Meloxicam
Synonym(s):4-Hydroxy-2-methyl-N-(5-methyl-2-thiazolyl)-2H-1,2-benzothiazine-3-carboxamide 1,1-dioxide;4-Hydroxy-2-methyl-N-(5-methyl-2-thiazoyl)-2H-1,2-benzothiazine-3-carboxamide-1,1-dioxide;Meloxicam;Meloxicam - CAS 71125-38-7 - Calbiochem
- CAS NO.:71125-38-7
- Empirical Formula: C14H13N3O4S2
- Molecular Weight: 351.4
- MDL number: MFCD00868752
- EINECS: 615-253-8
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:07:02
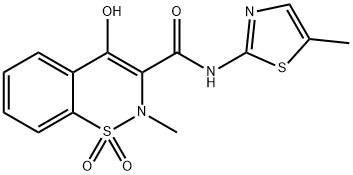
What is Meloxicam?
Description
Meloxicam is one of numerous medications that have human and veterinary uses. It is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) that, like most others in this class, is used to reduce pain, inflammation, and fever. Like most NSAIDs, it has several adverse side effects, including gastrointestinal bleeding, heart attack, and stroke.
More than 25 years ago, meloxicam was developed and marketed by the German pharmaceutical company Boehringer-Ingelheim. It is now off-patent and sold generically under a variety of trade names. For human use in the United States, two of its brand names are Mobic and Vivlodex.
Description
Known as a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID), Meloxicam is commonly used to treat pain or inflammation caused by rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis in adults. It is also used to treat juvenile rheumatoid arthritis in children who are at least 2 years old. It is effective to reduce pain, inflammation, swelling, and stiffness of the joints. Developed by Boehringer-Ingelheim, Meloxicam is a derivative of oxicam that can relieve the symptoms of arthritis, primary dysmenorrhea, fever with analgesic and antipyretic properties. Meloxicam was approved for use in April 2000.
Anti-inflammatory effects of meloxicam function by inhibiting the prostaglandin synthetase (cyclooxygenase 1 and 2) which results in a decrease of the synthesis of prostaglandins. As prostaglandins are chemicals that contribute to inflammation especially within joints, which leads to the common symptoms of pain, tenderness, and swelling associated with arthritis, inhibition of their synthesis can be associated with the analgesic and antipyretic effects of meloxicam. As a result, inflammation and its accompanying symptoms are reduced. Meloxicam starts to relieve pain about 30 to 60 minutes after administration.
Chemical properties
Meloxicam is a light yellow solid, practically insoluble in water, with higher solubility observed in strong acids and bases. It is very slightly soluble in methanol. Meloxicam has an apparent partition coefficient (log P)app = 0.1 in n-octanol/buffer pH 7.4. It has pKa values of 1.1 and 4.2.
Originator
Boehringer Ingelheim (Germany)
The Uses of Meloxicam
Preferential cyclooxygenase (COX-2) inhibitor. Sudoxicam and Meloxicam are nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) from the enol-carboxamide class.
The Uses of Meloxicam
An inhibitor of Cox-1 and Cox-2, selective for Cox-2.
Background
Meloxicam is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) used to relieve various types of pain, including pain caused by musculoskeletal conditions, osteoarthritis, and rheumatoid arthritis. With a longer half-life than most other NSAIDS, it is a favorable option for those who require once-daily dosing. Meloxicam is available in oral, transdermal, and intravenous formulations. It is a preferential COX-2 inhibitor, purportedly reducing the risk of adverse gastrointestinal tract effects, however, this is a topic of controversy.
Indications
Meloxicam is indicated for the symptomatic treatment of arthritis and osteoarthritis. In addition, it is indicated for the pauciarticular and polyarticular course of Juvenile Rheumatoid Arthritis (JRA) in patients aged 2 years old or above. Off-label uses include the treatment of dental or post-surgical pain. In addition to the above, meloxicam has also been studied in the treatment of neuropathic pain.
Meloxicam, in combination with bupivacaine, is indicated for postsurgical analgesia in adult patients for up to 72 hours following foot and ankle, small-to-medium open abdominal, and lower extremity total joint arthroplasty surgical procedures.
