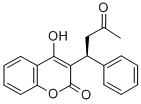
PHENPROCOUMON
- CAS NO.:435-97-2
- Empirical Formula: C18H16O3
- Molecular Weight: 280.32
- MDL number: MFCD00865273
- EINECS: 207-108-9
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:07:02
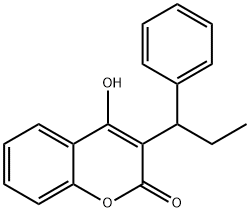
What is PHENPROCOUMON?
Absorption
Bioavailability is close to 100%
Toxicity
50=500 mg/kg. Symptoms of overdose includes suspected or overt abnormal bleeding (e.g., appearance of blood in stools or urine, hematuria, excessive menstrual bleeding, melena, petechiae, excessive bruising or persistent oozing from superficial injuries).
Chemical properties
White Solid
Originator
Liquamar ,Organon ,US,1958
The Uses of PHENPROCOUMON
Phenprocoumon is known for being an oral anti-coagulant.
Indications
Used for the prevention and treatment of thromboembolic disease including venous thrombosis, thromboembolism, and pulmonary embolism as well as for the prevention of ischemic stroke in patients with atrial fibrillation (AF).
Background
Coumarin derivative that acts as a long-acting oral anticoagulant.
Definition
ChEBI: A hydroxycoumarin that is 4-hydroxycoumarin which is substituted at position 3 by a 1-phenylpropyl group.
Manufacturing Process
8.3 parts by weight of powdered sodium in 300 parts by volume of benzene, 100 parts by weight of diethyl (1'-phenylpropyl)-malonate and 72 parts by weight of acetylsalicylic acid chloride are reacted together to form diethyl 1(o-acetoxybenzoy1)-1-(1'-phenylpropyl)malonate, which boils at 195°198°C/0.03 mm Hg.
10.3 parts of weight of diethyl 1-(o-acetoxybenzoyl)-1-(1'-phenylpropyl)malonate are dissolved in 60 parts by volume of absolute ether and to this solution are added portion. wise at 10°C, while stirring, 2.6 parts by weight of sodium methylate. The reaction mixture is stirred for 4 hours, whereupon it is poured into ice water. The ether solution is washed neutral with ice water. After having distilled off the ether, a thick oil consisting of 3-carbethoxy-3-(1'phenylpropyl)-4-oxo-dihydrocoumarinis obtained. This compound crystallized in butyl oxide and has a MP of 108°-109°C.
The 3-carbethoxy-3-(1'-phenylpropyl)-4-oxo-dihydrocoumarinmay be hydrolyzed and decarboxylated as follows. The crude product is heated to 85°C for 1/2 hour with 100 parts by volume of 5% aqueous sodium hydroxide, while agitating or stirring. To remove traces of undissolved oil, the cooled solution is treated with 1 part by weight of charcoal, whereupon it is filtrated and acidified to Congo reaction with dilute sulfuric acid. The 3-(1'phenylpropyl)-4-hydroxycoumarin formed is separated off and recrystallized in 80% ethanol, whereupon it melts at 178°-179°C according to US Patent 2,701,804.
brand name
Liquamar (Organon).
Therapeutic Function
Anticoagulant
Pharmacokinetics
Phenprocoumon, a coumarin anticoagulant, thins the blood by antagonizing vitamin K which is required for the production of clotting factors in the liver. Anticoagulants such as phenprocoumon have no direct effect on an established thrombus, nor do they reverse ischemic tissue damage (damage caused by an inadequate blood supply to an organ or part of the body). However, once a thrombus has occurred, the goal of anticoagulant treatment is to prevent further extension of the formed clot and prevent secondary thromboembolic complications which may result in serious and possibly fatal sequelae.
Synthesis
Phenprocoumon, 3-(|á-ethylbenzyl)-4-hydroxycoumarin (24.1.14), is synthesized by acylating sodium salts of diethyl ester (1-phenylpropyl)butyric acid with acetylsalicylic acid chloride, which forms the compound 24.1.12, which upon reaction with sodium ethoxide cyclizes to 3-(|á-ethylbenzyl)-2-carboethoxy-4-hydroxycoumarin (24.1.13). Alkaline hydrolysis of this product and further decarboxylation gives phenprocoumon(24.1.14).

Metabolism
Phenprocoumon is stereoselectively metabolized by hepatic microsomal enzymes (cytochrome P-450) to inactive hydroxylated metabolites (predominant route) and by reductases to reduced metabolites. Cytochrome P450 2C9 is the principal form of human liver P-450 responsible for metabolism.
Properties of PHENPROCOUMON
| Melting point: | 179-180° |
| Boiling point: | 463.2±45.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.261±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | Chloroform (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly) |
| form | Solid |
| pka | 4.50±1.00(Predicted) |
| color | White to Off-White |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Phenprocoumon (435-97-2) |
Safety information for PHENPROCOUMON
Computed Descriptors for PHENPROCOUMON
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 -
 42831-50-5 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID 98%View Details
42831-50-5 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID 98%View Details
42831-50-5 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1