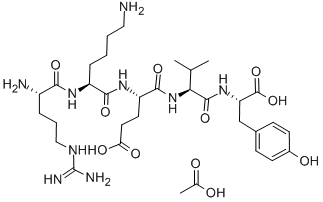
Pramlintide acetate
- CAS NO.:196078-30-5
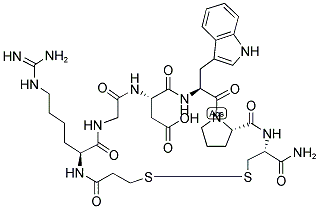
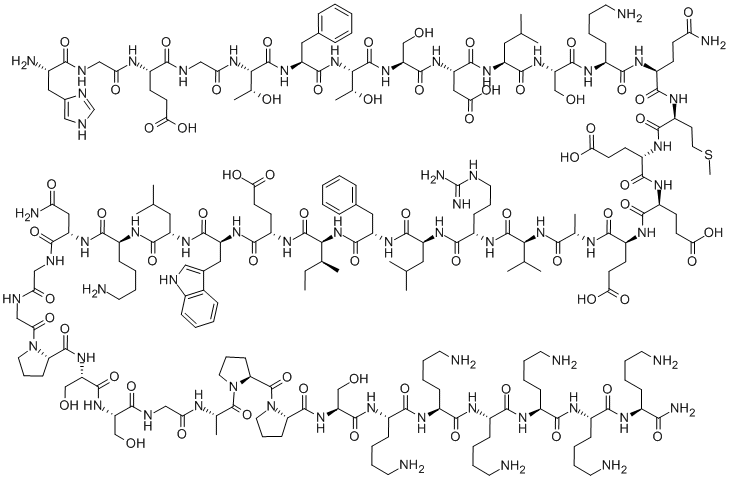
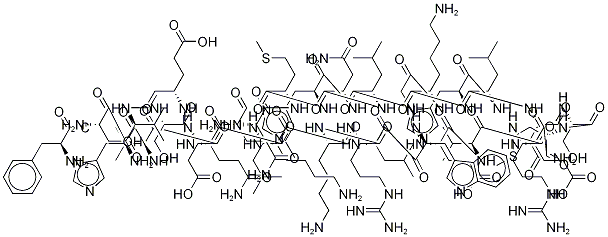
- Empirical Formula: C173H273N51O56S2
- Molecular Weight: 4027.46
- MDL number: MFCD08460172
- EINECS: 251-228-4
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-10-28 23:16:16

What is Pramlintide acetate?
Description
Pramlintide acetate is an injectable human amylin analog that has been launched for the treatment of both type 1 and type 2 diabetes, in conjunction with insulin. While it is also a 37-amino acid peptide, it differs from its parent predecessor by the substitution of Ala-25, Ser-28, and Ser-29 with prolines. Not only do these modifications improve the solubility of the peptide, they also eliminate the aggregation observed with amylin, resulting in a stable synthetic analog with retention of biological activity that is suitable for pharmaceutical use. As an indication of potency, Pramlintide acetate inhibits the binding of radioiodinated rat amylin to rat nucleus accumbens membranes with a Ki value of 23 pM. Its mechanism of action mimics amylin; as a neurohormone that is cosecreted with insulin from the pancreatic β cells in response to meals, it is involved in glucose homeostasis. Both peptides lower postprandial glucose levels by inhibiting glucagon and by restraining the vagus-mediated rate of gastric emptying, thereby, slowing intestinal carbohydrate absorption. Furthermore, amylin, orPramlintide acetate, has the added benefit of inducing postprandial satiety resulting in weight loss in the patients with type 2 diabetes. Since Pramlintide acetate slows gastric emptying, it is contraindicated in patients with gastroparesis and in patients taking drugs that alter gastrointestinal motility (anticholinergic agents, such as, atropine) or slow down the intestinal absorption of nutrients (such as α-glucosidase inhibitors). Pramlintide acetate is also contraindicated in patients with hypoglycemic tendencies; due to co-administration with insulin, severe insulin-induced hypoglycemia is a risk. The most commonly reported adverse events include nausea, vomiting, anorexia, headache, abdominal pain, fatigue, dizziness, coughing, and pharyngitis.
Chemical properties
Pramlintide acetate is White Solid
Originator
Amylin (US)
The Uses of Pramlintide acetate
Pramlintide acetate is an analogue of human amylin used in the treatment of insulin dependent diabetes.
What are the applications of Application
Used in the treatment of diabetes by mimicking human amylin.
brand name
Symlin (Amylin).
Clinical Use
Pramlintide acetate is a synthetic analogue of amylin (a 37-peptide) with proline substitutions at residues 25, 28, and 29. These substitutions change its physical properties such that it is commercially available for SC injection. When pramlintide is used in combination with insulin, it slows gastric emptying, lowers blood glucose levels after meals, and affords a feeling of fullness that leads to decreased caloric intake and the potential for weight loss. Pramlintide has been approved for use in adults with type I or type II diabetes as an adjunct along with insulin. The dose is quite different for type I (15–60 μg SC before meals) and type II diabetes (60–120 μg). The drug should be refrigerated before opening and may be kept at room temperature for up to 28 days after opening.
Properties of Pramlintide acetate
| Melting point: | >175°C (dec.) |
| storage temp. | Refrigerator |
| solubility | Acetic Acid (Slightly), DMSO (Slightly) |
| form | Solid |
| color | White to Off-White |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 196078-30-5(CAS DataBase Reference) |
Safety information for Pramlintide acetate
Computed Descriptors for Pramlintide acetate
New Products
Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL N-octanoyl benzotriazole 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid DIETHYL AMINOMALONATE HYDROCHLORIDE 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran



You may like
-
 2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 -
 733039-20-8 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 98+View Details
733039-20-8 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 98+View Details
733039-20-8