Carboxymethyl cellulose
Synonym(s):Carboxymethyl cellulose;CM-Cellulose
- CAS NO.:9000-11-7
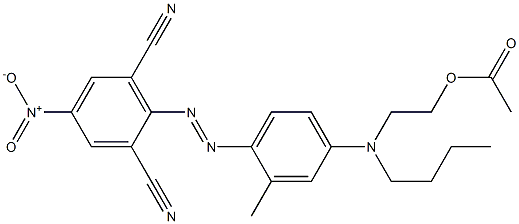
- Empirical Formula: C6H12O6
- Molecular Weight: 180.15588
- MDL number: MFCD00149018
- EINECS: 618-326-2
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-17 09:49:39
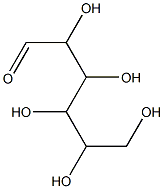
What is Carboxymethyl cellulose?
Absorption
No pharmacokinetic data available.
Toxicity
Rat oral LD50, rabbit dermal LD50, and rat inhalation LC50 of sodium carboxymethyl cellulose are 27000 mg/kg, >2 g/kg, and >5800 mg/m^3 (4 hours), respectively .
Chemical properties
White or almost white powder, hygroscopic.
Chemical properties
Cellulose is a natural substance normally present in most diets because it is the major structural carbohydrate of green
plants. Cellulose is essentially a linear polymer of glucopyranose units connected by α-1,4-glucoside links. In nature, cellulose is
present in plant cell walls as fibers. The molecular weight of the isolated cellulose is approximately 50,000 daltons. The principal
sources of cellulose for food-related purposes are cotton linters and wood pulp.
Chemical processing converts cellulose into forms or derivatives suitable for incorporation into food products or for use in food
packaging materials. For food use, the optimum degree of substitution of a carboxymethyl-residue on each anhydroglucopyranose
unit on cellulose is 0.95. By preliminary mild acid hydrolysis, the degree of polymerization (i.e., molecular size) of the cellulose
may be reduced before carboxymethylation. Control of the degree of substitution and the degree of polymerization during processing
results in production of a wide variety of derivatives that differ in such physical properties as gelling, temperature, viscosity and
dispersibility in water. Sodium carboxymethyl cellulose is used as a thickening agent and stabilizer in foods. Because carboxymethyl
cellulose is spontaneously converted to sodium salt in alkaline solution, it is probable that any distinction between carboxymethyl
cellulose and sodium carboxymethyl cellulose in foodstuffs is artificial.*
The Uses of Carboxymethyl cellulose
carboxymethyl cellulose (cellulose gum) is a thickener. used in cosmetic formulations when a reactant is not required or desired. often used in bath preparations, beauty masks, hand creams, and shampoos. It is considered a non-comedogenic raw material.
The Uses of Carboxymethyl cellulose
Pharmaceutic aid (suspending agent); pharmaceutic aid (tablet excipient); pharmaceutic aid (viscosity-increasing agent).
The Uses of Carboxymethyl cellulose
Carboxymethylcellulose(CMC) is a gum that is water-soluble cellulose ether manufactured by reacting sodium monochloroacetate with alkali cellulose to form sodium . It dissolves in hot or cold water and is fairly stable over a pH range of 5.0–10.0, but acidification below pH 5.0 will reduce the viscosity and stability except in a special acid-stable type of CMC. A variety of types are available which differ in viscosity and degree of substitution (the number of sodium groups per unit). It functions as a thickener, stabilizer, binder, film former, and suspending agent. It is used in a variety of foods to include dressings, ice cream, baked goods, puddings, and sauces. The usage range is from 0.05 to 0.5%. Also termed cellulose gum.
Indications
Indicated for the symptomatic relief of burning, irritation and discomfort of the eyes due to dryness or exposure to wind or sun.
Background
Carboxymethylcellulose is a cellulose derivative that consists of the cellulose backbone made up of glucopyranose monomers and their hydroxyl groups bound to carboxymethyl groups. It is added in food products as a viscosity modifier or thickener and emulsifier. It is also one of the most common viscous polymers used in artificial tears, and has shown to be effective in the treatment of aqueous tear-deficient dry eye symptoms and ocular surface staining . The viscous and mucoadhesive properties as well as its anionic charge allow prolonged retention time in the ocular surface . Sodium carboxymethylcellulose is the most commonly used salt.
Preparation
Sodium carboxymethyl cellulose is produced by treating wood pulp or cotton linters with alkali and monochloroacetic acid. It occurs as a white- or cream-colored powder or granules.
brand name
Celluvisc (Allergan); Refresh Plus, Cellufresh Formula (Allergan).
