S-Carboxymethyl-L-Cysteine
Synonym(s):3-carboxymethylthio-L -alanine;S-Carboxymethyl-L -cysteine
- CAS NO.:638-23-3
- Empirical Formula: C5H9NO4S
- Molecular Weight: 179.19
- MDL number: MFCD00002614
- EINECS: 211-327-5
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:08:57
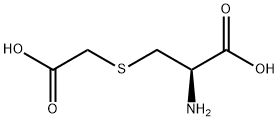
What is S-Carboxymethyl-L-Cysteine?
Absorption
Carbocisteine is rapidly absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract when taken orally with peak serum concentrations achieved within 1 to 1.7 hours.
Toxicity
The oral LD50 of carbocisteine in rats is >15000 mg/kg. An overdose with carbocisteine is likely to result in gastrointestinal discomfort with nausea and vomiting.
Chemical properties
white to slightly off-white amorphous powder
Originator
Rhinathiol,Kramer,Switz.
The Uses of S-Carboxymethyl-L-Cysteine
Carbocisteine is a mucolytic agent used in the treatment of respiratory disorders ranging from the influenza virus infection to chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD).
The Uses of S-Carboxymethyl-L-Cysteine
Labeled Carbocisteine, intended for use as an internal standard for the quantification of Carbocisteine by GC- or LC-mass spectrometry.
The Uses of S-Carboxymethyl-L-Cysteine
carbocysteine is an amino acid. It can be used to help control sebum production.
Background
Dyspnea and cough are common symptoms of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and other respiratory conditions characterized by increased mucus production. Individuals with COPD have a greater risk of pulmonary infection due to the growth and accumulation of viruses and bacteria in thick bronchial mucus. Carbocisteine is a mucolytic drug that alleviates respiratory symptoms and infections by reducing the viscosity of mucus, allowing it to be expelled.
Several licenses for this drug were withdrawn following serious and fatal paradoxical effects after carbocisteine therapy in children; respiratory dress, dyspnea, and cough aggravation were reported by physicians in France and Italy. Carbocisteine is currently not FDA or Health Canada approved, but is approved for use in Asia, Europe, and South America.
Indications
Carbocisteine is indicated over the counter and in prescription formulas to clear airway secretions in conditions associated with increased mucus.
What are the applications of Application
S-Carboxymethyl-L-cysteine is a mucolytic agent
Definition
ChEBI: S-carboxymethyl-L-cysteine is an L-cysteine thioether that is L-cysteine in which the hydrogen of the thiol group has been replaced by a carboxymethyl group. It has a role as a mucolytic. It is a L-cysteine thioether and a non-proteinogenic L-alpha-amino acid. It is a conjugate acid of a S-carboxylatomethyl-L-cysteine(1-).
Manufacturing Process
There were placed 120g of L-cysteine (0.5 mol) in a 2 liter three-necked flask
equipped with a stirrer thermometer and methanol/dry ice cooling and 1.5
liters of liquid ammonia were allowed to enter at -40°C. Then there were
added under continuous cooling 50 g (2.17 mols) of sodium metal in portions
of 1 to 2 g during the course of one hour. The end of the reaction was
recognized by the continuation of the blue color. After the end of the reaction
the excess sodium was destroyed by the addition of ammonium chloride and
the ammonia vaporized at normal pressure. The residue was taken up in 500
ml of water and concentrated in a vacuum to 200 ml in order to remove
residual ammonia, and again treated with 300 ml of water. The entire
operations were carried out under a nitrogen atmosphere.
The aqueous solution of the disodium salt of L-cysteine obtained is then
reacted at 20°C to 30°C under a nitrogen atmosphere in the course of 30
minutes with stirring with a solution of 104 g of chloroacetic acid (1.1 mols)
and 4 g of sodium pyrosulfite in 200 ml of water. It is also allowed to post
react for 15 minutes at 20°C, the solution clarified over activated carbon and
the filtrate treated with 90 ml of concentrated hydrochloric acid to a pH of
2.5.
