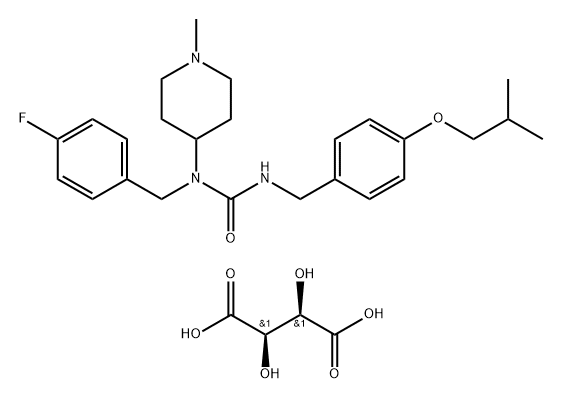
Pimavanserin
- CAS NO.:706779-91-1
- Empirical Formula: C25H34FN3O2
- Molecular Weight: 427.55
- MDL number: MFCD09953792
- EINECS: 1806241-263-5
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-23 21:30:31

What is Pimavanserin?
Absorption
The median Tmax of pimavanserin in clinical studies was 6 hours, regardless of the dose. The bioavailability of an oral tablet of pimavanserin and a solution were almost identical. Ingestion of a high-fat meal had no significant effect on the rate (Cmax) and extent (AUC) of pimavanserin exposure. Cmax decreased by about 9% while AUC increased by about 8% with a high-fat meal.
The major active circulating N-desmethylated metabolite, AC-279, has a median Tmax of 6 hours.
Toxicity
LD50 information for pimavanserin is not readily available in the literature. Pre-marketing clinical trials involving pimavanserin in approximately 1200 subjects and patients do not report symptoms of overdose. In healthy subject studies, nausea and vomiting were reported. There are no known antidotes for an overdose with this drug. Cardiovascular monitoring should begin immediately in the case of an overdose and continuous ECG monitoring is recommended. If antiarrhythmic drugs are administered in an overdose of pimavanserin, disopyramide, procainamide, and quinidine should not be used due to their potential for QT-prolonging effects. In the case of an overdose, consider the 57 hour plasma half-life of pimavanserin and the possibility of multiple drug involvement.
Description
Pimavanserin is an inverse agonist of the serotonin (5-HT) receptor subtype 5-HT2A (IC50 = 1.86 nM; Ki = 0.5 nM). It is selective for 5-HT2A over a panel of 65 ion channels, enzymes, and receptors (Kis = >100 nM). Pimavanserin reduces head-twitch behavior and prepulse inhibition deficits induced by the 5-HT2A receptor agonist DOI in rats at doses of 3 mg/kg, p.o. and 1-10 mg/kg, s.c., respectively. It also exhibits antipsychotic-like activity, reducing hyperactivity induced by (+)-MK-801 in mice. Pimavanserin acts synergistically with haloperidol or risperidone to suppress (+)-MK-801-induced hyperactivity and attenuates haloperidol- and risperidone-induced catalepsy in rats. Formulations containing pimavanserin have been used for the treatment of psychosis in Parkinson''s disease.
Chemical properties
Yellow Solid
The Uses of Pimavanserin
Drug used in the treatment of Parkinson’s disease psychosis.
The Uses of Pimavanserin
Drug used in the treatment of Parkinson’s disease and psychosis.
Background
Pimavanserin is an atypical antipsychotic indicated for the treatment of psychiatric disorders. Although the exact mechanism of action is unknown, it is thought that pimavanserin interacts with the serotonin receptors, particularly the 5-HT2A and HT2C receptors. Unlike other atypical antipsychotics, pimavanserin lacks inherent dopaminergic activity. In fact, pimavanserin is the first antipsychotic drug without D2 blocking activity. Therefore, pimavanserin can be used to treat psychotic symptoms without causing extrapyramidal or worsening motor symptoms.
Pimavanserin is marketed under the trade name NUPLAZID and developed by Acadia Pharmaceuticals. It was approved by the FDA in April 2016 for the treatment of hallucinations and delusions associated with Parkinson's disease psychosis thanks to favorable results from a pivotal six-week, randomized, placebo-controlled, parallel-group study. Pimavanserin was also under review as a potential treatment for dementia-related psychosis; however, as of April 2021, FDA approval has not been granted for this indication despite previous breakthrough designation.
