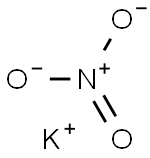
Potassium permanganate
Synonym(s):Permanganic acid potassium salt;Potassium permanganate
- CAS NO.:7722-64-7
- Empirical Formula: KMnO4
- Molecular Weight: 158.033949
- MDL number: MFCD00011364
- EINECS: 231-760-3
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-09-25 17:15:13
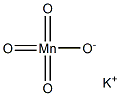
What is Potassium permanganate?
Description
Potassium permanganate, is composed of dark purple, odorless crystals with a blue metallic sheen. It is soluble in water, decomposes at 465°F (240°C), and is a powerful oxidizing material. Potassium permanganate is a dangerous fire and explosion risk in contact with organic materials. Potassium permanganate is incompatible with sulfuric acid, glycerin, and ethylene glycol. The four-digit UN identification number is 1490. The primary uses of potassium permanganate are as an oxidizer, bleach, or dye; during radioactive decontamination of the skin; and in the manufacture of organic chemicals.
Chemical properties
Potassium permanganate is a dark purple crystalline solid with a sweet taste that decompose at 240°C and explode in contact with oxidizable materials.Used as a disinfectant and analytical reagent, in dyes,bleaches,and medicines,and as a chemical intermediate.
Chemical properties
Potassium permanganate, permanganate of potash KMnO4, purple solid, soluble, formed by oxidation of acidified potassium manganate solution with chlorine, and then evaporating.
Physical properties
Dark purple rhombohedral crystal; density 2.703 g/cm3; stable in air;decomposes at about 240°C; moderately soluble in cold water, 6.38 g/100mL at 20°C, soluble in hot water, 25 g/100mL at 65°C; decomposed by alcohol, acetone and many organic solvents causing their oxidation; also decomposed by concentrated acids.
The Uses of Potassium permanganate
Potassium permanganate (KMnO4) is a dark purple-bluish sheen crystal with a slightly sweet taste. It is produced by oxidizing manganate in an electrolytic cell or by passing carbon dioxide through a hot solution of manganate and then cooling until permanganate crystals form. It is a strong oxidizing agent, particularly with organic matter, which makes it a good disinfectant, deodorizer, bleach, and antiseptic.
The Uses of Potassium permanganate

To a solution of the SM (50 g, 159. 2 mmol) in pyridine (300 mL) and H2O (300 mL) was added KMnO4 (100 g, 637.2 mmol) portionwise. The reaction mixture was stirred at 85 C for 6 h. After completion, the mixture was filtered through celite and the celite pad was washed with EtOH (2 x 1.0 L). The filtrate was concentrated to half its volume, then acidified with 1.5N HCl (500 mL) to pH ~2. The resulting precipitate was collected by filtration, washed with ether (2 x 150 mL), and dried in vacuo to provide the product as a white solid which was used in the next step without further purification. [30 g, 55.0%]
The Uses of Potassium permanganate
Bleaching resins, waxes, fats, oils, straw, cotton, silk and other fibers and chamois skins; dyeing wood brown; printing fabrics; washing CO2 in manufacture of mineral waters; exterminating Oidium tuckeri; photography; tanning leathers; purifying water; with formaldehyde solution to expel formaldehyde gas for disinfecting; as an important reagent in analytical and synthetic organic chemistry.
The Uses of Potassium permanganate
Potassium permanganate (KMnO4) is a purplish crystal-like oxidizing compound used as an
antiseptic and disinfectant to inhibit the growth of harmful skin microorganisms and bacteria.
Before antibiotics were available, it was used as a treatment for trench mouth and impetigo.
Trench mouth (necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis), also called “Vincent’s infection,” usually
affects young adults and is considered a form of periodontal disease. If untreated, it can lead
to the loss of gum tissue and eventually loss of teeth. Today, there are more effective treatments
for trench mouth than KMnO4.
Definition
potassium permanganate: A compound,KMnO4, forming purple crystalswith a metallic sheen, soluble inwater (intense purple solution), acetone,and methanol, but decomposedby ethanol; r.d. 2.70; decompositionbegins slightly above 100°C and iscomplete at 240°C. The compound isprepared by fusing manganese(IV)oxide with potassium hydroxide toform the manganate and electrolysingthe manganate solutionusing iron electrodes at about 60°C.An alternative route employs productionof sodium manganate by a similarfusion process, oxidation withchlorine and sulphuric acid, thentreatment with potassium chloride tocrystallize the required product.Potassium manganate(VII) is widelyused as an oxidizing agent and as adisinfectant in a variety of applications,and as an analytical reagent.