Definition
ChEBI: Meloxicam is a benzothiazine that is piroxicam in which the pyridin-2-yl group is replaced by a 5-methyl-1,3-thiazol-2-yl group. A non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug and selective inhibitor of COX-2, it is used particularly for the management of rheumatoid arthritis. It has a role as a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug, an antirheumatic drug, a cyclooxygenase 2 inhibitor and an analgesic. It is a benzothiazine, a monocarboxylic acid amide and a member of 1,3-thiazoles.
Indications
Meloxicam (Mobic), recently introduced for the treatment of osteoarthritis, is also used for rheumatoid arthritis and certain acute conditions. Although meloxicam is sometimes reported to be a selective COX-2 inhibitor, it is considerably less selective than celecoxib or rofecoxib. Its adverse effects are similar to those of piroxicam and other NSAIDs; however, the frequency of GI side effects is lower for meloxicam than for piroxicam and several other NSAIDs.
Manufacturing Process
A mixture of 26.9 g (0.1 mol) of the 1,1-dioxide of methyl 4-hydroxy-2- methyl-2H-1,2-benzothiazine-3-carboxylate and 12.5 g (0.11 mol) of 2- amino-5-methylthiazole was refluxed in 4 liters of xylene for 24 hours in a nitrogen atmosphere. The methanol formed by the reaction was removed by means of a 4-A-molecular sieve mounted in a Soxhlet-extractor. The hot reaction solution was filtered. Upon cooling and standing overnight, the crude product separated out of the filtrate in the form of crystals (32.0 g, 91% of theory). After recrystallization from ethylene chloride 26.0 g (74% of theory) of 4-hydroxy-2-methyl-N-(5-methyl-2-thiazolyl)-2H-1,2-benzothiazine-3- carboxamide-1,1-dioxide were obtained; M.P.: 254°C (decomp.).
brand name
Mobic (Boehringer Ingelheim).
Therapeutic Function
Antiinflammatory
General Description
Meloxicam (Mobic) is a selective COX-2 inhibitor amongoxicams indicated for use in RA and OA. It also has a relativelylong half-life of 15 to 20 hours and has a much lowerrate of serious GI side effects and a lower than average riskof nephropathy when compared with other conventionalNSAIDs.196 The recommended dose is 7.5 mg once dailywith a maximum of 15 mg/d. Meloxicam is metabolized inhumans mainly by CYP2C9 (with a minor contribution viaCYP3A4) to 5'-hydroxymethylmeloxicam and 5 carboxymeloxicam.
In large-scale comparative trials, meloxicam was foundto be at least as effective as most conventional NSAIDs inthe treatment of rheumatic disease or postoperative pain, buthas demonstrated a more favorable GI tolerability profile.
Biological Activity
Meloxicam is a selective inhibitor of COX-2 (IC50s = 11.8 and 143 μM for COX-2 and COX-1, respectively, in an enzyme activity assay) and a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID). Meloxicam (0.03%) reduces croton oil-induced increases in TNF-α and IL-1β mRNA levels and increases IL-10 mRNA levels in cornea in a rabbit model of acute ocular inflammation. It inhibits pleural plasma exudation in a carrageenan-induced rat model of pleurisy when administered at a dose of 3 mg/kg. In a canine model of unilateral osteoarthritis of the right stifle joint, meloxicam reduces prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) levels in plasma and right stifle joint synovial fluid when administered at a dose of 0.2 mg/kg. Formulations containing meloxicam have been used in the treatment of osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis.
Pharmacokinetics
Meloxicam is an anti-inflammatory, analgesic analgesic with antipyretic effects in fever. Prostaglandins are substances that contribute to inflammation. This drug also exerts preferential actions against COX-2, which may reduce the possible gastrointestinal effects of this drug.
In humans, meloxicam has demonstrated the ability to decrease erythrocyte sedimentation rate(ESR) in patients with rheumatoid arthritis, and to decrease ESR, C-reactive protein (CRP), as well as aquaporin-1 expression. As with other NSAIDS, prolonged use of meloxicum can result in renal or cardiovascular impairment or thrombotic cardiovascular events.
A note on gastrointestinal effects
As meloxicam preferentially inhibits COX-2, it is thought to cause less gastrointestinal irritation compared to other NSAIDS. Despite this, it still carries a risk of gastric inflammation, bleeding and ulceration. In one study, patients on meloxicam suffered from gastrointestinal symptoms at a rate of 13% compared to 19% of those on diclofenac. GI events were found to be less severe in the meloxicam-treated patients.
