Propachlor
Synonym(s):2-Chloro-N-isopropylacetanilide
- CAS NO.:1918-16-7
- Empirical Formula: C11H14ClNO
- Molecular Weight: 211.69
- MDL number: MFCD00078731
- EINECS: 217-638-2
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:15:32
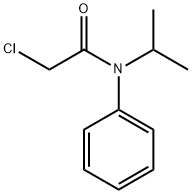
What is Propachlor?
Chemical properties
Tan powder. Mp 68C. Soluble in alcohol, benzene.
Chemical properties
Propachlor is a light tan solid.
The Uses of Propachlor
Herbicide.
The Uses of Propachlor
Selective preemergence herbicide used to control most annual grasses and some broad-leaved weeds in brassicas, corn, cotton, flax, leeks, maize, milo, onions, peas, roses, ornamental trees and shrubs, soybeans, sugarcane.
Definition
ChEBI: An anilide that consists of 2-chloroacetanilide bearing an N-isopropyl substituent.
General Description
Light tan solid. Corrosive to iron and steel. Used as an herbicide.
Air & Water Reactions
Hydrolyzed by strong acid and base.
Reactivity Profile
A chloroacetanilide derivative.
Hazard
Toxic by ingestion and skin absorption.
Agricultural Uses
Herbicide: 217-638-2 [Annex I Index No.: 616-008-00-8] Uses: A pre-emergence herbicide used to combat annual grasses and broad-leaved weeds in corn, sorghum, soybeans, cotton, sugar cane, sugar beets, vegetable crops, forage crops, pasture land and range land. Also used to control weeds in groundnuts, leeks, onions, peas, maize, roses and ornamental trees and shrubs. Not approved for use in EU countries. Not registered for use in the U.S. except California.
Trade name
AATRAM®[C]; ACLID®; AI3-51503®; ALBRASS®; BEXTON®[C]; CIPA®; CP 31393®; KARTEX A®; NITICID®; RAMROD®; RAMROD® 65; SATECID®; WALLOP®[C]
Potential Exposure
Those engaged in the manufacture, formulation and application of this preemergence herbicide which is used to combat annual grasses and broad-leaved weeds in corn, soybeans, cotton, sugar cane and vegetable crops.
Environmental Fate
Biological. In the presence of suspended natural populations from unpolluted aquatic
systems, the second-order microbial transformation rate constant determined in the laboratory was reported to be 1.1 × 10–9 L/organisms-hour (Steen, 1991).
Groundwater. According to the U.S. EPA (1986) propachlor has a high potential to
leach to groundwater.
Plant. In corn seedlings and excised leaves of corn, sorghum, sugarcane and barley,
propachlor was metabolized to at least three water-soluble products. Two of these metabolites were identified as a γ-glutamylcysteine conjugate of propachlor and a glutathione
conjugate of propachlor. It was postulated that both compounds were intermediate compounds in corn seedlings since they were not detected 3 days following treatment (Lamoureux et al., 1971).
Photolytic. When propachlor in an aqueous ethanolic solution was irradiated with UV
light (λ = 290 nm) for 5 hours, 80% decomposed to the following cyclic photo-products:
N-isopropyloxindole, N-isopropyl-3-hydroxyoxindole and a spiro compound. Irradiation
of propachlor in an aqueous solution containing riboflavin as a sensitizer resulted in
completed degradation of the parent compound. m-Hydroxypropachlor was the only compound identified in trace amounts which formed via ring hydroxylation (Rejt? et al., 1984).
Hydrolyzes under alkaline conditions forming N-isopropylaniline (Sittig, 1985) which is
also a product of microbial metabolism (Novick et al., 1986).
Chemical/Physical. Emits toxic fumes of nitrogen oxides and chlorine when heated
to decomposition (Sax and Lewis, 1987). Hydrolyzes under alkaline conditions forming
N-isopropylaniline (Sittig, 1985) which is also a product of microbial metabolism (Novicket al., 1986). Propachlor is rapidly hydrolyzed in Water (Yu et al., 1975a). The hydrolysis
half-lives at 68.0°C and pH values of 3.10 and 10.20 were calculated to be 36.6 and 1.2
days, respectively (Ellington et al., 1986).
Shipping
UN2811 Toxic solids, organic, n.o.s., Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials, Technical Name Required. UN2588 Pesticides, solid, toxic, Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials, Technical Name Required. UN3077 Environmentally hazardous sub- stances, solid, n.o.s., Hazard class: 9; Labels: 9-Miscellaneous hazardous material, Technical Name Required.
Incompatibilities
Incompatible with oxidizers (chlorates, nitrates, peroxides, permanganates, perchlorates, chlorine, bromine, fluorine, etc.); contact may cause fires or explo- sions. Keep away from alkaline materials, strong bases, strong acids, oxoacids, epoxides. Attacks carbon steel. Compounds of the carboxyl group react with all bases, both inorganic and organic (i.e., amines) releasing substantial heat, water and a salt that may be harmful. Incompatible with arsenic compounds (releases hydrogen cyanide gas), diazo compounds, dithiocarbamates, isocyanates, mercaptans, nitrides, and sulfides (releasing heat, toxic and possibly flam- mable gases), thiosulfates and dithionites (releasing hydrogen sulfate and oxides of sulfur).
Waste Disposal
Alkaline hydrolysis would yield N-isopropylaniline. However, incineration @ 850 ? C together with flue gas scrubbing is the preferred disposal method .
Properties of Propachlor
| Melting point: | 67-76°C |
| Boiling point: | 110°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 1.2420 |
| refractive index | 1.4932 (estimate) |
| Flash point: | 100 °C |
| storage temp. | 0-6°C |
| form | neat |
| pka | 0.30±0.50(Predicted) |
| Water Solubility | 0.7g/L(20 ºC) |
| Merck | 13,7885 |
| BRN | 2103903 |
| Dielectric constant | 2.8-2.9(0.0℃) |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 1918-16-7(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Acetamide, 2-chloro-n-(1-methylethyl)-n-phenyl-(1918-16-7) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Propachlor (1918-16-7) |
Safety information for Propachlor
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H311:Acute toxicity,dermal H317:Sensitisation, Skin H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H410:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P301+P312:IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician IF you feel unwell. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Propachlor
New Products
Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE DIETHYL AMINOMALONATE HYDROCHLORIDE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran




You may like
-
 Propachlor CAS 1918-16-7View Details
Propachlor CAS 1918-16-7View Details
1918-16-7 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 -
 733039-20-8 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 98+View Details
733039-20-8 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 98+View Details
733039-20-8