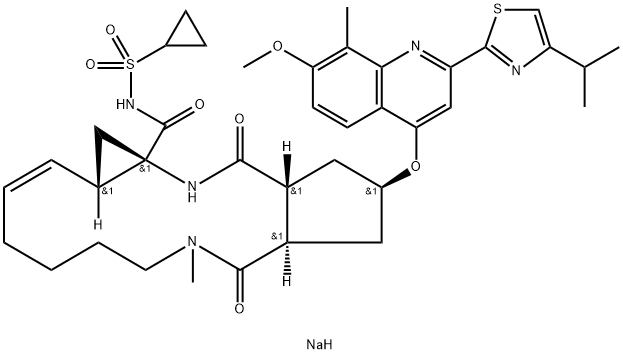
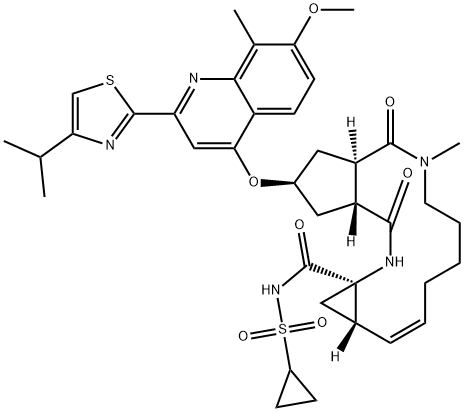
Simeprevir
- CAS NO.:923604-59-5
- Empirical Formula: C38H47N5O7S2
- Molecular Weight: 749.94
- MDL number: MFCD25563225
- EINECS: 689-150-1
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-19 23:02:33
What is Simeprevir?
Absorption
The mean absolute bioavailability of simeprevir following a single oral 150 mg dose of simeprevir capsule in fed conditions is 62%. Maximum plasma concentrations (Cmax) are typically achieved between 4 to 6 hours following the oral administration.
Toxicity
In a combination therapy with sofosbuvir, most common reported adverse effects is fatigue, headache and nausea. In case of triple therapy with PEG-Interferon Alfa-2A and ribavirin, most common adverse effects included rash (including photosensitivity), pruritus and nausea. Elevations of serum bilirubin may be observed due to inhibition of bilirubin transporters OATP1B1 and MRP2 by simeprevir.
Description
In September 2013, simeprevir (also known as TMC435) was approved in Japan (trade name Sovriad?) for the treatment of genotype 1 hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection in combination with pegylated interferon and ribavirin (PR). Simeprevir was approved for the same indication in November 2013 in the United States (trade name Olysio?) and Canada (trade name Galexos?). Simeprevir is the third HCV PI to receive approval and was discovered from an effort to optimize a novel series of cyclopentane-core macrocyclic HCV PIs. Unlike the earlier PIs, simeprevir does not rely on formation of a covalent intermediate to inhibit the enzyme, but instead gains binding affinity through a large P2 quinoline substituent that occupies an extended S2 subsite of HCV protease by induced fit. This pocket is not occupied by inhibitors such as telaprevir and boceprevir. Other key features of simeprevir are truncation of the P3 capping group (the N-methyl amide), use of an acylsulfonamide as an acid isostere, and incorporation of an isopropylthiazole group to give improved permeability. Simeprevir is a potent NS3/4A PI (Ki=0.36 nM), with antiviral activity in the HCV replicon assay (genotype 1b EC50=7.8 nM; genotype 1a EC50=28.4 nM). It is 25-fold less potent against HCV genotype 2, >1000 less potent for HCV genotype 3, but has 3-fold better potency for HCV genotype 4.
Originator
Tibotec and Medivir (Ireland and Sweden)
The Uses of Simeprevir
Simeprevir-d3 is labelled Simeprevir (S466500) which is a hepatitis C virus (NS3/4A) protease inhibitor. Simeprevir (S466500) is used for the cure and treatment of hepatitis C.