Clinical Use
In April 2000, the U.S. FDA approved meloxicam for the treatment of osteoarthritis. When meloxicam was initially introduced in the United Kingdom, it was promoted as a selective COX-2 inhibitor.
Toxicity
The oral LD50 in rats is 98 mg/kg. Signs and symptoms of overdose with meloxicam may include shallow breathing, seizure, decreased urine output, gastrointestinal irritation, nausea, vomiting, gastrointestinal bleeding, and black tarry stools. In the case of an overdose, offer supportive treatment and attempt to remove gastrointestinal contents. Cholestyramine has been shown to enhance the elimination of meloxicam.
Side Effects
Meloxicam may cause stomach upset, nausea, dizziness or diarrhoea, increased blood pressure, headache, easy bruising or bleeding; mental or mood changes; signs of kidney problems (e.g., changes in urine output), unexplained stiffness of the neck, symptoms of heart failure (e.g., swelling of the ankles or feet; unusual tiredness, unusual weight gain).
Meloxicam rarely causes serious (potentially fatal) liver disease. Include: nausea or vomiting, loss of appetite, dark-coloured urine, stomach or abdominal pain, and yellowing of the eyes or skin.
Very serious allergic reactions to Meloxicam are rare. Include: fever, swollen lymph nodes, rash, itching or swelling (especially of the face or tongue or throat), severe dizziness, and difficulty breathing. However, if you notice any symptoms of a severe allergic reaction, seek medical help immediately.
Synthesis
It can be synthesized in four steps from benzisothiazolo-3(2H)-one-1,1-dioxide. Reaction of benzothiazolo-3(2H)-one-1,1-dioxide with methyl chloroacetate gives the methyl 2(3H)-acetate derivative, which is isomerized with sodium methoxide in toluene-tert-butanol yielding methyl 4-hydroxy-2H-1,2-benzothiazine-3-carboxylate-1,1-dioxide. Subsequent methylation with methyl iodide in methanol yields the 2-methyl compound. Finally this compound is treated with 2-amino-5-methylthiazole in xylene.
Veterinary Drugs and Treatments
Meloxicam is principally used for the symptomatic treatment of osteoarthritis in dogs. Short-term (single dose injectable) use is also approved (in the USA) for cats for the control of postoperative pain and inflammation associated with orthopedic surgery, ovariohysterectomy and castration when administered prior to surgery.
Absorption
The absolute bioavailability oral capsules after a dose was 89% in one pharmacokinetic study. Cmax was reached 5–6 hours after administration of a single dose given after the first meal of the day. The Cmax doubled when the drug was administered in the fasting state. Despite this, meloxicam can be taken without regard to food, unlike many other NSAIDS.
Meloxicam formulated for instillation with bupivacaine produced varied systemic measures following a single dose of varying strength. In patients undergoing bunionectomy, 1.8 mg of meloxicam produced a Cmax of 26 ± 14 ng/mL, a median Tmax of 18 h, and an AUC∞ of 2079 ± 1631 ng*h/mL. For a 9 mg dose used in herniorrhaphy, the corresponding values were 225 ± 96 ng/mL, 54 h, and the AUC∞ was not reported. Lastly, a 12 mg dose used in total knee arthroplasty produced values of 275 ± 134 ng/mL, 36 h, and 25,673 ± 17,666 ng*h/mL.
Metabolism
Meloxicam is almost completely metabolized. CYP2C9 is the main enzyme responsible for the metabolism of meloxicam with minor contributions from CYP3A4. Meloxicam has 4 major metabolites with no activity determined. About 60% of the ingested dose is metabolized to 5'-carboxy meloxicam from hepatic cytochrome enzyme oxidation of an intermediate metabolite, 5’-hydroxymethylmeloxicam. Two other metabolites are likely produced via peroxidation.
Metabolism
Meloxicam, however, is less selective than celecoxib and much less selective than rofecoxib in in vitro studies. Meloxicam is readily absorbed when administered orally and is highly bound to plasma proteins. Meloxicam is extensively metabolized in the liver, primarily by CYP2C9 and, to a lesser extent, by CYP3A4. The advantages of meloxicam over celecoxib and rofecoxib in the treatment of osteoarthritis (or rheumatoid arthritis) are not readily apparent.
