Sodium selenite
Synonym(s):Selenious acid;Sodium salt
- CAS NO.:10102-18-8
- Empirical Formula: Na2O3Se
- Molecular Weight: 172.94
- MDL number: MFCD00003489
- EINECS: 233-267-9
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:15:32
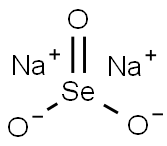
What is Sodium selenite?
Description
Sodium selenite (Na2SeO3) is a toxic inorganic salt that is highly soluble in water and insoluble in organic solvents. The crystal structure of the anhydrous salt has been variously reported as tetragonal or monoclinic.
In 1889, Irish chemists Sir Charles A. Cameron* and John Macallan produced Na2SeO3 and the previously unknown selenium oxychloride1 (SeOCl2) by heating selenium oxide (SeO2) with sodium chloride. This finding was reported in a pioneering series of articles on selenium chemistry.
In an improved 1929 synthesis, J. B. Krak at the Roessler and Hasslacher Chemical Co. (Perth Amboy, NJ) prepared Na2SeO3 by evaporating a solution of sodium hydroxide and selenious acid (H2SeO3) at 60–100 °C. Commercial Na2SeO3 is now made by heating an aqueous solution of SeO2 and NaOH to form its pentahydrate2, which is crystallized and then warmed to 40 °C to liberate the anhydrous salt.
Na2SeO3 and other selenite salts are used to “neutralize” green impurities during the manufacture of colorless glass. Iron-containing impurities in the natural silicas (e.g., sand) used to make glass absorb red and blue wavelengths of light, giving it a green appearance. Selenites have no color; but when they are dissolved in the glass mixture, they appear pinkish, counteracting the green hue and making the glass colorless.
Chemical properties
White to light beige crystals
Chemical properties
Sodium selenite is a white crystalline substance.
The Uses of Sodium selenite
Sodium selenite Na2O3Se is used in the production of red enamels and in the manufacture of clear red glass.
The Uses of Sodium selenite
Used in reducing carcinogenesis with potency greater than selenomethionene
The Uses of Sodium selenite
Removing green color from glass during its manufacture; alkaloidal reagent.
What are the applications of Application
Sodium selenite is used in reducing carcinogenesis
Definition
ChEBI: An inorganic sodium salt composed of sodium and selenite ions in a 2:1 ratio.
General Description
A white colored crystalline solid. Soluble in water and more dense than water. Contact may irritate skin, eyes and mucous membranes. Toxic by ingestion, inhalation and skin absorption.
Air & Water Reactions
Soluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
Sodium selenite is incompatible with strong acids.
Hazard
Toxic by ingestion.
Health Hazard
Toxic by ingestion. In humans, a concentration of 5 ppm in food or 0.5 ppm in milk or water has been estimated to be dangerous. Elemental selenium has low acute systemic toxicity, but dust or fumes can cause serious irritation of the respiratory tract.
Fire Hazard
May burn but will not ignite readily. When heated to decomposition, may emit toxic fumes of selenium and sodium oxide. Stable in air.
Flammability and Explosibility
Non flammable
Safety Profile
Poison by ingestion, intraperitoneal, intravenous, subcutaneous, intracervical, parenteral, and intramuscular routes. Experimental teratogenic and reproductive effects. Questionable carcinogen. Human mutation data reported. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of Se and Na2O. See also SELENIUM COMPOUNDS.
Potential Exposure
Sodium selenite is used in glass manufacturing and as an alkaloidal reagent; for removing green color from glass during its manufacture; alkaloidal reagent; reagent in bacteriology; testing germination of seeds; decorating porcelain; as a livestock feed additive.
Shipping
UN2630 Selenates or Selenites, Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials.
Purification Methods
Crystallise sodium selenite from a saturated aqueous solution where its solubility is 68% at 20o to give the pentahydrate salt. This yields the anhydrous salt on heating at 40o. [Fehér in Handbook of Preparative Inorganic Chemistry (Ed. Brauer) Academic Press Vol I p 431 1963].
Incompatibilities
The aqueous solution is a medium strong base. Reacts with water, strong acids; hot surfaces; causing decomposition and a toxic hazard.
Waste Disposal
Liquid or solid: make a strongly acidic solution using hydrochloric acid. Slowly add sodium sulfite to the cold solution. Stir mixture producing sulfur dioxide. Heat, forming dark-gray selenium and black tellurium. Let stand overnight. Filter and dry. Ship to supplier.
Properties of Sodium selenite
| Melting point: | >350 °C (lit.) |
| Density | 3.1[at 20℃] |
| vapor pressure | 0.133Pa at 20℃ |
| storage temp. | Store at RT. |
| solubility | Water (Slightly) |
| solubility | 900 g/l |
| appearance | colorless crystals or white powder |
| form | powder |
| color | white |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Water Solubility | 950 g/L (20 ºC) |
| Sensitive | Hygroscopic |
| Merck | 14,8673 |
| Exposure limits | ACGIH: TWA 0.2 mg/m3 NIOSH: IDLH 1 mg/m3; TWA 0.2 mg/m3 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 10102-18-8(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Disodium selenite (10102-18-8) |
Safety information for Sodium selenite
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H317:Sensitisation, Skin H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H411:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P260:Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P302+P352:IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of soap and water. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Sodium selenite
| InChIKey | BVTBRVFYZUCAKH-UHFFFAOYSA-L |
Sodium selenite manufacturer
New Products
4-Fluorophenylacetic acid 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate (6-METHYL-[1,3]DITHIOLO[4,5-b]QUINOXALIN-2-ONE INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 Sodium selenite, Anhydrous CAS 10102-18-8View Details
Sodium selenite, Anhydrous CAS 10102-18-8View Details
10102-18-8 -
 Sodium Selenite Anhydrous extrapure CAS 10102-18-8View Details
Sodium Selenite Anhydrous extrapure CAS 10102-18-8View Details
10102-18-8 -
 Sodium Selenite Anhydrous extrapure AR CAS 10102-18-8View Details
Sodium Selenite Anhydrous extrapure AR CAS 10102-18-8View Details
10102-18-8 -
 Sodium selenite CAS 10102-18-8View Details
Sodium selenite CAS 10102-18-8View Details
10102-18-8 -
 Sodium selenite, anhydrous, GR 99% CAS 10102-18-8View Details
Sodium selenite, anhydrous, GR 99% CAS 10102-18-8View Details
10102-18-8 -
 Sodium selenite, anhydrous, 98% CAS 10102-18-8View Details
Sodium selenite, anhydrous, 98% CAS 10102-18-8View Details
10102-18-8 -
 Sodium selenite CAS 10102-18-8View Details
Sodium selenite CAS 10102-18-8View Details
10102-18-8 -
 Sodium Selenite CAS 10102-18-8View Details
Sodium Selenite CAS 10102-18-8View Details
10102-18-8