Strontium chloride
Synonym(s):Additive Screening Solution 27/Kit-No 78374;Strontium dichloride
- CAS NO.:10476-85-4
- Empirical Formula: Cl2Sr
- Molecular Weight: 158.53
- MDL number: MFCD00011249
- EINECS: 233-971-6
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-17 09:49:57
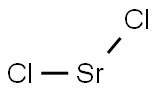
What is Strontium chloride?
Absorption
About 30 percent of ingested strontium is absorbed into the blood through the gut . The amount of strontium absorbed tends to decrease with age and is higher (about 60 percent) in children in their first year of life . Once it is absorbed into the blood, most of it ends up in bone; with the remainder going to soft tissues or being excreted in urine, feces, and sweat . About 8 percent of ingested strontium remains in the body after 30 days, and this decreases to about 4 percent after 1 year .
Toxicity
Overdosage with strontium chloride toothpaste formulations has not been reported.
Description
Strontium chloride is the inorganic salt consisting of strontium and chloride. In organic synthesis, it can be used as the resource for the manufacturing of other kinds of strontium compound. Compared with the sulfide, it has the advantage of not reacting with oxygen and carbon dioxide, which facilitates industrial handling.

Strontium chloride hexahydrate is used in toothpastes for sensitive teeth.It can also be used to reduce the tooth sensitivity through covering the microscopic tubules in the dentin with nerve endings which has been exposed to gum recession. It can be further used as a red coloring agent in pyrotechnics. Recent study has also shown that a novel topical formulation containing strontium chloride can effectively reduce the intensity and duration of cowhage-induced itch. In biological research, it has been successfully used to induce activation of mouse oocytes in nuclear transfer and other experiments, which is important in understanding the mechanisms of fertilization and early embryonic development.
Strontium chloride is not classified as a dangerous material in transport regulations.
Chemical properties
White crystalline powder
Chemical properties
Strontium chloride, SrCl2 is a salt of strontium and chlorine. It is ionic and water-soluble. It is less toxic than barium chloride [CAS: 10361-37-2] BaCl2, though more toxic than calcium chloride CaCl2. It emits a bright red color when heated in a flame. Strontium chloride can be prepared from strontium hydroxide or strontium carbonate reacting with hydrochloric acid. It can also be prepared by the union of the elements, strontium and chlorine.
Physical properties
Strontium chloride has the formula SrCl2 and the
molecular weight of 247.43 g/cm3. It is a typical salt, forming neutral aqueous solutions.
Strontium chloride can be prepared by treating strontium hydroxide or strontium carbonate with hydrochloric acid:
Sr(OH)2+ 2HCl→SrCl2+ 2H2O
SrCO3+ 2HCl→SrCl2+ CO2+H2O
Crystallization from a cold aqueous solution gives
the hexahydrate, SrCl2·6H2O. Dehydration of this
salt occurs in stages, commencing above 61°C and
ending at 320°C, where full dehydration occurs. The dihydrate, SrCl2·2H2O, is a metastable form before
the anhydrate begins to form at 200°C. The hydrates
formed in solution have one, two or six waters of
crystallization.
SrCl2·6H2O is a hexagonal system consisting of colorless
long-needle crystals. It loses four crystal waters of hydration at 61.4°C to form plate crystals of SrCl2·2H2O which become the monohydrate at 100°C and anhydrate at 200°C.
Another common hydrate, SrCl2·2H2O, is composed
of white, crystalline needles which have a sharp, bitter taste. It can be prepared by fusing SrCO3 with CaCl2 at high temperature and then extracting the melt with water. The solution is then concentrated and then crystallized to form SrCl2·6H2O, which is then dehydrated at 68°C to form the dihydrate.Anhydrous strontium chloride is a colorless crystal or a white powder with a molecular weight of 158.53 g/mol and a density of 3.05 g/cm3. Its melting point is 875°C and its boiling point is 1250°C. It is easily soluble
in water but slightly soluble in anhydrous alcohol and acetone. It is not soluble in liquid ammonia.
The Uses of Strontium chloride
Strontium chloride are white needles made by fusing calcium chloride with sodium carbonate. It is soluble in water and alcohol. Strontium chloride was a popular halide for making collodion-chloride printing-out emulsions.
The Uses of Strontium chloride
Radioactive agent.
The Uses of Strontium chloride
Strontium chloride is the precursor to other
compounds of strontium, such as yellow SrCrO4, which
is used as a corrosion inhibitor for aluminum. Strontium
chloride is the compound usually used as a red coloring
agent in fireworks. It imparts a much more intense red
color to the flames than other alternatives. It is employed
in small quantities in glass making and metallurgy. The
radioactive isotope, strontium-89, used for the treatment
of bone cancer. It is usually administered in the form of
strontium chloride. Seawater aquaria require small amounts of strontium chloride, which is consumed in
the production of the exoskeletons of certain planktons.
SrCl2 is useful in reducing tooth sensitivity by forming a barrier over microscopic tubules in the dentin-containing nerve endings that have become exposed by gum recession.