Indications
Pimavanserin is indicated for the treatment of hallucinations and delusions associated with Parkinson’s disease psychosis.
Definition
ChEBI: Pimavanserin is a member of the class of ureas in which three of the four hydrogens are replaced by 4-fluorobenzyl, 1-methylpiperidin-4-yl, and 4-(isopropyloxy)benzyl groups. An atypical antipsychotic that is used (in the form of its tartrate salt) for treatment of hallucinations and delusions associated with Parkinson's disease. It has a role as an antipsychotic agent, a 5-hydroxytryptamine 2A receptor inverse agonist and a serotonergic antagonist. It is a member of ureas, a member of piperidines, a member of monofluorobenzenes, an aromatic ether and a tertiary amino compound. It is a conjugate base of a pimavanserin(1+).
General Description
Pimavanserin(706779-91-1) is a novel first-line drug of antipsychotic symptoms belongs to non-dopaminergic neurotransmitters with the drug targets being serotonin 2A receptor (5-HT2A), which can selectively block the 5-HT 2A receptor without affecting the action of dopamine with the routine administration being treatment via oral administration once daily. There are evidences showing that the drug is quite effective in the treatment of Parkinson's disease psychosis with well tolerance. Moreover, it does not block the dopamine receptors, and therefore does not lead to worsening of symptoms of Parkinson's disease. A 6-week-lasting randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial has included 199 patients and evaluated the safety and efficacy of pimavanserin.
Biological Activity
Pimavanserin is an inverse agonist of the serotonin (5-HT) receptor subtype 5-HT2A (IC50 = 1.86 nM; Ki = 0.5 nM). It is selective for 5-HT2A over a panel of 65 ion channels, enzymes, and receptors (Kis = >100 nM). Pimavanserin reduces head-twitch behavior and prepulse inhibition deficits induced by the 5-HT2A receptor agonist DOI in rats at doses of 3 mg/kg, p.o. and 1-10 mg/kg, s.c., respectively. It also exhibits antipsychotic-like activity, reducing hyperactivity induced by (+)-MK-801 in mice. Pimavanserin acts synergistically with haloperidol or risperidone to suppress (+)-MK-801-induced hyperactivity and attenuates haloperidol- and risperidone-induced catalepsy in rats. Formulations containing pimavanserin have been used for the treatment of psychosis in Parkinson''s disease.
Pharmacokinetics
Pimavanserin's unique actions on serotonin receptors improve symptoms of hallucinations and delusions associated with Parkinson's disease. In clinical studies, 80.5% of individuals treated with pimavanserin reported improvement in symptoms. Pimavanserin does not worsen motor functioning in patients with Parkinson's disease psychosis.
In vitro, pimavanserin acts as an inverse agonist and antagonist at serotonin 5-HT2A receptors with high binding affinity (Ki value 0.087 nM) and at serotonin 5-HT2C receptors with lower binding affinity (Ki value 0.44 nM). Pimavanserin shows low binding to sigma 1 receptors (Ki value 120 nM) and has no appreciable affinity (Ki value >300 nM), to serotonin 5-HT2B, dopaminergic (including D2), muscarinic, histaminergic, or adrenergic receptors, or to calcium channels.
The effect of pimavanserin on the QTc interval was evaluated in a randomized placebo- and positive-controlled double-blind, multiple-dose parallel thorough QTc study in 252 healthy subjects. A central tendency analysis of the QTc data at steady-state demonstrated that the maximum mean change from baseline (upper bound of the two-sided 90% CI) was 13.5 (16.6) msec at a dose of twice the therapeutic dose. A pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic analysis with pimavanserin suggested a concentration-dependent QTc interval prolongation in the therapeutic range.
In the 6-week, placebo-controlled effectiveness studies, mean increases in QTc interval of ~5-8 msec were observed in patients receiving once-daily doses of pimavanserin 34 mg. These data are consistent with the profile observed in a thorough QT study in healthy subjects. Sporadic QTcF values ≥500 msec and change from baseline values ≥60 msec were observed in subjects treated with pimavanserin 34 mg; although the incidence was generally similar for pimavanserin and placebo groups. There were no reports of torsade de pointes or any differences from placebo in the incidence of other adverse reactions associated with delayed ventricular repolarization in studies of pimavanserin, including those patients with hallucinations and delusions associated with Parkinson’s disease psychosis.
