Potassium perchlorate
Synonym(s):Potassium perchlorate;Potassium perchlorate (KClO4 )
- CAS NO.:7778-74-7
- Empirical Formula: ClKO4
- Molecular Weight: 138.55
- MDL number: MFCD00011362
- EINECS: 231-912-9
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-10 11:56:18
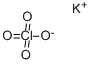
What is Potassium perchlorate ?
Absorption
Perchlorate is rapidly absorbed from the gastrointestinal (GI) tract after ingestion . The time to reach peak plasma levels of perchlorate is approximately 3 hours following oral administration . As potassium perchlorate is an organic compound with complete ionization in water, dermal absorption through intact skin is unlikely .
Toxicity
In a mice study, the LD50 was reported as 3621 mg/kg of following 33 weeks of oral administration . A study reports that at doses of 400 mg/d for several weeks had adverse effects such as GI irritation, skin rash, and lymphadenopathy but cited no serious complications . In patients treated with 400 to 1,000 mg perchlorate daily, cases of agranulocytosis and fatal aplastic anemia have been reported. Several deaths from aplastic anemia in patients treated with perchlorate at doses of 400 to 1000 mg/d for 8 to 33 weeks were also reported . The last report of fatal bone marrow toxicity related to treatment with potassium perchlorate was in the 1960s .
Chemical properties
Potassium perchlorate occurs as a colorless crystal or crystalline powder. It decomposes at 400℃ and may also decompose by organic matter, oxidizable substances and on concussion. Potassium perchlorate is soluble in 65 parts cold water, 15 parts boiling water and is practically insoluble in alcohol.

Physical properties
Colorless crystals or white crystalline powder; rhombohedral structure;density 2.52 g/cm3; melts around 610°C under controlled conditions; decomposes at 400°C; slightly soluble in cold water 0.75 g/100mL at 0°C, soluble in boiling water, 21.8 g/100mL at 100°C; practically insoluble in alcohol; insoluble in ether.
The Uses of Potassium perchlorate
Potassium perchlorate is used in ammunition percussion caps, explosive primers, fireworks and propellants. It acts as a solid rocket propellant. It is also used as an oxidizer in colored pyrotechnic compositions and flash powder. It is used as an antithyroid and involved in the treatment of hyperthyroidism. The mixture of anthracene and sulfur with potassium perchlorate is used for generating black smoke signaling.
The Uses of Potassium perchlorate
In explosives, pyrotechnics and photography, in analytical chemistry.
The Uses of Potassium perchlorate
Potassium perchlorate,is the first such compound discovered, is used in pyrotechnics and has the highest percentage of oxygen (60.1%).
Background
Potassium perchlorate is an inorganic salt with the chemical formula KClO4. It is a strong oxidizer with the lowest solubility of the alkali metal perchlorates. Potassium is most commonly used in flares and automobile airbags . The use of potassium perchlorate as a component in sealing gaskets for food containers has been revoked by the FDA following the use being abandoned by the industry . Potassium perchlorate acts as a competitive inhibitor of iodine uptake by the thyroid gland and attenuates the production of the thyroid hormone. Thus the use of potassium perchlorate has been extensive for hyperthyroidism during the last 50 years, particularly in the late 1950s and early 1960s . The therapeutic use of potassium perchlorate in thyroid disorders has been ceased due to a high risk for developing aplastic anemia and nephrotic syndrome .
Indications
No current FDA- or EMA-approved therapeutic indications.
What are the applications of Application
Potassium perchlorate (reagent grade) is an antithyroid agent
Indications
The perchlorate ion of potassium perchlorate, KClO4, is a competitive inhibitor of thyroidal I- transport via the Sodium Iodide Symporter (NIS).This drug can cause fatal aplastic anemia and gastric ulcers and is now rarely used. If administered with careful supervision, in limited low doses and for only brief periods, serious toxic effects can be avoided. The compound is especially effective in treating iodine-induced hyperthyroidism, which may occur, for example, in patients treated with the antiarrhythmic compound amiodarone. Perchlorate ion can also be used in a diagnostic test of I- incorporation into Tg, the so-called perchlorate discharge test.
Preparation
The potassium perchlorate can be separated from the potassium chloride because it is less soluble in water; however, the preferred production route involves anodic oxidation of cold chloride solutions using a high voltage and high current density. The alkali perchlorates can also be prepared by neutralizing perchloric acid with alkali carbonates, or by metathesis between ammonium perchlorate and alkali sulphates.
General Description
A white crystalline solid. Forms explosive mixtures wilh certain combustible materials. Difficult to burn, but will accelerate burning of combustible materials. Prolonged exposure to fire or heat may result in an explosion. Used in explosives, pyrotechnics, photography.
Air & Water Reactions
Slight solubility in water (7.55 mg /mL of cold water).
Reactivity Profile
Potassium perchlorate is a strong oxidizing agent. Explosively decomposes at or over 400°C. Decomposed by organic matter (reducible material) and on concussion [Merck 11th ed. 1989]. Mixture with powdered magnesium is a friction-sensitive explosive [Safety Eng. Reports 1947]. Incompatible with reducing agents, such as: metal powders aluminum, titanium, barium, magnesium, nickel, and various metal hydrides, sulfur.