Mode of action
Meloxicam, a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID), by shutting down prostaglandin synthesis, it has antiinflammatory, antipyretic and analgesic properties. This is accomplished by preferentially inhibiting the COX-2 system relative to the COX-I which also leads to an improved GI safety profile relative to naproxen, diclofenac and prioxicam. It can also interfere with neutrophil function like degranulation. Meloxicam did not inhibit proteoglycan synthesis in osteroarthitic cartilage or chondrocytes and had no effect on platelet aggregation. It is metabolized by the P450 2C9 system into four metabolites which are all inactive.
References
[1] https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Meloxicam
[2] https://www.drugbank.ca/drugs/DB00814
[3] https://www.drugs.com/meloxicam.html
[4] http://www.medicinenet.com/meloxicam/article.htm
[5] K OGINO. Evaluation of pharmacological profile of meloxicam as an anti-inflammatory agent, with particular reference to its relative selectivity for cyclooxygenase-2 over cyclooxygenase-1.[J]. Pharmacology, 1997, 55 1: 44-53. DOI:10.1159/000139511.
[6] CHRISTOPHER J JONES. In vivo effects of meloxicam and aspirin on blood, gastric mucosal, and synovial fluid prostanoid synthesis in dogs.[J]. American journal of veterinary research, 2002, 63 11: 1527-1531. DOI:10.2460/ajvr.2002.63.1527.
[7] S NOBLE J A B. Meloxicam.[J]. Drugs, 1996, 51 3: 424-430; discussion 431-32. DOI:10.2165/00003495-199651030-00007.
[8] BANDOO C CHATALE Mariam S D. Synthesis and in-vivo taste assessment of meloxicam pivalate.[J]. Drug Development and Industrial Pharmacy, 2019, 45 10: 1590-1598. DOI:10.1080/03639045.2019.1628250.
Properties of Meloxicam
| Melting point: | 255 °C |
| Density | 1.613±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | DMSO: soluble |
| form | Off-white solid |
| pka | 4.08 in water; 4.24 ± 0.01 in water/ethanol (1:1); 4.63 ± 0.03 in water/ethanol (1:4) |
| color | yellow |
| Water Solubility | practically insoluble in water(0.154 mg/mL), with higher solubility observed in strong acids and bases. |
| Merck | 14,5826 |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| InChI | InChI=1S/C14H13N3O4S2/c1-8-7-15-14(22-8)16-13(19)11-12(18)9-5-3-4-6-10(9)23(20,21)17(11)2/h3-7,18H,1-2H3,(H,15,16,19) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | 2H-1,2-Benzothiazine-3-carboxamide, 4-hydroxy-2-methyl-N-(5-methyl-2-thiazolyl)-, 1,1-dioxide (71125-38-7) |
Safety information for Meloxicam
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H301:Acute toxicity,oral |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P270:Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. P301+P310:IF SWALLOWED: Immediately call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician. P405:Store locked up. P501:Dispose of contents/container to..… |
Computed Descriptors for Meloxicam
| InChIKey | ZRVUJXDFFKFLMG-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | S1(=O)(=O)C2=CC=CC=C2C(O)=C(C(NC2=NC=C(C)S2)=O)N1C |
Meloxicam manufacturer
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 Meloxicam 99%View Details
Meloxicam 99%View Details -
 Meloxicam 99%View Details
Meloxicam 99%View Details -
 71125-38-7 Meloxicam 98%View Details
71125-38-7 Meloxicam 98%View Details
71125-38-7 -
 Meloxicam 71125-38-7 98%View Details
Meloxicam 71125-38-7 98%View Details
71125-38-7 -
 71125-38-7 99%View Details
71125-38-7 99%View Details
71125-38-7 -
 71125-38-7 Meloxicam 98%View Details
71125-38-7 Meloxicam 98%View Details
71125-38-7 -
 MELOXICAM CAS 71125-38-7View Details
MELOXICAM CAS 71125-38-7View Details
71125-38-7 -
 Meloxicam 98% CAS 71125-38-7View Details
Meloxicam 98% CAS 71125-38-7View Details
71125-38-7