Background
Simeprevir is a hepatitis C virus (HCV) NS3/4A protease inhibitor indicated in patient's with HCV genotype 1 for the treatment of chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection. HCV is a single-stranded RNA virus that is categorized into nine distinct genotypes, with genotype 1 being the most common in the United States, and affecting 72% of all chronic HCV patients . Like all NS3/4A inhibitors, simeprevir is a serine protease inhibitor in similarity to Boceprevir and Telaprevir but is classified as a second generation protease inhibitor. This class of antiviral drugs were the first direct acting antivirals approved but are associated with lower cure rates than newer drugs. Broad use of simeprevir occurred when it was used in combination with a newer drug, Sofosbuvir. Inhibiting HCV NS3/4A protease in a potent and highly specific manner, simeprevir is a direct-acting antiviral agent against the hepatitis C virus. Since the viral protease NS3/4A complex is essential for cleaving the HCV encoded polyprotein into individual viral proteins facilitating replication , the drug blocks the viral replication process. It is shown to display synergistic effects with interferon-α and HCV NS5B inhibitor, and additive effects with ribavirin in HCV replicon cells . Unlike first generation serine protease inhibitors, simprevir has a sightly different resistance profile where limited therapeutic efficacy of the drug is observed with NS3 Q80K polymorphic variants and simeprevir-specific amino acid position of 168 also results in higher treatment failure rates . The observed prevalence of the N3 Q80K polymorphism was 30% in subjects infected with HCV genotype 1a and 0.5% in subjects infected with HCV genotype 1b .
According to 2017 American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases (AASLD) and 2015 consensus guidelines from the Canadian Association for the Study of the Liver (CASL), simeprevir can be used as first-line or second-line threapies for treatment-na?ve patients as adjunct to sofosbuvir treatment for genotype 1 or PEG-Interferon/ribavirin combination therapy for genotype 1 or 4. The combination therapy of simeprevir and other antiviral agents are initiated in HCV-positive patients with the intent to cure, or achieve a sustained virologic response (SVR), after 12 weeks of daily therapy. SVR and eradication of HCV infection is associated with significant long-term health benefits including reduced liver-related damage, improved quality of life, reduced incidence of Hepatocellular Carcinoma, and reduced all-cause mortality .
Simeprevir was approved by the FDA in November 2014 and is marketed under the brand name Olysio as oral tablets. Administered once daily with food, 150mg simeprevir capsule is used in combination with Sofosbuvir in patients with HCV genotype 1 without cirrhosis for 12 week duration. In patients with HCV genotype 1 with compensated cirrhosis, the treatment is directed for 24 week duration. Sustained virologic response 12 weeks after planned end of treatment (SVR12) was achieved in 170/176 (97%) subjects without cirrhosis treated with 12 weeks simeprevir in combination with sofosbuvir (FDA Label). The overall SVR12 was 88% (44/50) in treatment-na?ve patients with cirrhosis .
Simeprevir is also used in treatment of HCV genotype 4 patients with or without cirrhosis and is taken with Peginterferon alfa-2a and Ribavirin; this triple therapy allows shortening treatment duration from 48 weeks or longer to 12 or 24 weeks depending on prior response status and presence of HIV-1 co-infection. Prior to initiation of treatment with Peginterferon alfa-2a and Ribavirin, screening for the presence of virus with the NS3 Q80K polymorphism is strongly recommended and if detected, alternative treatment should be considered instead to prevent therapeutic failure. The SVR12 was 83% (29/35) in treatment-na?ve patients and 86% (19/22) in relapsing patients.
Indications
Indicated for the treatment of adults with chronic hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection: typically in combination with sofosbuvir in patients with HCV genotype 1 without cirrhosis or with compensated cirrhosis and in combination with peginterferon alfa (Peg-IFN-alfa) and ribavirin (RBV) in patients with HCV genotype 1 or 4 without cirrhosis or with compensated cirrhosis.
Resistance: Reduced susceptibility to simeprevir was most commonly associated with the viral NS3 Q80K polymorphism. Amino acid substitutions at NS3 positions S122, R155 and/or D168 are also shown to reduce susceptibility to simeprevir in genotype 1a/b patients.
What are the applications of Application
Simeprevir is Simeprevir is a hepatitis C virus (HCV) NS3/4A protease inhibitor
Definition
ChEBI: Simeprevir is an azamacrocycle and a lactam.
brand name
Sovriad
Pharmacokinetics
Simeprevir is a direct-acting antiviral agent and inhibitor for HCV NS3/4A protease, which is an important enzyme required for viral replication. Unlike Boceprevir and Telaprevir, simeprevir is a competitive, reversible, macrocyclic, noncovalent inhibitor. The macromolecular cyclic portion of the molecule improves the affnity and selectivity characteristics, which allows rapid association and slow dissociation to the protein target through noncovalent binding .