Background
Strontium chloride (SrCl2) is a salt of strontium and chloride. SrCl2 is useful in reducing tooth sensitivity by forming a barrier over microscopic tubules in the dentin containing nerve endings that have become exposed by gum recession . This kind of barrier protection for tooth hypersensitivity has, however, been superseded by other toothpaste formulations and ingredients designed to be nerve calming agents instead . Such strontium chloride toothpaste formulations may subsequently not be available for sale anymore in certain parts of the world .
Indications
When employed as an ingredient in toothpaste formulations, strontium chloride is predominantly indicated for treating teeth hypersensitivity .
What are the applications of Application
Strontium chloride is a biochemical that enhances osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells
Definition
strontium chloride: A white compound, SrCl2. The anhydrous salt (cubic; r.d. 3.05; m.p. 872°C; b.p. 1250°C) can be prepared by passing chlorine over heated strontium. It is deliquescent and readily forms the hexahydrate, SrCl2·6H2O (r.d. 2.67).This can be made by neutralizing hydrochloric acid with strontium carbonate, oxide, or hydroxide. Strontium chloride is used for military flares.
Preparation
Strontium chloride is obtained by dissolving strontium carbonate in concentrated hydrochloric acid. The hexahydrate, SrCl2 · 6H2O [10025-70-4], is formed on crystallizing below 61℃. On dehydration, the hexahydrate dissolves in its water of crystallization at 61℃. After passing through the di- and monohydrate stages, strontium chloride becomes fully dehydrated at 320℃.
brand name
Stronscan-85 (Abbott).
General Description
Strontium chloride hexahydrate (SrCl2·6H2O) is a hydrated alkaline earth metal chloride. On γ-irradiation at 77°K, it affords a radical having e.s.r. parameters resembling with HO2. Its chlorine electric field gradient (EFG) and chemical shift (CS) tensors have been evaluated by employing solid-state 35/37Cl NMR spectroscopy.
Pharmacokinetics
As an active ingredient in a toothpaste formulation, strontium chloride and the rest of the toothpaste product that it is incorporated into is designed to come into contact with and topically coat the teeth that are being brushed and is not supposed to be swallowed. The regular use of the toothpaste maintains protection that strontium chloride provides against tooth sensitivity despite the normal everyday wear, tear, and cleaning of teeth.
Metabolism
Strontium can bind to proteins and, based on its similarity to calcium, probably forms complexes with various inorganic anions, such as carbonate and phosphate, and carboxylic acids, such as citrate and lactate . Strontium can also interact with ligands that normally bind calcium, like hypoxyapatite, the main component of mineralized bone, and a variety of calcium-binding and calcium transport proteins that are important in the physiological disposition of calcium in cells, including Ca2+ adenosine triphosphatases, Na+Ca+ antiport], and Ca2+ channels .
References
Papoiu, A. D., et al. "A novel topical formulation containing strontium chloride significantly reduces the intensity and duration of cowhage-induced itch." Acta dermato-venereologica 93.5(2013):520-6.
Minkoff, S, and S. Axelrod. "Efficacy of strontium chloride in dental hypersensitivity. " Journal of Periodontology 58.7(1987):470.
Joyce, James A. "Ornamental colored flame candle." US, US2481019. 1949.
Ma, S. F., et al. "Parthenogenetic activation of mouse oocytes by strontium chloride: a search for the best conditions. " Theriogenology 64.5(2005):1142-57.
Properties of Strontium chloride
| Melting point: | 874 °C (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 1250 °C/1 atm (lit.) |
| Density | 3 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.) |
| refractive index | 1.650 |
| Flash point: | 1250°C |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | H2O: soluble |
| form | powder |
| color | White |
| Specific Gravity | 3.052 |
| Water Solubility | It is soluble in water, slightly soluble in ethanol, acetone. Insoluble in ammonia. |
| Sensitive | Hygroscopic |
| Merck | 14,8840 |
| Stability: | hygroscopic |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 10476-85-4(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Strontium dichloride(10476-85-4) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Strontium chloride (SrCl2) (10476-85-4) |
Safety information for Strontium chloride
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Corrosion Corrosives GHS05 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H318:Serious eye damage/eye irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Strontium chloride
Strontium chloride manufacturer
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

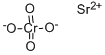
You may like
-
 Strontium chloride 98%View Details
Strontium chloride 98%View Details -
 Strontium chloride 98%View Details
Strontium chloride 98%View Details -
 Strontium chloride CAS 10476-85-4View Details
Strontium chloride CAS 10476-85-4View Details
10476-85-4 -
 Strontium Chloride CAS 10476-85-4View Details
Strontium Chloride CAS 10476-85-4View Details
10476-85-4 -
 Strontium Chloride CAS 10476-85-4View Details
Strontium Chloride CAS 10476-85-4View Details
10476-85-4 -
 Strontium Chloride CAS 10476-85-4View Details
Strontium Chloride CAS 10476-85-4View Details
10476-85-4 -
 Powder Strontium Chloride 98%, For LaboratoryView Details
Powder Strontium Chloride 98%, For LaboratoryView Details
10025-70-4 -
 Strontium ChlorideView Details
Strontium ChlorideView Details
10025-70-4