Preparation
Potassium permanganate is produced from manganese ore containing at least 60% manganese dioxide, MnO2. The finely ground ore is mixed with 50%potassium hydroxide and heated at about 350°C in rotary kilns. This converts manganese dioxide to potassium manganate:
MnO22+ 4KOH + O2→2K2MnO4+ 2H2O
Potassium manganate obtained above is oxidized to the permanganate either by electrolysis or by chemical oxidation. Electrolytic oxidation is more common. Electrolytic cells have cathodes made of iron rods and nickel-plated anodes. Potassium manganate melt is extracted with water prior to its elec-trolysis and then electrolyzed at a cell voltage of 2.3V and current of about 1,400 amp. Permanganate is produced at theanode and water is reduced to gaseous hydrogen and hydroxyl ions at the cathode:
2K2MnO44+ 2H2O →2KMnO4+ 2KOH + H2.
Indications
Potassium permanganate (KMnO4) is an oxidizing agent that is rapidly rendered inactive in the presence of organic material. The oxidizing action of the chemical is purportedly responsible for its germicidal activity. It is also an astringent and a fungicide. This preparation stains the skin and clothing, and undissolved crystals will cause a chemical burn. It is used less commonly now (primarily as an antifungal agent) and may be little better than water as a wet dressing. A 1:4,000 to 1:16,000 dilution is used on weeping or denuded surfaces (one crushed 65-mg tablet dissolved in 250 to 500 mL; one 330-mg tablet dissolved in 1,500 mL to 3,000 mL). For use as a medicated bath, 8 g (approximately 2 tsp) should be dissolved in 200 L (a full bathtub) of water to produce about a 1:25,000 dilution. Skin stains may be removed with a weak solution of oxalic acid or sodium thiosulfate.
General Description
A purplish colored crystalline solid. Noncombustible but accelerates the burning of combustible material. If the combustible material is finely divided the mixture may be explosive. Contact with liquid combustible materials may result in spontaneous ignition. Contact with sulfuric acid may cause fire or explosion. Used to make other chemicals and as a disinfectant.
Air & Water Reactions
Soluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
Potassium permanganate is a very powerful oxidizing agent, particularly in acidic surroundings. Reacts with incandescence with aluminum carbide [Mellor 5:872. 1946-47]. Grinding with antimony or arsenic causes ignition of the metals [Mellor 12:322. 1946-47]. Mixtures with acetic acid or acetic anhydride may explode if not kept cold [Von Schwartz 1918. p. 34]. Explosions can occur when acidified solutions come in contact with benzene, carbon disulfide, diethyl ether, ethyl alcohol, petroleum, or organic matter. Contact with glycerol may produce an explosion [Pieters 1957. p. 30]. Contact with concentrated hydrogen peroxide solution can produce an explosion [Haz. Chem. Data 1973. p. 230]. Contact with solid hydroxylamine produces an immediate white flame [Mellor 8:294. 1946-47]. Transport through a polypropylene tube ignited the tube [MCA Case History 1842. 1972]. Mixing with concentrated sulfuric acid in a vessel containing moisture caused an explosion (due to formation of manganese heptoxide) [Delhez 1967].
Hazard
Dangerous fire and explosion risk in contact with organic materials, powerful oxidizing agent.
Health Hazard
Burns and stains the skin dark brown. If ingested will cause severe distress of gastro-intestinal system. May be fatal if over 4 oz. are consumed.
Fire Hazard
Behavior in Fire: May cause fire on contact with combustibles. Containers may explode.
Flammability and Explosibility
Non flammable
Industrial uses
This is a crystalline substance with a deep purple color, extremely soluble in water
(60 g/L). At a temperature above 200 °C, KMnO4 decomposes according to the following
reaction:
2KMnO4 +Heat?
K2MnO4 + MnO2 + O2
Potassium permanganate has a depressing effect on most sulfide minerals including
sphalerite, pyrrhotite and chalcopyrite. It has been used to depress pyrrhotite and arsenopyrite
in a pyrite flotation alkaline circuit. Studies were carried out on the depression of copper
in copper–molybdenite separation with promising results. There is very little known
about the depressing action of KMnO4 in relation to pH.
Safety Profile
A human poison by ingestion. Poison experimentally by Flammable by chemical reaction. A powerful oxidizer. A dangerous explosion hazard; handle with care. Explosions may occur in contact with organic or readily oxidizable materials, either when dry or in solution. Dangerous; keep away from combustible materials. Explodes on contact with acetic acid, acetic anhydride, ammonium nitrate, dimethylformamide, formaldehyde, concentrated hydrochloric acid, potassium chloride + sulfuric acid, sulfuric acid + water. Forms sensitive explosive mixtures with aluminum powder + ammonium nitrate + glyceryl nitrate + nitrocellulose, ammonium perchlorate, arsenic, phosphorus, sulfur, slag wool, titanium. Ignites on contact with Aldi dimethyl sulfoxide, ethylene glycol, H2S3, HCl, H2SO4, (H2SO4 + organic matter), (H2SO4 + KCl), NH4ClO4, NH3, NH4, NO3, NH2OH, organic matter, wood, oxygenated organic compounds (e.g., ethylene glycol, propane-l,2-diol, erythritol, mannitol, triethanolamine, 3-chloropropane-l,2-diol, acetaldehyde, isobutyraldehyde, benzaldehyde, acetylacetone, esters of ethylene glycol, lactic acid, acetic acid, oxalic acid). proper condtions with acetone + tert- butylamine, alcohols + nitric acid, aluminum carbide, ammonia + sulfuric acid, antimony, coal + peroxomonosulfuric acid, dichloromethylsilane, dimethyl sulfoxide, ethanol + sulfuric acid, glycerol, concentrated hydrofluoric acid, hydrogen peroxide, hydrogen trisulfide, hydroxylamine, carbon, organic nitro compounds, polypropylene, 3,4,4'- trimethyldiphenyl sulfone. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of K2O. See also PERMAN GANATES.
