Sodium amide
Synonym(s):Sodium amide crystalline
- CAS NO.:7782-92-5
- Empirical Formula: H2NNa
- Molecular Weight: 39.01
- MDL number: MFCD00011117
- EINECS: 231-971-0
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:15:30
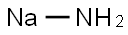
What is Sodium amide?
Chemical properties
grey powder
Physical properties
White crystalline powder with odor of ammonia; orthogonal crystals; density 1.39 g/cm3; melts at 210°C; begins to volatilize at 400°C; decomposes at 500°C; decomposed by water and hot alcohol; in fused state it dissolves zinc, magnesium and other metals, as well as, quartz, glass, and silicates.
The Uses of Sodium amide
Sodium Amide is widely used in organic chemical synthesis as a strong base in reactions such as in the preparation of phenylacetylene from 1,2-dibromophenylethane. Also used in the synthesis of 2,6-diamination of substituted pyridines as initiator of heterogeneous chichibabin reaction.
The Uses of Sodium amide
Reagent for: Synthesis of allylic amines and amides1 Synthesis of antibacterials2 Aggregative activation and heterocyclic chemistry3 Phenylation with diphenyliodonium chloride4
The Uses of Sodium amide
Dehydrating agent. In the production of indigo and hydrazine. Intermediate in the preparation of sodium cyanide. In ammonolysis reactions, in Claisen condensations, alkylation of nitriles and ketones, synthesis of ethynyl Compounds, acetylenic carbinols. Fused NaNH2 dissolves metallic Mg, Zn, Mo, W, quartz, glass, silicates and other substances.
What are the applications of Application
Sodium amide is a useful reagent
Definition
A white ionic solid formed by passing dry ammonia over sodium at 300–400°C. The compound reacts with water to give sodium hydroxide and ammonia. It reacts with red-hot carbon to form sodium cyanide and with nitrogen(I) oxide to form sodium azide. Sodamide is used in the Castner process and in the explosives industry.
Preparation
Sodium amide is prepared by passing dry ammonia gas over sodium metal at 350°C: 2Na + 2NH3 → 2NaNH2 + H2Also, it may be prepared by reacting sodium metal with liquid ammonia in the presence of a catalyst such as iron(III) nitrate. The compound must be stored in well-sealed containers free from air or moisture.
Reactions
Sodamide, sodamine, NaNH2, white solid, formed by reaction of sodium metal and dry NH3 gas at 350 °C (662 °F), or by solution of the metal in liquid ammonia. Reacts with carbon upon heating, to form sodium cyanide, and with nitrous oxide to form sodium azide, NaN3.
General Description
Odorless colorless solid. Denser than water.
Air & Water Reactions
Highly flammable. Reacts violently with water and bursts into flame.
Reactivity Profile
Sodium amide is a powerful reducing agent. Reacts violently with oxidizing agents. Reacts violently with steam and water to form caustic NaOH and NH3 vapors [Bergstrom et al., Chem. Reviews, 12:6 1932]. May form explosive compounds in the presence of water and carbon dioxide [Handling Chemicals Safely 1980 p 826]. Liable to deflagration upon heating and friction. Forms an explosive peroxide on storage. When Sodium amide and chromic anhydride are mixed together a vigorous reaction results; the same occurs with other oxidizing agents including dinitrogen tetraoxide, potassium chlorate, sodium nitrite. [Mellor 11:234 1946-47]. Reaction with 1,1-diethoxy-2- chloroethane produces sodium ethoxyacetylide, which is extremely pyrophoric [Rutledge 1968 p. 35]. Reactions with halogenated hydrocarbons may be violently explosive. Sodium amide forms toxic and flammable H2S gas with CS2. (714).
Hazard
Flammable, dangerous fire risk.
Health Hazard
Ammonia gas formed by reaction of solid with moisture irritates eyes and skin. Solid causes caustic burns of eyes and skin. Ingestion burns mouth and stomach in same way as caustic soda and may cause perforation of tissue.
Fire Hazard
Special Hazards of Combustion Products: Toxic and irritating ammonia gas may be formed.
