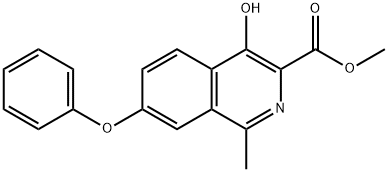
Roxadustat
- CAS NO.:808118-40-3
- Empirical Formula: C19H16N2O5
- Molecular Weight: 352.34
- MDL number: MFCD20040519
- EINECS: 813-400-2
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-07-28 17:37:18
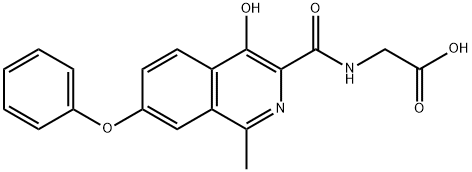
What is Roxadustat?
Description
Roxadustat is an orally administered, small molecule hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) prolyl hydroxylase inhibitor that is being developed by FibroGen, in collaboration with Astellas and AstraZeneca, for the treatment of anaemia in patients with dialysis-dependent chronic kidney disease (CKD), non-dialysis-dependent CKD and in patients with myelodysplastic syndromes.
The Uses of Roxadustat
Roxadustat is a hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) prolyl hydroxylase inhibitor used to increase white blood cell levels in blood and hematopoietic progenitor cells in bone marrow.
Indications
Roxadustat is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with symptomatic anemia associated with chronic kidney disease (CKD).
Background
Roxadustat is a first-in-class hypoxia-inducible factor prolyl hydroxylase inhibitor used to treat anemia associated with chronic kidney disease. It works by reducing the breakdown of the hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF), which is a transcription factor that stimulates red blood cell production in response to low oxygen levels. Roxadustat was first approved by the European Commission in August 2021.
Definition
ChEBI: Roxadustat is an N-acylglycine resulting from the formal condensation of the amino group of glycine with the carboxy group of 4-hydroxy-1-methyl-7-phenoxyisoquinoline-3-carboxylic acid. It is an inhibitor of hypoxia inducible factor prolyl hydroxylase (HIF-PH). It has a role as an EC 1.14.11.2 (procollagen-proline dioxygenase) inhibitor and an EC 1.14.11.29 (hypoxia-inducible factor-proline dioxygenase) inhibitor. It is a member of isoquinolines, an aromatic ether and a N-acylglycine.
Toxicity
There are limited information on the LD50 values of roxadustat.
Single doses of roxadustat 5 mg/kg (up to 510 mg) in healthy subjects led to a transient increase in heart rate, an increased frequency of mild to moderate musculoskeletal pain, headaches, sinus tachycardia, and less commonly, low blood pressure. All these effects were non-serious in nature. Roxadustat overdose can elevate hemoglobin levels above the desired level (10 - 12 g/dL), which should be managed with discontinuation of roxadustat treatment or reduction of drug dosage with careful monitoring and appropriate supportive treatment. Roxadustat and its metabolites are not significantly removed by hemodialysis.
Side Effects
Roxadustat is reported to increase VEGF, a signal protein that can activate tumor growth and also is considered to cause pulmonary hypertension. In phase 3 trial conducted at 29 sites in China, roxadustat treatment was found to cause hyperkalemia, i.e., increase in serum potassium, and metabolic acidosis in patients.
Pharmacokinetics
Roxadustat dose-dependently improves iron bioavailability, increases hemoglobin production, and increases red blood cell mass in patients with anemia. In non-dialysis-dependent CKD patients with anemia, roxadustat maintained Hb for up to 2?years. It has a comparable efficacy to erythropoietin-stimulating agents in achieving Hb response. Roxadustat also reduces cholesterol levels from baseline, regardless of the use of statins or other lipid-lowering agents.
Side Effects
The most common side effects include hypertension, vascular access thrombosis (formation of blood clots in the blood vessels associated with dialysis), diarrhea, peripheral edema (swelling especially of the ankles and feet), hyperkalemia and nausea.
