Succinimide
Synonym(s):2,5-Pyrrolidinedione;Succinimide
- CAS NO.:123-56-8
- Empirical Formula: C4H5NO2
- Molecular Weight: 99.09
- MDL number: MFCD00005495
- EINECS: 204-635-6
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-01-27 09:38:02
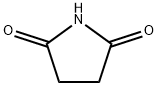
What is Succinimide?
Description
Succinimide is a natural product found in Xanthium strumarium and Panax notoginseng with data available.Succinimide is a colorless acicular crystal or thin solid with light brown luster. It tastes sweet. Easily soluble in water, alcohol or sodium hydroxide solution, insoluble in ether, chloroform, etc.
Succinimide dispersants appear as dark or brown-colored liquids with a thickness or viscosity similar to heavy syrup. They have little or no solubility in water, and because they are denser than water, will sink in a water environment. They are readily soluble in oil and lighter weight hydrocarbons, such as gasoline. Succinimide dispersants have very low vapor pressure and little noticeable odor at ambient temperatures.
Chemical properties
white crystalline powder
The Uses of Succinimide
Succinimide is a cycle imide of succinic acid that is present in numerous biologically active compounds including anticonvulsants, antitremor, anti-Parkinson's agents.
Succinimide is the key intermediate for deamidation of asparagine (Asn) and isom-erization of aspartic acid (Asp) residues in a protein or peptide, either in vivo or invitro (Wakankar and Borchardt 2006). Formation of succinimide is the rate-deter-mining step in these reactions.
The Uses of Succinimide
Succinimide is used in organic syntheses and in industrial silver plating processes. It is a reagent that is used in the synthesis of Lumiflavin (L473900), which is a toxic photolysis product of vitamin B2 (R415000). Further, it is used to form covalent bonds between proteins, peptides and plastics. In addition to this, it is used as an important raw material for the synthesis of heterocyclic compounds through N-acyliminium cyclizations.
Definition
ChEBI: Succinimide is a dicarboximide that is pyrrolidine which is substituted by oxo groups at positions 2 and 5. It is a pyrrolidinone and a dicarboximide.
Preparation
To a flask equipped with a dropping funnel, mechanical stirrer, and a 40 cm long side arm of not less than 10 mm inside diameter is added 236 gm (2.0 mole) of succinic acid. The flask is cooled and 270 ml (4.0 moles) of 28% aqueous ammonia is slowly added with stirring. The flask is rapidly heated with an oil bath until 200 ml of water distils. The temperature of the bath is rapidly raised to 275°C. Succinimide starts to distil over the range 275-289°C, to afford 168 gm of crude product which solidifies on cooling. The intermediate fraction, boiling between 102° and 275°C, is redistilled to afford 10.0 gm of crude succinimide, b.p. 275-289°C. The combined product (178 gm) is added to 178 gm of hot ethanol. The solution is cooled, the crystals filtered, washed with 25 ml of cold ethanol, and dried to afford 163-164 gm (82-83%), m.p. 123-125°C. Approximately 4-5 gm of additional product may be obtained by concentrating the mother liquor.
Recent Japanese patents suggested inert aprotic solvents such as cyclic amides (e.g., N-methylpyrrolidone, N-acetyl-2-pyrrolidone, DMF, or tet-ramethylurea) and azeotroping solvents (e.g., toluene, 0-xylene, hexane, or pentane) or other high-boiling solvents (e.g., chlorobenzene or chlo-rotoluene) as dehydrating agents for the formation of imides from dibasic acids (e.g., 3- and/or 4) hydroxyphthalic acid with a large variety of diamines including diaminosiloxanes such as bis (3-aminopropyl)-tetra-methylsiloxane.

Synthesis Reference(s)
Journal of the American Chemical Society, 102, p. 7448, 1980 DOI: 10.1021/ja00545a009
Organic Syntheses, Coll. Vol. 2, p. 562, 1943
Flammability and Explosibility
Non flammable
Synthesis
Succinimide is obtained by the reaction of succinic acid with ammonia. Succinic acid and water are added into the reaction pot, and succinimide can be produced by ammonia reaction. Succinic acid can also be put into the reaction pot, drop ammonia, stir to dissolve and react, heat it to 102 ℃, evaporate the water, and then carry out vacuum distillation. When the temperature rises to 180 ℃, start collecting succinimide fraction to obtain the finished product.
Purification Methods
Crystallise the imide from EtOH (1mL/g) or water. [Beilstein 21 H 369, 21/9 V 438.]
Properties of Succinimide
| Melting point: | 123-125 °C (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 285-290 °C (lit.) |
| Density | 1.41 |
| vapor pressure | <1 hPa (50 °C) |
| refractive index | 1.4166 (estimate) |
| Flash point: | 201 °C |
| storage temp. | Store below +30°C. |
| solubility | 330g/l |
| form | Powder or Flakes |
| pka | 9.6(at 25℃) |
| color | Off-white to beige to light brown |
| PH | 4-6 (200g/l, H2O) |
| Odor | nearly odorless |
| Water Solubility | Soluble in water and ethanol. Insoluble in ether and chloroform. |
| Merck | 14,8871 |
| BRN | 108440 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 123-56-8(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | 2,5-Pyrrolidinedione(123-56-8) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Succinimide (123-56-8) |
Safety information for Succinimide
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Succinimide
| InChIKey | KZNICNPSHKQLFF-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 123-56-8 Succinimide 98%View Details
123-56-8 Succinimide 98%View Details
123-56-8 -
 123-56-8 99%View Details
123-56-8 99%View Details
123-56-8 -
 Succinimide 98%View Details
Succinimide 98%View Details
123-56-8 -
 123-56-8 SUCCINIMIDE 99%View Details
123-56-8 SUCCINIMIDE 99%View Details
123-56-8 -
 Succinimide CAS 123-56-8View Details
Succinimide CAS 123-56-8View Details
123-56-8 -
 Succinimide, 99% CAS 123-56-8View Details
Succinimide, 99% CAS 123-56-8View Details
123-56-8 -
 SUCCINIMIDE For Synthesis CAS 123-56-8View Details
SUCCINIMIDE For Synthesis CAS 123-56-8View Details
123-56-8 -
 Succinimide CAS 123-56-8View Details
Succinimide CAS 123-56-8View Details
123-56-8