Clinical Use
HCV NS3/4A serine protease inhibitor:
Treatment of hepatitis C in combination with other
treatment
Synthesis
Commercial 2-methyl-3-methoxybenzoic acid (153) was treated
with diphenylphosphorylazide (DPPA) and triethylamine to
affect a Curtius rearrangement and the resulting isocyanate was
trapped with t-butanol to produce the Boc-protected aniline 154
in quantitative yield. Upon removal of the Boc protecting group
with TFA, the resulting aniline was reacted with boron trichloride
followed by the addition of acetonitrile and aluminum trichloride
to affect Friedel¨CCrafts acylation to give aminoacetophenone 155
in 40% yield. Acylation of the amino group with 4-isopropylthiazole-
2-carbonyl chloride (156) gave ketoamide 157 in 90% yield,
which was treated with potassium tert-butoxide in t-butanol at
100 ?? to furnish quinolinol 158 in 88% yield.
Use of a ring closing metathesis approach, enabling the synthesis
of the macrocyclic portion of the drug and ultimately simeprevir,
is described. Hydrogenation of commercial
trans-cyclopentanone-3,4-dicarboxylic acid (159) over Raney Ni in
the presence of triethylamine followed by cyclization to the
lactone using 2-chloro-4,6-dimethoxy-1,3,5-triazine (CDMT) and
N-methylmorpholine (NMM), and subsequent cinchonidine salt
formation gave lactone acid 160 in 26% yield over the 3 steps in
97% ee. Next, amide coupling with N-methylhexenylamine using
N-ethoxycarbonyl-2-ethoxy-1,2-dihydroquinoline (EEDQ), Fischer
esterification, and subsequent introduction of the quinolinol fragment
158 under Mitsunobu conditions using triphenylphosphine
(PPh3) and diisopropyl azodicarboxylate (DIAD) provided methyl
ester 161 in 65% overall yield for the three steps. Saponification
of the ester with lithium hydroxide followed by EEDQ-promoted
coupling to (1R,2S)-1-amino-2-vinyl-cyclopropane ethyl ester
(162) and Boc protection of the resulting amide gave the RCM
substrate, diene 163 in 95% yield for the two steps.
Macrocyclization of 163 using the second generation M2 catalyst
under dilute concentration in refluxing toluene followed
by acidic removal of the amide protecting group gave cycloalkene
ester 164 in high yield. Saponification of the ester, activation of the
resulting acid with 1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)carbodiimide
(EDCI), and coupling with cyclopropylsulfonamide led to
simeprevir (XXI) in high overall yield.

Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Anti-arrhythmics: possible increased risk of
bradycardia with amiodarone.
Antibacterials: concentration possibly increased by
clarithromycin - avoid; concentration of both drugs
increased with erythromycin - avoid; concentration
reduced by rifampicin and possibly rifabutin - avoid.
Antidepressants: concentration possibly reduced by
St John’s wort - avoid.
Antiepileptics: concentration possibly reduced
by carbamazepine, fosphenytoin, oxcarbazepine,
phenobarbital, phenytoin and primidone - avoid.
Antifungals: concentration possibly increased by
fluconazole, itraconazole, ketoconazole, posaconazole
and voriconazole - avoid.
Antivirals: concentration of both drugs increased
with darunavir - avoid; concentration reduced
by efavirenz; avoid with etravirine; concentration
possibly reduced by nevirapine - avoid;
concentration increased by ritonavir - avoid.
Ciclosporin: avoid concomitant use, increased
simeprevir concentration.
Cobicistat: concentration possibly increased by
cobicistat - avoid.
Metabolism
Simeprevir undergoes hepatic metabolism. The primary metabolic pathway involves CYP3A system-mediated oxidation. Involvement of CYP2C8 and CYP2C19 cannot be excluded.
Metabolism
Hepatically metabolised. In vitro experiments with human
liver microsomes indicated that simeprevir primarily
undergoes oxidative metabolism by the hepatic CYP3A4
system.
Elimination of simeprevir occurs via biliary excretion.
Following a single oral administration of 200 mg
[14C]-simeprevir to healthy subjects, on average 91% of
the total radioactivity was recovered in faeces. Unchanged
simeprevir in faeces accounted for on average 31% of the
administered dose. Renal clearance plays an insignificant
role in its elimination.
Properties of Simeprevir
| Density | 1.38 |
| storage temp. | Store at -20°C |
| solubility | insoluble in H2O; insoluble in EtOH; ≥18.75 mg/mL in DMSO |
| form | solid |
| pka | 4.47±0.40(Predicted) |
| color | White to off-white |
Safety information for Simeprevir
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Simeprevir
Simeprevir manufacturer
BDR Pharmaceuticals International Pvt Ltd
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 923604-59-5 Simeprevir 98%View Details
923604-59-5 Simeprevir 98%View Details
923604-59-5 -
 2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1