Polymethylene polyphenyl polyisocyanate
Synonym(s):PAPI 2027;PMDI;Polymethylene polyphenyl isocyanate
- CAS NO.:9016-87-9
- Empirical Formula: C8H7NO2
- Molecular Weight: 149.14668
- MDL number: MFCD00072953
- EINECS: 922-627-7
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-01-06 13:21:43
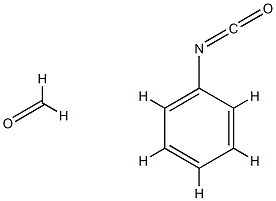
What is Polymethylene polyphenyl polyisocyanate?
Description
Polymethylene polyphenyl polyisocyanate is a chain extender and a cross-linker that is used in the formation of a polyurethane system by forming amide linkages (?NCO).
Chemical properties
liquid
The Uses of Polymethylene polyphenyl polyisocyanate
Poly[methylene(polyp?henyl Isocyanate)?] is an engineering polymer used in the synthesis of highly resiliant polyurethane foams with flame retardancy.Environmental toxin on US EPA Toxic Release Inventory list (TRI) list.
Definition
A polymer of diphenylmethane-4,4′-diisocyanate.
What are the applications of Application
Polymethylene polyphenyl polyisocyanate can be used as a cross-linker to DNA and CTMA based films for the fabrication of biomaterials for organic electronic devices. It can be used in the formation of polyurethane based materials for non-linear optical applications.
General Description
Dark-brown liquid with a weak odor. Sinks in water.
Air & Water Reactions
Reacts with water slowly forming heavy scum and liberating carbon dioxide gas. Dangerous pressure can build up if container is sealed.
Reactivity Profile
Polymethylene polyphenyl polyisocyanate reacts with water slowly forming heavy scum and liberating carbon dioxide gas. Dangerous pressure can build up if container is sealed. Base-catalysed reactions of isocyanates with alcohols should be carried out in inert solvents. Such reactions in the absence of solvents often occur with explosive violence [Wischmeyer 1969].
Hazard
Questionable carcinogen.
Health Hazard
Inhalation causes breathlessness, chest discomfort, and reduced pulmonary function; wheezing, cough, and sputum may also occur. Contact with liquid irritates eyes and skin. Ingestion causes irritation of mouth and stomach.
Fire Hazard
Behavior in Fire: Containers may explode.
Safety Profile
Moderately toxic by ingestion. Mildly toxic by inhalation. Questionable carcinogen with experimental neoplastigenic data by implant route. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of NOx.
Properties of Polymethylene polyphenyl polyisocyanate
| Boiling point: | 392 °C5 mm Hg |
| Density | 1.2 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
| vapor density | 8.6 (vs air) |
| refractive index | n |
| Flash point: | >230 °F |
| storage temp. | Refrigerator, Under inert atmosphere |
| solubility | DMSO (Sparingly), Ethyl Acetate (Slightly), Methanol (Soluble) |
| form | Oil |
| color | Yellow to Orange |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents, alcohols. May decompose in moist air, or on contact with water. |
| InChI | InChI=1S/C7H5NO.CH2O/c9-6-8-7-4-2-1-3-5-7;1-2/h1-5H;1H2 |
| IARC | 3 (Vol. 19, Sup 7) 1987 |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Polymeric diphenylmethane diisocyanate (9016-87-9) |
Safety information for Polymethylene polyphenyl polyisocyanate
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06  Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H317:Sensitisation, Skin H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H330:Acute toxicity,inhalation H334:Sensitisation, respiratory H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation H351:Carcinogenicity H373:Specific target organ toxicity, repeated exposure |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P202:Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood. P260:Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P302+P352:IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of soap and water. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Polymethylene polyphenyl polyisocyanate
| InChIKey | JTEOXXUIKUHXLD-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | O=C=NC1C([H])=C([H])C([H])=C([H])C=1[H].O=C([H])[H] |
New Products
Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate (S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one N-octanoyl benzotriazole 3,4-Dibenzyloxybenzaldehyde 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) 4-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 MDI-DBA Oligomers Standard CASView Details
MDI-DBA Oligomers Standard CASView Details -
 N-Vinylformamide 99%View Details
N-Vinylformamide 99%View Details
13162-05-5 -
 2-ethyl-6-methyl-3-hydroxypyridine succinate 99%View Details
2-ethyl-6-methyl-3-hydroxypyridine succinate 99%View Details
127464-43-1 -
 2-ETHYLPYRIDINE 100-71-0 99%View Details
2-ETHYLPYRIDINE 100-71-0 99%View Details
100-71-0 -
 7439-89-6 Electrolytic Iron Flakes 99.9% MaxView Details
7439-89-6 Electrolytic Iron Flakes 99.9% MaxView Details
7439-89-6 -
 7439-89-6 98.0% MinView Details
7439-89-6 98.0% MinView Details
7439-89-6 -
 Reduced Iron Powder 99.8% MaxView Details
Reduced Iron Powder 99.8% MaxView Details
7439-89-6 -
 Electrolytic Iron Powder 7439-89-6 99.8% MaxView Details
Electrolytic Iron Powder 7439-89-6 99.8% MaxView Details
7439-89-6