Hazard
Fire risk in contact with organic materials, strong oxidizing agent. Strong irritant.
Health Hazard
Inhalation, ingestion or contact (skin, eyes) with vapors or substance may cause severe injury, burns or death. Fire may produce irritating, corrosive and/or toxic gases. Runoff from fire control or dilution water may cause pollution.
Fire Hazard
These substances will accelerate burning when involved in a fire. Some may decompose explosively when heated or involved in a fire. May explode from heat or contamination. Some will react explosively with hydrocarbons (fuels). May ignite combustibles (wood, paper, oil, clothing, etc.). Containers may explode when heated. Runoff may create fire or explosion hazard.
Flammability and Explosibility
Not classified
Pharmacokinetics
Potassium perchlorate inhibits thyroid iodide transport. The clinical use of potassium perchlorate in hyperthyroidism, such as Graves' disease and amiodarone-induced hypothyroidism, have been investigated in various studies. Thyroid dysfunction occurs in about 15-20% of the patients receiving long-term amiodarone therapy . In patients with amiodarone-induced hypothyroidism, short-term administration of potassium perchlorate resulted in restoration of euthyroidism in most patients . Euthyroidism promoted by potassium perchlorate does not persist unless amiodarone treatment is withdrawn .
Safety Profile
An experimental teratogen. A powerful oxidizer. Severe irritant to skin, eyes, and mucous membranes. Has been implicated in aplastic anemia. Absorption can cause methemoglobinemia and hdney injury. It has been involved in many industrial explosions. Explodes on contact with aluminum + barium nitrate + potassium nitrate + water. Forms explosive mixtures with aluminum powder + titanium dioxide, ethylene glycol (240°C), cotton lint (245°C), furfural (27O°C), lactose, metal powders (e.g., aluminum, iron, magnesium, molybdenum, nickel, tantalum, titanium), sulfur, titanium hydride. Reaction with ethanol + heat forms the explosive ethyl perchlorate. Violent reaction or igmtion under the proper conditions with aluminum + aluminum fluoride, barium chromate + tungsten or titanium, boron + magnesium + silicone rubber, ferrocenium lammine- tetrahs(thiocyanat0-N) chromate(1-), potassium hexacyanocobaltate(3-), Al + Mg, charcoal, F2, Ni + Ti, reducing agents. When heated to decomposition it emits very toxic fumes of K2O and Cl-. See also PERCHLORATES.
Metabolism
Perchlorate ions are not reported to undergo metabolism .
Purification Methods
It crystallises from boiling water (5mL/g) on cooling. Dry it under vacuum at 105o.
Properties of Potassium perchlorate
| Melting point: | 400 °C (dec.)(lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 400°C |
| Density | 2.52 |
| vapor density | 4.8 (vs air) |
| vapor pressure | 0Pa at 25℃ |
| storage temp. | Store at +5°C to +30°C. |
| solubility | H2O: 0.1 M at 20 °C, clear, colorless |
| form | Powder |
| Specific Gravity | 2.52 |
| color | Clear colorless to slightly yellow |
| Odor | Odorless |
| PH | 5.0 (10g/l, H2O, 25℃) |
| PH Range | 5.0 - 6.5 |
| Water Solubility | 17 g/L (20 ºC) |
| Sensitive | Hygroscopic |
| Merck | 14,7653 |
| Solubility Product Constant (Ksp) | pKsp: 1.98 |
| Stability: | Stable. Strong oxidiser - contact with combustible materials may lead to fire or explosion. Incompatible with reducing agents, organic materials. Forms explosive mixtures with alcohols. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 7778-74-7(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Potassium perchlorate(7778-74-7) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Perchloric acid, potassium salt (1:1) (7778-74-7) |
Safety information for Potassium perchlorate
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Flame Over Circle Oxidizers GHS03  Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H271:Oxidising liquids;Oxidising solids H302:Acute toxicity,oral |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P210:Keep away from heat/sparks/open flames/hot surfaces. — No smoking. |
Computed Descriptors for Potassium perchlorate
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

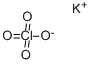
You may like
-
 Potassium perchlorate, anhydrous, For analysis ACS CAS 7778-74-7View Details
Potassium perchlorate, anhydrous, For analysis ACS CAS 7778-74-7View Details
7778-74-7 -
 Potassium perchlorate, GR 99%+ CAS 7778-74-7View Details
Potassium perchlorate, GR 99%+ CAS 7778-74-7View Details
7778-74-7 -
 POTASSIUM PERCHLORATE AR/ACS CAS 7778-74-7View Details
POTASSIUM PERCHLORATE AR/ACS CAS 7778-74-7View Details
7778-74-7 -
 Potassium perchlorate CAS 7778-74-7View Details
Potassium perchlorate CAS 7778-74-7View Details
7778-74-7 -
 Potassium Perchlorate Powder Chemical, Purity: 98%View Details
Potassium Perchlorate Powder Chemical, Purity: 98%View Details
7778-74-7 -
 Potassium PerchlorateView Details
Potassium PerchlorateView Details
7778-74-7 -
 20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 -
 3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
