Rivastigmine
Synonym(s):N-Ethyl-N-methylcarbamic acid 3-[(1S)-1-(dimethylamino)ethyl]phenyl-ester;Ethylmethyl-carbamic acid 3-[(1S)-1-(dimethylamino)ethyl]phenyl ester;N-Ethyl-N-methyl-carbamic acid 3-[(1S)-1-(dimethylamino)ethyl]phenyl ester tartrate;Rivastigmine tartrate;S-Rivastigmine tartrate
- CAS NO.:123441-03-2
- Empirical Formula: C14H22N2O2
- Molecular Weight: 250.34
- MDL number: MFCD00871496
- EINECS: 602-936-0
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-03 18:03:33
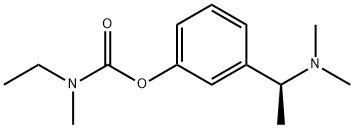
What is Rivastigmine?
The Uses of Rivastigmine
Antidepressant
Background
Rivastigmine is a parasympathomimetic or cholinergic agent for the treatment of mild to moderate dementia of the Alzheimer's type. Rivastigmine is a cholinesterase inhibitor that inhibits both butyrylcholinesterase and acetylcholinesterase.
Indications
For the treatment of mild to moderate dementia associated with Parkinson's disease or of the Alzheimer's type.
What are the applications of Application
(S)-Rivastigmine is an isomer of Rivastigimine, an acterylcholinesterase inhibitor
Definition
ChEBI: A carbamate ester obtained by formal condensation of the carboxy group of ethyl(methyl)carbamic acid with the phenolic OH group of 3-[(1S)-1-(dimethylamino)ethyl]phenol. A reversible cholinesterase inhibitor.
brand name
Exelon (Novartis).
General Description
Rivastigmine (Exelon, EA 713) is apseudoirreversible noncompetitive carbamate inhibitor ofAChE. Although the half-life is approximately 2 hours,the inhibitory properties of this agent last for 10 hours becauseof the slow dissociation of the drug from the enzyme.The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved its usein mild-to-moderate Alzheimer disease in April 2000. InJuly 2007, rivastigmine was granted approval for use inmanaging mild-to-moderate dementia associated withParkinson disease.
Pharmacokinetics
Rivastigmine is a parasympathomimetic and a reversible cholinesterase inhibitor. An early pathophysiological feature of Alzheimer's disease that is associated with memory loss and cognitive deficits is a deficiency of acetylcholine as a result of selective loss of cholinergic neurons in the cerebral cortex, nucleus basalis, and hippocampus. Tacrine is postulated to exert its therapeutic effect by enhancing cholinergic function. While the precise mechanism of rivastigmine's action is unknown, it is postulated to exert its therapeutic effect by enhancing cholinergic function. This is accomplished by increasing the concentration of acetylcholine through reversible inhibition of its hydrolysis by cholinesterase. If this proposed mechanism is correct, rivastigmine's effect may lessen as the disease progresses and fewer cholinergic neurons remain functionally intact.
Pharmacokinetics
Rivastigmine is a centrally selective, arylcarbamate AChEI that was approved in 2000 for oral administration in the treatment of AD. It has an elimination half-life of 1.4 to 1.7 hours but is able to inhibit AChE for up to 10 hours. Because of the slow dissociation of the carbamylated enzyme, it has been referred to as a pseudo-irreversible AChEI. Like donepezil, rivastigmine exhibits a low level of hepatotoxicity. It is rapidly and extensively hydrolyzed in the CNS by cholinesterase with minimal involvement of CYP450. The phenolic metabolite is excreted primarily via the kidneys.
Clinical Use
Mild-moderate dementia in Alzheimer’s disease
Idiopathic Parkinson’s disease
Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Muscle relaxants: enhances effect of suxamethonium;
antagonises effect of non-depolarising muscle
relaxants.
Metabolism
Rivastigmine is rapidly metabolized by cholinesterase-mediated hydrolysis.
Metabolism
Rivastigmine is the tertiary amines that are rapidly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract, as are tacrine, donepezil, and galanthamine, whereas quaternary ammonium compounds are poorly absorbed after oral administration. Nevertheless, quaternary ammonium compounds like neostigmine and pyridostigmine are orally active if larger doses are employed. Only the quaternary ammonium inhibitors do not readily enter the CNS. Because of their high lipid solubility and low molecular weight, most of the organophosphates are absorbed by all routes of administration; even percutaneous exposure can result in the absorption of sufficient drug to permit the accumulation of toxic levels of these compounds.
Properties of Rivastigmine
| Boiling point: | 316.2±34.0 °C(Predicted) |
| alpha | D20 -32.1° (c = 5 in ethanol) |
| Density | 1.038±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| Flash point: | 145℃ |
| storage temp. | Sealed in dry,Store in freezer, under -20°C |
| solubility | Chloroform (Sparingly), Ethyl Acetate (Slightly) |
| pka | pKa 8.99 (Uncertain) |
| form | Powder |
| color | Colorless to light yellow |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 123441-03-2(CAS DataBase Reference) |
Safety information for Rivastigmine
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H300:Acute toxicity,oral H411:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P270:Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P391:Collect spillage. Hazardous to the aquatic environment P301+P310:IF SWALLOWED: Immediately call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician. P405:Store locked up. |
Computed Descriptors for Rivastigmine
Rivastigmine manufacturer
ALS India Life Sciences Pvt. Ltd
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 123441-03-2 Rivastigmine Hydrogen Tartrate 98%View Details
123441-03-2 Rivastigmine Hydrogen Tartrate 98%View Details
123441-03-2 -
 123441-03-2 98%View Details
123441-03-2 98%View Details
123441-03-2 -
 Rivastigmine 98%View Details
Rivastigmine 98%View Details
123441-03-2 -
 Rivastigmine 123441-03-2 99%View Details
Rivastigmine 123441-03-2 99%View Details
123441-03-2 -
 Rivastigmine 97% CAS 123441-03-2View Details
Rivastigmine 97% CAS 123441-03-2View Details
123441-03-2 -
 Rivastigmine CAS 123441-03-2View Details
Rivastigmine CAS 123441-03-2View Details
123441-03-2 -
 Rivastigmine CAS 123441-03-2View Details
Rivastigmine CAS 123441-03-2View Details
123441-03-2 -
 123441-03-2 98.89%View Details
123441-03-2 98.89%View Details
123441-03-2