Thereby the S-carboxymethyl-L-cysteine precipitates out in crystalline form.
The product is filtered off with suction, well stirred in 500 ml of water, again
filtered with suction and dried in a vacuum at 70°C. The yield is 92% based
on L-cysteine.
brand name
Loviscol (Wyeth-Ayerst); Mucofan (Wyeth-Ayerst).
Therapeutic Function
Mucolytic, Expectorant, Nasal antiinfective
Biochem/physiol Actions
S-Carboxymethyl-L-cysteine is studied as a small molecule mucoactive drug in vivo. These studies include analyzing the oxidative metabolism of S-carboxymethyl-L-cysteine by enzymes such as phenylalanine monooxygenase(s).
Pharmacokinetics
Due to its mucolytic effects, carbocisteine significantly reduces sputum viscosity, cough, dyspnea and fatigue. Additionally, it prevents pulmonary infections by decreasing accumulated mucus in the respiratory tract; this is especially beneficial in preventing exacerbations of COPD caused by bacteria and viruses. It has in-vitro anti-inflammatory activity with some demonstrated action against free radicals.
Safety Profile
contact. A riot control agent. When heated
Metabolism
Metabolic pathways for carbocisteine include acetylation, decarboxylation, and sulfoxidation, leading to the formation of pharmacologically inactive carbocisteine derivatives. Significant variability exists in metabolism due to genetic polymorphism in sulfoxidation capacity. Two cytosolic enzymes are responsible for the metabolism of carbocisteine: cysteine dioxygenase and phenylalanine 4-hydroxylase. Reduced metabolism can cause increased exposure to carbocisteine, explaining variable clinical response between patients who may polymorphisms affecting the enzymes responsible for carbocisteine metabolism. It is generally accepted that sulfodixation is the main metabolic pathway of carbocisteine, however, one group of researchers found a novel urinary metabolite, S-(carboxymethylthio)-L-cysteine (CMTC). No cysteinyl sulfoxide metabolites were found in the urine of patients taking carbocisteine in this study.
Properties of S-Carboxymethyl-L-Cysteine
| Melting point: | 208-213 °C (dec.) |
| Boiling point: | 417.3±45.0 °C(Predicted) |
| alpha | -31 º (c=1, 10% NaH2CO3) |
| Density | 1.315 (estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.5216 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | Aqueous Acid, Aqueous Base (Sparingly, Sonicated) |
| form | Amorphous Powder |
| pka | 2.06±0.10(Predicted) |
| color | White to slightly off-white |
| Water Solubility | SOLUBLE IN COLD WATER |
| Merck | 14,1802 |
| BRN | 1725012 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 638-23-3(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | L-Cysteine, S-(carboxymethyl)- (638-23-3) |
Safety information for S-Carboxymethyl-L-Cysteine
Computed Descriptors for S-Carboxymethyl-L-Cysteine
S-Carboxymethyl-L-Cysteine manufacturer
Innovative Health Care (India) Pvt. Ltd.
REXIN Laboratories (Redson Group)
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 CARBOCISTEINE 99%View Details
CARBOCISTEINE 99%View Details -
 638-23-3 98%View Details
638-23-3 98%View Details
638-23-3 -
 S-Carboxymethyl-L-cysteine 97% CAS 638-23-3View Details
S-Carboxymethyl-L-cysteine 97% CAS 638-23-3View Details
638-23-3 -
 S-(Carboxymethyl)-L-cysteine CAS 638-23-3View Details
S-(Carboxymethyl)-L-cysteine CAS 638-23-3View Details
638-23-3 -
 L-Carbocisteine 98%View Details
L-Carbocisteine 98%View Details
638-23-3 -
 L-Carbocisteine 638-23-3 98%View Details
L-Carbocisteine 638-23-3 98%View Details
638-23-3 -
 S-Carboxymethyl-L-cysteine CAS 638-23-3View Details
S-Carboxymethyl-L-cysteine CAS 638-23-3View Details
638-23-3 -
 Carbocisteine CAS 638-23-3View Details
Carbocisteine CAS 638-23-3View Details
638-23-3