Ropinirole
- CAS NO.:91374-21-9
- Empirical Formula: C16H24N2O
- Molecular Weight: 260.37
- MDL number: MFCD00864147
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-13 21:11:14
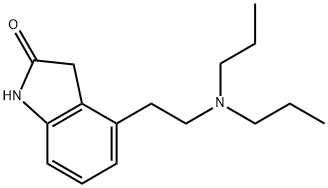
What is Ropinirole?
Absorption
Ropinirole is rapidly absorbed after oral administration, reaching peak concentration in approximately 1 to 2 hours , .
Absolute bioavailability was 45% to 55%, suggesting approximately 50% hepatic first-pass effect . The bioavailability of ropinirole prolonged release compared to the immediate release tablets is about 100% .
Ingestion of food does not affect the absorption of ropinirole, although its Tmax was increased by 2.5 hours and its Cmax was reduced by approximately 25% when the drug is taken with a high-fat meal .
Toxicity
Overdose
Symptoms of overdose include agitation, chest pain, confusion, drowsiness, facial muscle movements, grogginess, increased jerkiness of movement, symptoms of low blood pressure (dizziness, light-headedness)upon standing, nausea, and vomiting .
Carcinogenicity
Two-year carcinogenicity studies of ropinirole were performed on animal models at oral doses of 5, 15, and 50 mg/kg/day and in rats at oral doses of 1.5, 15, and 50 mg/kg/day.
There was an increase in testicular Leydig cell adenomas at all doses tested in rats. The hormonal mechanisms thought to be involved in the development of these tumors in rats are not considered relevant to humans. In mice, there was an increase in benign uterine endometrial polyps at a dose of 50 mg/kg/day. The highest dose not associated with this observation (15 mg/kg/day) is three times the maximum recommended human dose on a mg/m2 basis .
Mutagenesis
Ropinirole was not found to be mutagenic or clastogenic during in vitro assays, or in the in vivo mouse micronucleus test .
Effects on reproduction
When given to female rats prior to and during mating and throughout pregnancy, ropinirole led to disruption of implantation at oral doses of 20 mg/kg/day (8 times the MRHD on a mg/m2 basis) or higher. This effect in rats is believed to be due to the prolactin-lowering effects of ropinirole.
Use in Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category C. There are no sufficient and well-controlled studies done in pregnant women. In animal reproduction studies, ropinirole has demonstrated adverse effects on embryo-fetal development, including teratogenicity .
The Uses of Ropinirole
Antiparkinsonian (D2receptor agonist).
Background
Ropinirole, also known as ReQuip, is a non-ergoline dopamine agonist used in Parkinson's disease and restless legs syndrome , . It is manufactured by GlaxoSmithKline Pharmaceuticals. Ropinirole was initially approved in 1997 by the FDA for the management of Parkinson's disease. In 2005, it was the first drug approved in the US for the management of primary moderate to severe restless legs syndrome .
In 2008, the extended-release capsules of ropinirole were approved, allowing for less frequent dosing, therefore increased compliance, and offering a similar side effect profile and efficacy to previous formulations of ropinirole .
Definition
ChEBI: Ropinirole is a member of indolones and a tertiary amine. It has a role as a dopamine agonist, an antiparkinson drug, a central nervous system drug and an antidyskinesia agent.
Indications
For the treatment of the signs and symptoms of Parkinson's disease and for the treatment of primary moderate-severe restless legs syndrome .
brand name
Requip (GlaxoSmithKline).
Synthesis Reference(s)
Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 28, p. 1533, 1985 DOI: 10.1021/jm00148a028
Pharmacokinetics
Effects on Parkinson's and restless leg syndrome
This drug promotes the relief or improvement of symptoms of Parkinson's or restless leg syndrome by stimulatory actions on dopamine receptors, which regulate movement.
Effects on blood pressure
Clinical experience with dopamine agonists, including ropinirole, suggests an association with impaired abilities in regulating blood pressure with resulting orthostatic hypotension, especially with patients undergoing dose escalation. In some patients in clinical studies, blood pressure changes were associated with orthostatic symptoms, bradycardia, and, in one case in a healthy volunteer, transient sinus arrest accompanied by syncope . The mechanism of orthostatic hypotension caused by ropinirole is assumed to be due to a D2-mediated blunting of noradrenergic response to a standing position, followed by a decrease in peripheral vascular resistance. Nausea is also a frequent symptom which accompanies orthostatic signs and symptoms .
Effects on prolactin
At oral doses as low as 0.2 mg, ropinirole suppressed serum prolactin concentrations in healthy male volunteers.
Ropinirole had no dose-related effect on ECG wave form and rhythm in young, healthy, male volunteers in the range of 0.01 to 2.5 mg .
Effects on QT interval
Ropinirole had no dose- or exposure-related effect on average QT intervals in healthy male and female volunteers at doses up to 4 mg/day. The effect of ropinirole on QTc intervals at higher exposures reached either due to drug interactions, hepatic dysfunction, or at higher doses has not been adequately evaluated .
Clinical Use
Anti-Parkinson agent
Restless legs syndrome (RLS)
Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Antipsychotics: antagonism of anti-Parkinsonian
effect - avoid.
Metoclopramide: antagonism of anti-Parkinsonian
effect - avoid.
Oestrogens: concentration increased.
Metabolism
Ropinirole is hepatically metabolised by the cytochrome P450 enzyme, CYP1A2, and excreted in the urine as inactive metabolites.
Metabolism
Ropinirole is heavily metabolized by the liver. The most important metabolic pathways are N- despropylation and hydroxylation to form the N-despropyl metabolite and hydroxy metabolites , both of which are inactive .
The N-despropyl metabolite is then converted to carbamyl glucuronide, carboxylic acid, and N-despropyl hydroxy metabolites. Following this process, the hydroxy metabolite of ropinirole is glucuronidated at a rapid rate .
In vitro studies show that the major cytochrome P450 enzyme involved in the metabolism of ropinirole is CYP1A2 , .
Properties of Ropinirole
| Melting point: | 243-250°C |
| Boiling point: | 410.5±45.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.040±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| pka | 14.17±0.20(Predicted) |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 91374-21-9(CAS DataBase Reference) |
Safety information for Ropinirole
Computed Descriptors for Ropinirole
Ropinirole manufacturer
Ralington Pharma
New Products
Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate (S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL N-octanoyl benzotriazole 4-Hydrazinobenzoic acid 3,4-Dibenzyloxybenzaldehyde 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) 4-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 91374-21-9 Ropinirole 98%View Details
91374-21-9 Ropinirole 98%View Details
91374-21-9 -
 Ropinirole 98%View Details
Ropinirole 98%View Details -
 Ropinirole 91374-21-9 98%View Details
Ropinirole 91374-21-9 98%View Details
91374-21-9 -
 91374-21-9 Ropinirole 98%View Details
91374-21-9 Ropinirole 98%View Details
91374-21-9 -
 91374-21-9 95-99%View Details
91374-21-9 95-99%View Details
91374-21-9 -
 N-Vinylformamide 99%View Details
N-Vinylformamide 99%View Details
13162-05-5 -
 2-ethyl-6-methyl-3-hydroxypyridine succinate 99%View Details
2-ethyl-6-methyl-3-hydroxypyridine succinate 99%View Details
127464-43-1 -
 2-ETHYLPYRIDINE 100-71-0 99%View Details
2-ETHYLPYRIDINE 100-71-0 99%View Details
100-71-0