ACENOCOUMAROL
Synonym(s):(±)-Acenocoumarin;3-(α-Acetonyl-p-nitrobenzyl)-4-hydroxy-coumarin
- CAS NO.:152-72-7
- Empirical Formula: C19H15NO6
- Molecular Weight: 353.33
- MDL number: MFCD00137816
- EINECS: 205-807-3
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-19 23:02:33
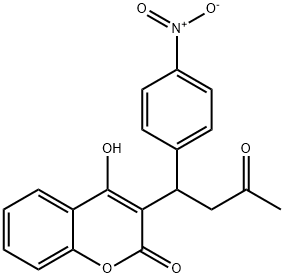
What is ACENOCOUMAROL?
Absorption
Rapidly absorbed orally with greater than 60% bioavailability. Peak plasma levels are attained 1 to 3 hours following oral administration.
Toxicity
The onset and severity of the symptoms are dependent on the individual's sensitivity to oral anticoagulants, the severity of the overdosage, and the duration of treatment. Bleeding is the major sign of toxicity with oral anticoagulant drugs. The most frequent symptoms observed are: cutaneous bleeding (80%), haematuria (with renal colic) (52%), haematomas, gastrointestinal bleeding, haematemesis, uterine bleeding, epistaxis, gingival bleeding and bleeding into the joints. Further symptoms include tachycardia, hypotension, peripheral circulatory disorders due to loss of blood, nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea and abdominal pains.
Chemical properties
White Crystalline Solid
Originator
Sintrom ,Geigy ,US ,1957
The Uses of ACENOCOUMAROL
R-Enantiomer of Acenocoumarol. Vitamin K antagonist; structurally similar to Warfarin. Anticoagulant
The Uses of ACENOCOUMAROL
S-Enantiomer of Acenocoumarol. Vitamin K antagonist; structurally similar to Warfarin. Anticoagulant
The Uses of ACENOCOUMAROL
antimicrobial
The Uses of ACENOCOUMAROL
Anticoagulant agent: Vitamin K antagonist
What are the applications of Application
Acenocoumarol is an anticoagulant vitamin K antagonist
Background
Acenocoumarol is a coumarin derivative used as an anticoagulant. Coumarin derivatives inhibit the reduction of vitamin K by vitamin K reductase. This prevents carboxylation of vitamin K-dependent clotting factors, II, VII, IX and X, and interferes with coagulation. Hematocrit, hemoglobin, international normalized ratio and liver panel should be monitored. Patients on acenocoumarol are prohibited from giving blood.
Indications
For the treatment and prevention of thromboembolic diseases. More specifically, it is indicated for the prevention of cerebral embolism, deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolism, thromboembolism in infarction and transient ischemic attacks. It is used for the treatment of deep vein thrombosis and myocardial infarction.
Definition
ChEBI: A hydroxycoumarin that is warfarin in which the hydrogen at position 4 of the phenyl substituent is replaced by a nitro group.
Manufacturing Process
16 parts of 4-hydroxycoumarin and 19 parts of 4-nitrobenzalacetoneare
thoroughly mixed and heated for 12-14 hours in an oil bath, the temperature
of which is between 135°C and 140°C. After cooling, the melt is dissolved in a
little acetone. The solution is slowly added to a lye made up from 6 parts of
sodium hydroxide in 400 parts of water while stirring and then the mixture is
stirred for 30 minutes. A little animal charcoal is then added, the mixture is
stirred for a further 15 minutes, 400 parts of water are added and the
charcoal and undissolved components are separated by filtration under
suction. The clear solution is made acid to Congo red paper with hydrochloric
acid and the product which is precipitated is filtered off under suction. 3-[α-
(4'-Nitrophenyl)-β-acetylethyl]-4-hydroxycoumarin is obtained. MP 196-199°C.
It should be noted that the process is akin to that for Warfarin except that 4-
nitrobenzalacetone replaces benzalacetone as a raw material.
Therapeutic Function
Anticoagulant, Vitamin
Pharmacokinetics
Acenocoumarol inhibits the reduction of vitamin K by vitamin K reductase. This prevents carboxylation of certain glutamic acid residues near the N-terminals of clotting factors II, VII, IX and X, the vitamin K-dependent clotting factors. Glutamic acid carboxylation is important for the interaction between these clotting factors and calcium. Without this interaction, clotting cannot occur. Both the extrinsic (via factors VII, X and II) and intrinsic (via factors IX, X and II) are affected by acenocoumarol.
