Sodium oxide
Synonym(s):Disodium monoxide;Disodium oxide
- CAS NO.:1313-59-3
- Empirical Formula: Na2O
- Molecular Weight: 61.98
- MDL number: MFCD00046201
- EINECS: 215-208-9
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-17 09:49:44
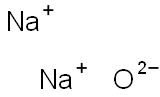
What is Sodium oxide?
Chemical properties
white to grey granules or powder
Chemical properties
Sodium is a strong alkaline flux of low toxicity that creates brightly colored glazes. Its exact melting point is 1652°F (900°C) but it begins melting at about 1580°F (860°C), so it's best to begin to reduce high-sodium glazes at this point.

Sodium oxide is a powerful flux at all temperatures. You'll often see it written as KNaO because it's similar to potassium oxide (K2O) in color response and expansion and contraction rate. Often the insoluble source of sodium oxide includes some potassium oxide; for example, feldspars, which are the primary source of sodium in high-fire glazes, usually contain varying amounts of both sodium and potassium oxides.Most sodium oxide sources are soluble and can act as deflocculants in a glaze slurry or a casting slip. Glazes such as copper red or carbon trap shinos,which have soluble sources of sodium oxide like soda ash, borax, ornepheline syenite, can easily become deflocculated.
One interesting characteristic of sodium oxide is that it's volatile above 2012°E (1100°C)and will cause flashing on a clay body as it leaves the glaze. For this rcason it's widely used in such vapor glazing techniques as soda and salt firing.
Sodium exhibits a low viscosity and low surface tension so if it's used in high enough quantities it will cause glazes to run. It also has a high expansion and contraction rate and will often cause crazing in glazes.Sodium oxidc creatcs soft glaze surfaces that are easily abraded by cutlery, acids,and bases (detergents).
Insoluble sources of sodium oxide include sodium feldspars,Minspar, Kona F-4, NC-4, Bainbridge, Eureka, Godfrey, and cryolite. It's also present in potash feldspars, including Custer, G-200, K-200, Plastic Vitrox, Cornwall stone,volanic ash, and rottenstone.Soluble forms of sodium oxide include soda ash, baking soda, salt, borax, unwashed wood as, Gerstley borate and its substitutes, and sodium silicate. Nepheline syenite and most frits are slightly soluble.
The Uses of Sodium oxide
Sodium oxide is used in chemical manufacturing, ceramics and glasses. Ethylbenzene dehydrogenation and carbon dioxide shift-reaction occurs using a sodium oxide/alumina catalyst. It is employed as catalyzing gasification of CO2 on carbon.
The Uses of Sodium oxide
As a dehydrating agent; in certain chemical reactions as a polymerizing or condensing agent.
The Uses of Sodium oxide
Sodium oxide has been used as a coating precursor on organic polymer films during the plasma modification to analyze its antimicrobial properties.
What are the applications of Application
Sodium oxide is a significant component of manufactured glass
Definition
A white solid formed by burning sodium in a deficiency of oxygen or alternatively by reducing sodium peroxide or sodium hydroxide with the requisite amount of sodium. It reacts violently with water to form sodium hydroxide and with acids to form solutions of their salts. Sodium monoxide forms cubic crystals. It dissolves in liquid ammonia to give a mixture of sodamide and sodium hydroxide.
Definition
sodium monoxide: A whitish-greydeliquescent solid, Na2O; r.d. 2.27;sublimes at 1275°C. It is manufacturedby oxidation of the metal in alimited supply of oxygen and purifiedby sublimation. Reaction with waterproduces sodium hydroxide. Its commercialapplications are similar tothose of sodium hydroxide.
General Description
Sodium oxide is a strong alkaline oxide, commonly used as an active flux in ceramic glazes.
Flammability and Explosibility
Not classified
Properties of Sodium oxide
| Melting point: | >400°C |
| Boiling point: | sublimes at 1274℃ [HAW93] |
| Density | 2.27 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.) |
| vapor pressure | 0Pa at 20℃ |
| solubility | reacts with H2O |
| form | Beads |
| color | White to gray |
| Specific Gravity | 2.27 |
| Water Solubility | Soluble in water. |
| Sensitive | Air & Moisture Sensitive |
| Merck | 14,8651 |
| Stability: | Stable. Reacts violently with water, acids and with many other compounds. Store under dry inert gas. May lead to fire in contact with combustible material. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 1313-59-3(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Sodium oxide (1313-59-3) |
Safety information for Sodium oxide
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Flame Over Circle Oxidizers GHS03  Corrosion Corrosives GHS05 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H271:Oxidising liquids;Oxidising solids H314:Skin corrosion/irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P210:Keep away from heat/sparks/open flames/hot surfaces. — No smoking. P220:Keep/Store away from clothing/…/combustible materials. P260:Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P303+P361+P353:IF ON SKIN (or hair): Remove/Take off Immediately all contaminated clothing. Rinse SKIN with water/shower. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Sodium oxide
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 sodium oxide 98%View Details
sodium oxide 98%View Details -
 Sodium oxide CAS 1313-59-3View Details
Sodium oxide CAS 1313-59-3View Details
1313-59-3 -
 Sodium oxide CAS 1313-59-3View Details
Sodium oxide CAS 1313-59-3View Details
1313-59-3 -
 Sodium oxide CAS 1313-59-3View Details
Sodium oxide CAS 1313-59-3View Details
1313-59-3 -
 Sodium oxide CAS 1313-59-3View Details
Sodium oxide CAS 1313-59-3View Details
1313-59-3 -
 Sodium OxideView Details
Sodium OxideView Details
1313-59-3 -
 Sodium OxideView Details
Sodium OxideView Details
1313-59-3 -
 Sodium Oxide PowderView Details
Sodium Oxide PowderView Details
1313-59-3