Side Effects
Pimavanserin is a medication used to treat hallucinations and delusions associated with Parkinson's disease psychosis. Like all medications, it carries the risk of side effects. Common side effects of pimavanserin may include:
Bloating or swelling of the face, arms, hands, lower legs, or feet
confusion
nausea
rapid weight gain
unusual weight gain or loss
www.mayoclinic.org
Enzyme inhibitor
This orally active atypical non-dopaminergic antipsychotic[ (FWfree-base = 427.56 g/mol; CAS 706779-91-1 (free base) and 706782-28-7 (tartrate salt)), also known as ACP-103, Nuplazid? and N-(4-fluorophenylmethyl)- N-(1-methyl-piperidin-4-yl)-N'-(4-(2-methylpropyloxy)phenyl-methyl)carbamide, is a potent inverse agonist and antagonist at serotonin 5-HT2A receptors (Ki = 0.087 nM) and less so at serotonin 5-HT2C receptors (Ki = 0.44 nM). Pimavanserin shows low binding to σ1 receptors (Ki = 120 nM), with no appreciable affinity (Ki > 300 nM) to serotonin 5-HT2B, dopaminergic (including D2), muscarinic, histaminergic, or adrenergic receptors, or to calcium channels. 5-HT2A receptor dysregulation is implicated in both the etiology and treatment of schizophrenia, and the same receptor plays an active role in the regulation of sleep architecture. Nuplazid is specifically indicated in its FDA approval (April, 2016) for the treatment of hallucinations and delusions associated with Parkinson disease. Significantly, 5-HT2A serotonin receptor antagonists differentially regulate 5-HT2A receptor protein level in vivo. See also Ketanserin; RH-34; Risperidone; Ritanserin; Setoperone; Volinanserin.
Metabolism
Pimavanserin is mainly metabolized CYP3A4 and CYP3A5 hepatic cytochrome enzymes, and to a lesser extent by CYP2J2, CYP2D6, and other cytochrome and flavin-containing monooxygenase enzymes. CYP3A4 metabolizes pimavanserin to its major active metabolite, AC-279.
Storage
Store at -20°C
Mode of action
The mechanism of action of pimavanserin in the treatment of hallucinations and delusions associated with Parkinson’s disease psychosis is unknown. However, the effect of pimavanserin could be mediated through a combination of inverse agonist and antagonist activity at serotonin 5-HT2A receptors and to a lesser extent at serotonin 5-HT2C receptors.
www.accessdata.fda.gov
Properties of Pimavanserin
| Melting point: | 100-103oC |
| Boiling point: | 604.2±55.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.15±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | Refrigerator |
| solubility | Methanol (Slightly) |
| form | Solid |
| pka | 13.52±0.46(Predicted) |
| color | Pale Yellow to Pale Orange |
| InChI | InChI=1S/C25H34FN3O2/c1-19(2)18-31-24-10-6-20(7-11-24)16-27-25(30)29(23-12-14-28(3)15-13-23)17-21-4-8-22(26)9-5-21/h4-11,19,23H,12-18H2,1-3H3,(H,27,30) |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 706779-91-1(CAS DataBase Reference) |
Safety information for Pimavanserin
Computed Descriptors for Pimavanserin
| InChIKey | RKEWSXXUOLRFBX-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | N(CC1=CC=C(F)C=C1)(C1CCN(C)CC1)C(NCC1=CC=C(OCC(C)C)C=C1)=O |
Pimavanserin manufacturer
ALS India Life Sciences Pvt. Ltd
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 706779-91-1 99%View Details
706779-91-1 99%View Details
706779-91-1 -
 Pimavanserin 97% (HPLC) CAS 706779-91-1View Details
Pimavanserin 97% (HPLC) CAS 706779-91-1View Details
706779-91-1 -
 Pimavanserin 706779-91-1 97.39%View Details
Pimavanserin 706779-91-1 97.39%View Details
706779-91-1 -
 3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 -
 3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 -
 4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
5305-40-8