Industrial uses
Carboxymethyl cellulose is manufactured with molecular weights ranging from 50,000 to 800,000. Several modifications are of interest to flotation because they display good depressing properties for highly floatable magnesium-bearing minerals. These include sodium salts of phenolphthalein ether cellulose and ethanesulfo cellulose.
Industrial uses
Lignin sulfonate is used as dispersant, flocculant and depressant. Lignin is an amorphous polyphenolic compound derived from enzymatic polymerization of three phenylpropanoid monomers.
Pharmacokinetics
In a randomized clinical study of patients with mild or moderate forms of eye dryness, ophthalmic treatment with sodium carboxymethylcellulose resulted in a diminished frequency of symptoms compared to the placebo group . Carboxymethylcellulose interacts with human corneal epithelial cells to facilitate corneal epithelial wound healing and attenuate eye irritation in a dose-dependent manner . It exhibits protective actions on the ocular surface in various applications; it mediates cytoprotective effects on the ocular surface when applied prior to contact lenses and reduces the incidence of epithelial defects during LASIK .
Carcinogenicity
Sarcomas were produced at the site of repeated subcutaneous injection of aqueous solutions of carboxymethylcellulose. It should be noted, however, that massive doses were given and therefore there must have been considerable local trauma.
Metabolism
No pharmacokinetic data available.
Properties of Carboxymethyl cellulose
| Density | 1.050 g/cm3(Temp: 15-18 °C) |
| FEMA | 2239 | CARBOXYMETHYLCELLULOSE |
| solubility | Practically insoluble in anhydrous ethanol. It swells with water to form a suspension and becomes viscid in 1 M sodium hydroxide. |
| form | preswollen, microgranular |
| color | White to off-white |
| Odor | odorless |
| Stability: | Stable. Combustible. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| InChI | InChI=1S/C6H12O6/c7-1-3(9)5(11)6(12)4(10)2-8/h1,3-6,8-12H,2H2 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 9000-11-7(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Cellulose, carboxymethyl ether (9000-11-7) |
Safety information for Carboxymethyl cellulose
Computed Descriptors for Carboxymethyl cellulose
| InChIKey | GZCGUPFRVQAUEE-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | C(=O)C(O)C(O)C(O)C(O)CO |
Carboxymethyl cellulose manufacturer
New Products
Indole Methyl Resin tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Boc-His(Boc)-OH 2-CTC Resin 4-Chloro-7-tosy1-7Hpyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine 5,7-Dibromo-1H-indole 2,5-dichloro-N-hydroxy-4,6-dimethylpyridine-3-carboximidamide 2,2-Dimethoxy-7-azaspiro[3.5]nonane hydrochloride 4-chloromethyl-5-methyl-1,3-dioxol-2-one (DMDO-Cl) R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-((2-hydroxyethyl)thio)benzoic acid 1-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-2-PYRROLIDINONE Methyl 6-methylnicotinate 3-Pyridineacrylic acid tert-Butyl carbazate TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 1,3-Diethyl-1,3-Diphenylurea Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
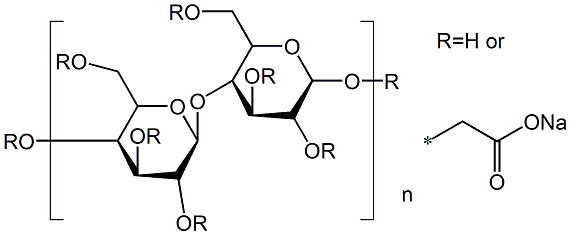




You may like
-
 9000-11-7 98%View Details
9000-11-7 98%View Details
9000-11-7 -
 Carboxymethyl cellulose 98%View Details
Carboxymethyl cellulose 98%View Details
9000-11-7 -
 Carboxymethyl cellulose 9000-11-7 98%View Details
Carboxymethyl cellulose 9000-11-7 98%View Details
9000-11-7 -
 9000-11-7 Carboxymethyl cellulose 98%View Details
9000-11-7 Carboxymethyl cellulose 98%View Details
9000-11-7 -
 9000-11-7 Carboxymethyl cellulose 99%View Details
9000-11-7 Carboxymethyl cellulose 99%View Details
9000-11-7 -
 9000-11-7 Carboxymethyl cellulose 99%View Details
9000-11-7 Carboxymethyl cellulose 99%View Details
9000-11-7 -
 Carboxymethyl cellulose CASView Details
Carboxymethyl cellulose CASView Details -
 Carmellose CAS 9000-11-7View Details
Carmellose CAS 9000-11-7View Details
9000-11-7
