram-negative organisms. However, many strains of an individual species may be resistant. Sulfonamides inhibit multiplication of bacteria by acting as competitive inhibitors of p-aminobenzoic acid in the folic acid metabolism cycle. Bacterial sensitivity is the same for the various sulfonamides, and resistance to one sulfonamide indicates resistance to all. Most sulfonamides are readily absorbed orally. However, parenteral administration is difficult, since the soluble sulfonamide salts are highly alkaline and irritating to the tissues. The sulfonamides are widely distributed throughout all tissues. High levels are achieved in pleural, peritoneal, synovial, and ocular fluids. Although these drugs are no longer used to treat meningitis, CSF levels are high in meningeal infections. Their antibacterial action is inhibited by pus.
Pharmacokinetics
Oral absorption: Very good
Cmax 3 g oral: c. 50 mg/L after 3–4 h
Plasma half-life :7–12 h
Volume of distribution: 0.36 L/kg
Plasma protein binding: c. 40%
Absorption and distribution
Adequate blood concentrations are easily achieved and
maintained after oral administration. It is well distributed
and penetrates in therapeutic concentrations into
the CSF, but because of resistance it is no longer the
drug of choice in meningitis. It crosses the placenta and
enters breast milk to achieve concentrations around 20%
of plasma levels.
Metabolism and excretion
Sulfadiazine is subject to acetylation in the liver. The acetyl
derivative lacks antibacterial activity and is excreted more
slowly (half-life 8–18 h). Parent compound and metabolite
are both excreted mainly by glomerular filtration.
Clinical Use
Urinary tract infection
Nocardiasis
Chancroid
Toxoplasmosis (in combination with pyrimethamine)
Meningococcal infections
Prophylaxis of rheumatic fever
Side Effects
In addition to side effects common to the group, sulfadiazine inhibits the metabolism of phenytoin. The risk of crystalluria can be reduced by high fluid intake and alkalization of the urine.
Safety Profile
Poison by intravenous route. Moderately toxic by ingestion and intraperitoneal routes. Human systemic effects by ingestion: hematuria, anuria, general anesthesia, gastrointestinal effects. Experimental teratogenic and reproductive effects. When heated to decomposition it emits very toxic fumes of NOx and SOx.
Synthesis
Sulfadiazine, N1 -2-pyrimidinylsulfanilamide (33.1.7), is synthesized by reacting 4-acetylaminobenzenesulfonyl chloride with 2-aminopyrimidine, which gives an acetanilide derivative (33.1.6). The subsequent hydrolysis of this product with a base leads to the formation of the desired sulfadiazine.

Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Antibacterials: increased risk of crystalluria with
methenamine.
Anticoagulants: effect of coumarins enhanced;
metabolism of phenindione possibly inhibited.
Antiepileptics: antifolate effect and concentration of
phenytoin increased.
Antimalarials: increased risk of antifolate effect with
pyrimethamine.
Antipsychotics: avoid concomitant use with
clozapine (increased risk of agranulocytosis).
Ciclosporin: reduced levels of ciclosporin; increased
risk of nephrotoxicity.
Cytotoxics: increase risk of methotrexate toxicity
Metabolism
Not Available
Metabolism
Sulfadiazine is metabolised in the liver to the acetylated form, with elimination predominantly via the kidneys. Urinary excretion of sulfadiazine and its acetyl derivative is dependent on pH; when the urine is acidic about 30% is excreted unchanged in both fast and slow acetylators, whereas when the urine is alkaline about 75% is excreted unchanged by slow acetylators.
Properties of Sulfadiazine
| Melting point: | 253 °C (dec.) (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 512.6±52.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.3780 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.6440 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | Soluble in dimethyl sulfoxide. |
| pka | pKa 2.21(H2O
t = 25
I = 0.5 (NaCl)) (Uncertain) |
| form | powder |
| color | white |
| Water Solubility | 67.13mg/L(25 ºC) |
| Merck | 14,8903 |
| BRN | 6733588 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 68-35-9(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Sulfadiazine(68-35-9) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Benzenesulfonamide, 4-amino-N-2-pyrimidinyl- (68-35-9) |
Safety information for Sulfadiazine
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Health Hazard GHS08  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H362:Reproductive toxicity, effects on or via lactation H411:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P202:Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood. P260:Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P263:Avoid contact during pregnancy/while nursing. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P301+P312:IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician IF you feel unwell. P308+P313:IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention. |
Computed Descriptors for Sulfadiazine
Sulfadiazine manufacturer
New Products
1-Boc-4-cyanopiperidine tert-Butyl carbazate 1-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-2-PYRROLIDINONE TETRABUTYLAMMONIUM CYANIDE TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 3-Pyridineacrylic acid Nickel(II) perchlorate hexahydrate, 98% 4-Bromophenylacetonitrile, 95% 3-Bromo-4-fluoroaniline, 97% Sodium tetraborate decahydrate, 98% Palladium(II) acetate, trimer, Pd 99% 4-Bromo-2-chlorotoluene, 97% Tadalafil Clopidogrel bisulfate Sitagliptin Phosphate Monohydrate Cabergoline Fexofinadine HCl Etoricoxib 4-Amino Acetophenone 2-Chloro Acetophenone Amlodipine Base 2,3,5-Triiodobenzoic Acid Pyrrolidine Diiodo PentoxideRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 Sulphadiazine 99%View Details
Sulphadiazine 99%View Details -
 Sulfadiazine 95% CAS 68-35-9View Details
Sulfadiazine 95% CAS 68-35-9View Details
68-35-9 -
 Sulfadiazine CAS 68-35-9View Details
Sulfadiazine CAS 68-35-9View Details
68-35-9 -
 Sulfadiazine CAS 68-35-9View Details
Sulfadiazine CAS 68-35-9View Details
68-35-9 -
 Sulfadiazine CAS 68-35-9View Details
Sulfadiazine CAS 68-35-9View Details
68-35-9 -
 Sulfadiazine CAS 68-35-9View Details
Sulfadiazine CAS 68-35-9View Details
68-35-9 -
 Sulfadiazine CAS 68-35-9View Details
Sulfadiazine CAS 68-35-9View Details
68-35-9 -
 Sulfadiazine CAS 68-35-9View Details
Sulfadiazine CAS 68-35-9View Details
68-35-9