Clinical Use
Anticoagulant
Safety Profile
Poison by intraperitoneal route.Moderately toxic by ingestion. A human teratogen by anunspecified route. When heated to decomposition it emitstoxic fumes such as NOx.
Synthesis
Acenocoumarin, 3-(α-acetonyl-p-nitrobenzyl)-4-hydroxycoumarin (24.1.11), is synthesized by a scheme completely analogous to making warfarin, but using p-nitrobenzalacetone.
Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs There are many significant interactions with
coumarins. Prescribe with care with regard to the
following:
Anticoagulant effect enhanced by: alcohol,
amiodarone, anabolic steroids, aspirin, aztreonam,
bicalutamide, cephalosporins, chloramphenicol,
cimetidine, ciprofloxacin, fibrates, clopidogrel,
cranberry juice, danazol, dipyridamole, disulfiram,
dronedarone, esomeprazole, ezetimibe, fibrates,
fluconazole, flutamide, fluvastatin, grapefruit juice,
itraconazole, ketoconazole, levamisole, levofloxacin,
macrolides, methylphenidate, metronidazole,
miconazole, nalidixic acid, neomycin, norfloxacin,
NSAIDs, ofloxacin, omeprazole, pantoprazole,
paracetamol, penicillins, propafenone, ritonavir,
rosuvastatin, SSRIs, simvastatin, sulfinpyrazone,
sulphonamides, tamoxifen, testosterone, tetracyclines,
thyroid hormones, tigecycline, toremifene, tramadol,
trimethoprim, valproate, vitamin E, voriconazole.
Anticoagulant effect decreased by: acitretin,
azathioprine, carbamazepine, enteral feeds,
enzalutamide, fosphenytoin, griseofulvin, oral
contraceptives, phenobarbital, phenytoin, primidone,
rifamycins, St John’s wort (avoid), sucralfate, vitamin
K.
Anticoagulant effects enhanced / reduced by: anion
exchange resins, corticosteroids, dietary changes,
efavirenz, fosamprenavir, tricyclics.
Analgesics: increased risk of bleeding with IV
diclofenac and ketorolac - avoid concomitant use.
Anticoagulants: increased risk of haemorrhage with
apixaban, dabigatran, edoxaban and rivaroxaban -
avoid.
Antidiabetic agents: enhanced hypoglycaemic
effect with sulphonylureas also possible changes to
anticoagulant effect.
Ciclosporin: there have been a few reports of altered
anticoagulant effect; decreased ciclosporin levels have
been seen rarely.
Cytotoxics: increased risk of bleeding with erlotinib;
enhanced anticoagulant effect with capecitabine,
etoposide, fluorouracil, ifosfamide, sorafenib and
tegafur; reduced effect with mercaptopurine and
mitotane.
Metabolism
Extensively metabolized in the liver via oxidation forming two hydroxy metabolites and keto reduction producing two alcohol metabolites. Reduction of the nitro group produces an amino metabolite which is further transformed to an acetoamido metabolite. Metabolites do not appear to be pharmacologically active.
Metabolism
Acenocoumarol is extensively metabolised, although the metabolites appear to be pharmacologically inactive in man. 29% is excreted in the faeces and 60% in the urine, with less than 0.2% of the dose being renally excreted unchanged.
Properties of ACENOCOUMAROL
| Melting point: | 196-1990C |
| Boiling point: | 486.76°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 1.3979 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.5000 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | -20°C Freezer |
| solubility | DMSO, heptane and xylene: ≥17mg/mL |
| pka | pKa 4.7 (Uncertain) |
| form | powder |
| color | white to tan |
Safety information for ACENOCOUMAROL
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P270:Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. P301+P312:IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician IF you feel unwell. P302+P352:IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of soap and water. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for ACENOCOUMAROL
ACENOCOUMAROL manufacturer
Ralington Pharma
KPS Chemicals And Pharmaceuticals
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 152-72-7 Acenocoumarol 98%View Details
152-72-7 Acenocoumarol 98%View Details
152-72-7 -
 152-72-7 99%View Details
152-72-7 99%View Details
152-72-7 -
 Acenocoumarol 152-72-7 98%View Details
Acenocoumarol 152-72-7 98%View Details
152-72-7 -
 Acenocoumarol 99%View Details
Acenocoumarol 99%View Details
152-72-7 -
 Acenocoumarol CAS 152-72-7View Details
Acenocoumarol CAS 152-72-7View Details
152-72-7 -
 Acenocoumarol CAS 152-72-7View Details
Acenocoumarol CAS 152-72-7View Details
152-72-7 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1