Synthesis
Preparation of roxadustat of formula 1 was described in a patent application WO2004108681, where the roxadustat is prepared in 11 steps from initial chemical compound 4-nitro-1,2-dicarbonitrile of formula 2. Reaction of dicarbonitrile of formula 2 with phenol and potash in the first step leads to preparation of corresponding phenoxy derivate of formula 3, 4-phenoxyphthalic acid of formula 4 is prepared by the following hydrolysis effect of potassium hydroxide in methanol, from which a solid-phase mixture with glycine is created for reaction in a melt with temperature of 210°C to 220°C, which provides corresponding phthalimide of formula 5. After that, phthalimide of formula 5 is esterified to corresponding methyl ester of formula 6. Then, expansion of the ring is performed by the effect of sodium butanolate to butyl-7-phenoxy-1,4-dihydroxy isoquinoline-3-carboxylate of formula 7. Hydroxyl group of derivative of formula 7 in a position 1 is then replaced by bromine using phosphorus oxybromide under the alkaline conditions resulting in creation of isoquinoline derivative of formula 8. Further the alkaline hydrolysis is carried out to provide an acid of formula 9. Then the lithiation is carried out, capture of lithium salt with methyl iodide, and in the second step, the hydroxyl group and carboxyl function are protected by benzyl group resulting in the derivative of formula 10. By the effect of potassium hydroxide the derivative of formula 10 is hydrolyzed to the carboxylic acid of formula 11, from which the derivative 12 is prepared under the conditions of glycine benzyl ester. The final step of synthesis of roxadustat of formula 1 is deprotection of benzyl groups by means of hydrogenation reaction (Diagram 1). 
A Scalable Synthesis of Roxadustat (FG-4592)
Absorption
Roxadustat plasma exposure (AUC and Cmax) increases dose-proportionally within the recommended therapeutic dose range. In a three times per week dosing regimen, steady-state roxadustat plasma concentrations are achieved within one week (three doses) with minimal accumulation. Maximum plasma concentrations (Cmax) are usually achieved at two hours post dose in the fasted state. Administration of roxadustat with food decreased Cmax by 25% but did not alter AUC as compared with the fasted state.
Metabolism
In vitro, roxadustat is a substrate for CYP2C8 and UGT1A9 enzymes. Roxadustat is primarily metabolized to hydroxy-roxadustat and roxadustat O-glucuronide. Unchanged roxadustat was the major circulating component in human plasma and detectable metabolites in human plasma constituted less than 10% of total drug-related material exposure. No human-specific metabolites were observed but roxadustat O-glucuronide was detected in human urine sample.
Metabolism
Roxadustat is metabolized by cytochrome P450 (CYP)2C8 and uridine diphosphate-glucuronosyltransferase (UGT)1A9. Roxadustat is primarily metabolized through 2 main metabolic pathways: hydroxylation/oxidation followed by sulfation, producing metabolites 4'-hydroxy roxadustat and 4'-O-sulfate conjugates of 4'-hydroxy roxadustat, together accounting for 20% of the radioactive dose. The O-glucuronidation produces metabolite 4-O-β-glucuronide of roxadustat, representing 28% of the dose. Minor metabolic routes included glucosidation producing 4-O-β-glucoside of roxadustat (8.1% of the dose), acyl glucuronidation producing acyl-1-O-β-glucuronide of roxadustat (0.6% of the dose), and demethylation producing N-descarboxymethyl roxadustat oxide and Ndescarboxymethyl roxadustat (together ~3.6% of the dose).
Storage
Store at -20°C
Mode of action
Roxadustat is a novel, orally bioavailable, potent and reversible HIF-PH inhibitor (HIF-PHI) that transiently induces HIF stabilization and leads to a functional HIF transcriptional response that mimics the erythropoietic response associated with exposure of humans to intermittent hypoxia. roxadustat increases hemoglobin levels with a mechanism of action that is different from that of ESAs. Roxadustat activates the body’s natural protective response to reduced oxygen levels in the blood. This response involves the regulation of multiple, complementary processes that promote a coordinated erythropoietic response and increase the blood’s oxygen-carrying capacity.