Potential Exposure
Potassium permanganate is used in solutions as a disinfectant, topical antibacterial agent; deodorizer, bleaching agent; and in air and water purification.
Shipping
UN1490 Potassium permanganate, Hazard Class: 5.1; Labels: 5.1-Oxidizer.
Purification Methods
Crystallise it from hot water (4mL/g at 65o), then dry it in a vacuum desiccator over CaSO4. Phillips and Taylor [J Chem Soc 4242 1962] cooled an aqueous solution of KMnO4, saturated at 60o, to room temperature in the dark, and filtered it through a No.4 porosity sintered-glass filter funnel. The solution was allowed to evaporate in air in the dark for 12hours, and the supernatant liquid was decanted from the crystals, which were dried as quickly as possible with filter paper.
Incompatibilities
Potassium permanganate is a powerful oxidizing agent, that is, it will initiate a fire or explosion if brought into contact with reducing materials; combustibles, organic materials; strong acids; or oxidizable solid, liquid or gas; glycerin, ethylene glycol; polypropylene, hydroxyl- amine, hydrogen trisulfide; antimony, arsenic, sulfuric acid; hydrogen peroxide; phosphorus, and any finely divided combustible material. It will decompose, and release oxygen, if brought into contact with heat, alcohol, acids, ferrous salts; iodides and oxalates.
Waste Disposal
React with reducing agent, neutralize and flush to sewer
Properties of Potassium permanganate
| Melting point: | 240°C |
| Density | 1.01 g/mL at 25 °C |
| vapor pressure | <0.01 hPa (20 °C) |
| storage temp. | Store at RT. |
| solubility | H2O: 0.1 M at 20 °C, complete, violet |
| form | solution (volumetric) |
| appearance | Purple/grey crystals |
| color | Purple |
| Specific Gravity | 2.703 |
| PH | 8 (H2O, 20°C) |
| Water Solubility | 6.4 g/100 mL (20 ºC) |
| Sensitive | Light Sensitive |
| Merck | 14,7655 |
| Stability: | Stable, but contact with combustible material may cause fire. Substances to be avoided include reducing agents, strong acids, organic material, combustible materials, peroxides, alcohols and chemically active metals. Strong oxidant. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 7722-64-7(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Potassium permanganate (7722-64-7) |
Safety information for Potassium permanganate
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Flame Over Circle Oxidizers GHS03  Corrosion Corrosives GHS05  Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Health Hazard GHS08  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H272:Oxidising liquids;Oxidising solids H302:Acute toxicity,oral H314:Skin corrosion/irritation H373:Specific target organ toxicity, repeated exposure H410:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P210:Keep away from heat/sparks/open flames/hot surfaces. — No smoking. P260:Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P303+P361+P353:IF ON SKIN (or hair): Remove/Take off Immediately all contaminated clothing. Rinse SKIN with water/shower. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Potassium permanganate
Potassium permanganate manufacturer
C.H. Chemicals
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 Potassium Permanganate extrapure AR CAS 7722-64-7View Details
Potassium Permanganate extrapure AR CAS 7722-64-7View Details
7722-64-7 -
 Potassium Permanganate (Crystal & Powder)View Details
Potassium Permanganate (Crystal & Powder)View Details
7722-64-7 -
 Potassium Permanganate, Crystal, 50Kg CanView Details
Potassium Permanganate, Crystal, 50Kg CanView Details
7722-64-7 -
 Potassium Permanganate Ar, Purity: 99 %View Details
Potassium Permanganate Ar, Purity: 99 %View Details
7722-64-7 -
 POTASSIUM PERMANGANATE CAS 7722-64-7View Details
POTASSIUM PERMANGANATE CAS 7722-64-7View Details
7722-64-7 -
 Potassium Permanganate, Granules, 40Kg BagView Details
Potassium Permanganate, Granules, 40Kg BagView Details
7722-64-7 -
 Technical Grade Potassium PermanganateView Details
Technical Grade Potassium PermanganateView Details
7722-64-7 -
 Powder POTASSIUM PERMANGANATE LR 99% 500 GM, For Laboratory/Analytical UseView Details
Powder POTASSIUM PERMANGANATE LR 99% 500 GM, For Laboratory/Analytical UseView Details
7722-64-7