Safety Profile
An intense irritant to tissue, skin, and eyes. Flammable by chemical reaction. Ignites or explodes with heat or grinding. Explosive reaction with moisture, chromium trioxide, potassium chlorate, halocarbons (e.g., 1,l -diethoxy-2chloroethane), oxidants, sodium nitrite, air. Can become explosive in storage. Violent reaction with dinitrogen tetraoxide. Will react with water or steam to produce heat and toxic and corrosive fumes of sodium hydroxide and ammonia. When heated to decomposition it emits highly toxic fumes of NH3 and Na2O. See also AMIDES.
Purification Methods
It reacts violently with H2O and is soluble in liquid NH3 (1% at 20o). It should be stored in wax-sealed containers in small batches. It is very hygroscopic and absorbs CO2 and H2O. If the solid is discoloured by being yellow or brown in colour, then it should be destroyed as it can be highly EXPLOSIVE. It should be replaced if discoloured. It is best destroyed by covering it with much toluene and slowly adding dilute EtOH with stirring until all the ammonia is liberated (FUME CUPBOARD). [Dennis & Bourne Inorg Synth I 74 1939, Schenk in Handbook of Preparative Inorganic Chemistry (Ed. Brauer) Academic Press Vol I p 465 1963, Bergstrom Org Synth Coll Vol III 778 1955.]
Properties of Sodium amide
| Melting point: | 210 °C (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 400 °C (lit.) |
| Density | 1.39 g/cm3 (25℃) |
| Flash point: | 85 °F |
| storage temp. | Store below +30°C. |
| solubility | reacts with H2O |
| form | crystalline |
| color | Greyish white powder |
| Odor | Ammonia like |
| Water Solubility | REACTS VERY VIOLENTLY, EVEN EXPLOSIVELY |
| Sensitive | Air & Moisture Sensitive |
| Merck | 14,8576 |
| Stability: | Stability Flammable. Reacts violently with water producing very toxic fumes. In case of fire do not use water, but instead smother with soda ash. May form explosive peroxides if heated, or if stored for extended periods in contact with air or oxygen. Incompatible with water and aqueous solutions, carbon dioxide, halogenated hydrocarbo |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 7782-92-5(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Sodium amide (Na(NH2)) (7782-92-5) |
Safety information for Sodium amide
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Flame Flammables GHS02  Corrosion Corrosives GHS05  Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H225:Flammable liquids H261:Substances And Mixtures Which, In Contact With Water,Emit Flammable Gases H304:Aspiration hazard H314:Skin corrosion/irritation H336:Specific target organ toxicity,single exposure; Narcotic effects H373:Specific target organ toxicity, repeated exposure H412:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P210:Keep away from heat/sparks/open flames/hot surfaces. — No smoking. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P231+P232:Handle under inert gas. Protect from moisture. P301+P330+P331:IF SWALLOWED: Rinse mouth. Do NOT induce vomiting. P303+P361+P353:IF ON SKIN (or hair): Remove/Take off Immediately all contaminated clothing. Rinse SKIN with water/shower. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Sodium amide
Sodium amide manufacturer
JSK Chemicals
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
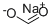
You may like
-
 4-Chlorobenzhydryl Amide 7782-92-5 99%View Details
4-Chlorobenzhydryl Amide 7782-92-5 99%View Details
7782-92-5 -
 Sodium amide CAS 7782-92-5View Details
Sodium amide CAS 7782-92-5View Details
7782-92-5 -
 Sodium amide CAS 7782-92-5View Details
Sodium amide CAS 7782-92-5View Details
7782-92-5 -
 Sodamide CAS 7782-92-5View Details
Sodamide CAS 7782-92-5View Details
7782-92-5 -
 SODAMIDE Extra Pure CAS 7782-92-5View Details
SODAMIDE Extra Pure CAS 7782-92-5View Details
7782-92-5 -
 Sodium amide CAS 7782-92-5View Details
Sodium amide CAS 7782-92-5View Details
7782-92-5 -
 Sodium amide CAS 7782-92-5View Details
Sodium amide CAS 7782-92-5View Details
7782-92-5 -
 Sodium amide crystalline CAS 7782-92-5View Details
Sodium amide crystalline CAS 7782-92-5View Details
7782-92-5