Clinical claims and research
Roxadustat (FG-4592), an oral medication, is one of the medications currently undergoing Phase 3 studies. In their phase 2a study studying anemic CKD patients, the medication showed increases in erythropoietin and hemoglobin levels as well as a reduction in hepcidin concentrations with 0.7 to 2.0 mg/kg given 2 or 3 times per week compared to controls within 4 weeks of treatment with no adverse events observed. Roxadustat was then studied in hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis patients and raised hemoglobin by 20 g/L in 7 weeks of treatment with 4.3 mg/kg weekly for 12 weeks. The current phase 3 studies will continue to evaluate Roxadustat compared to epoetin alpha(NCT02174731 ) and epoetin alpha or darbepoetin alpha (NCT02278341) in CKD patients on dialysis.
Current market and forecast
Roxadustat is approved in EU member states, including the EEA countries, as well as in Japan, China, Chile and South Korea for the treatment of anemia of CKD in adult patients on dialysis (DD) and not on dialysis (NDD). Several other licensing applications for roxadustat have been submitted by Astellas and AstraZeneca to regulatory authorities across the globe and are currently in review.
Astellas and FibroGen are collaborating on the development and commercialization of roxadustat for the potential treatment of anemia of CKD in territories including Japan, Europe, Turkey, Russia and the Commonwealth of Independent States, the Middle East, and South Africa. FibroGen and AstraZeneca are collaborating on the development and commercialization of roxadustat for the potential treatment of anemia of CKD in the U.S., China, other markets in the Americas, in Australia/New Zealand, and Southeast Asia.
Properties of Roxadustat
| Melting point: | 199-215°C |
| Boiling point: | 684.3±55.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.389 |
| storage temp. | -20°C |
| solubility | Soluble in DMSO (up to at least 25 mg/ml). |
| form | solid |
| pka | 2.46±0.10(Predicted) |
| color | Off-white or white |
| Stability: | Stable for 1 year from date of purchase as supplied. Solutions in DMSO may be stored at -20°C for up to 2 months. |
| InChI | InChI=1S/C19H16N2O5/c1-11-15-9-13(26-12-5-3-2-4-6-12)7-8-14(15)18(24)17(21-11)19(25)20-10-16(22)23/h2-9,24H,10H2,1H3,(H,20,25)(H,22,23) |
Safety information for Roxadustat
Computed Descriptors for Roxadustat
| InChIKey | YOZBGTLTNGAVFU-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | C(O)(=O)CNC(C1=C(O)C2=C(C(C)=N1)C=C(OC1=CC=CC=C1)C=C2)=O |
Roxadustat manufacturer
Kavya Pharma
New Products
Indole Methyl Resin tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Boc-His(Boc)-OH 2-CTC Resin 4-Chloro-7-tosy1-7Hpyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine 5,7-Dibromo-1H-indole 2,5-dichloro-N-hydroxy-4,6-dimethylpyridine-3-carboximidamide 2,2-Dimethoxy-7-azaspiro[3.5]nonane hydrochloride 4-chloromethyl-5-methyl-1,3-dioxol-2-one (DMDO-Cl) R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-((2-hydroxyethyl)thio)benzoic acid 1-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-2-PYRROLIDINONE Methyl 6-methylnicotinate 3-Pyridineacrylic acid tert-Butyl carbazate TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 1,3-Diethyl-1,3-Diphenylurea Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 808118-40-3 Roxadustat (Form A and L-Proline Co-Crystal) 98%View Details
808118-40-3 Roxadustat (Form A and L-Proline Co-Crystal) 98%View Details
808118-40-3 -
 Roxadustat 97%View Details
Roxadustat 97%View Details -
 Roxadustat 99%View Details
Roxadustat 99%View Details
808118-40-3 -
 808118-40-3 Roxadustat 98%View Details
808118-40-3 Roxadustat 98%View Details
808118-40-3 -
 FG-4592 98% (HPLC) CAS 808118-40-3View Details
FG-4592 98% (HPLC) CAS 808118-40-3View Details
808118-40-3 -
 Roxadustat CAS No: 808118-40-3View Details
Roxadustat CAS No: 808118-40-3View Details
808118-40-3 -
 Pyridine 99.5% HPLC /UV SpectroscopyView Details
Pyridine 99.5% HPLC /UV SpectroscopyView Details
110-86-1 -
 Thiourea 99% ARView Details
Thiourea 99% ARView Details
62-56-6
