Warfarin sodium
Synonym(s):3-(α-Acetonylbenzyl)-4-hydroxycoumarin sodium salt;4-Hydroxy-3-(3-oxo-1-phenylbutyl)coumarin
- CAS NO.:129-06-6
- Empirical Formula: C19H15O4.Na
- Molecular Weight: 330.31
- MDL number: MFCD00083223
- EINECS: 204-929-4
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-01-27 09:38:02
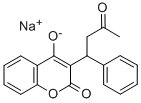
What is Warfarin sodium ?
Chemical properties
Colorless solid
Originator
Coumadin ,Endo,US,1954
The Uses of Warfarin sodium
Warfarin Sodium (Crystalline Clathrate) is used for pharmaceutical care for patients with chronic heart failure and renal dysfunction.
The Uses of Warfarin sodium
central stimulant
The Uses of Warfarin sodium
Rodenticide.
What are the applications of Application
Warfarin Sodium is an inhibitor of VKOR and CYP2C9.
Manufacturing Process
About 0.1 mol each of 4-hydroxycoumarin and benzalacetone are dissolved, in
any desired order, in about three times their combined weight of pyridine. The
solution is refluxed for about 24 hours, and then allowed to cool; after which
it is poured into about 15 volumes of water, and acidified to about pH 2 by the
addition of hydrochloric acid. An oil separates, and on cooling and standing
overnight solidifies. The solid product is recovered, as by filtration, and
recrystallized from ethanol, according to US Patent 2,427,578.
The base melts at about 161°C. It is a white crystalline solid, soluble in hot
ethyl alcohol and substantially insoluble in cold water; it dissolves in alkali
solutions with formation of the salt. The yield is about 40%.
Then, as described in US Patent 2,777,859, warfarin may be reacted with
NaOH to give a sodium salt solution. Crystalline warfarin sodium may be
prepared as described in US Patent 2,765,321.
brand name
Athrombin (Purdue Frederick); Coumadin (Bristol-Myers Squibb); Jantoven (USl); Panwarfin (Abbott).
Therapeutic Function
Anticoagulant
General Description
Slightly bitter crystalline powder. An anticoagulant used as a rodenticide.
General Description
Warfarin sodium, 3-( -acetonylbenzyl)-4-hydroxycoumarin sodium salt (Coumadin,Panwarfin), is a white, odorless, crystalline powder, with aslightly bitter taste; it is slightly soluble in chloroform and solublein alcohol or water. A 1% solution has a pH of 7.2 to 8.5.
Reactivity Profile
A coumarin derivative, a lactone. Lactones are similar to esters reactive chemistries.
Health Hazard
Warfarin sodium is highly toxic orally in humans.
Fire Hazard
When heated to decomposition, Warfarin sodium emits toxic fumes of sodium oxide.
Clinical Use
By virtue of its great potency, warfarin sodium at firstwas considered unsafe for use in humans and was used veryeffectively as a rodenticide, especially against rats. At theproper dosage level, however, it can be used in humans, especiallythrough the intravenous route.
Safety Profile
Poison to humans by ingestion. Experimental poison by ingestion and intravenous routes. Human systemic effects by ingestion: dermatitis. Human reproductive effects by ingestion: fetotoxicity, abnormal condition of newborn at birth, other newborn physical effects, and teratogenic effects includmg developmental abnormalities of the eye and ear, craniofacial area, skin and appendages, musculoskeletal system, cardiovascular system, and gastrointestinal system of the fetus. ,4n experimental teratogen. Other experimental reproductive effects. Mutation data reported. An anticoagulant drug. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of Na2O.
Veterinary Drugs and Treatments
In veterinary medicine, warfarin is used primarily for the oral, long-term treatment (or prevention of recurrence) of thrombotic conditions, primarily in cats, dogs, or horses. Use of warfarin in veterinary species is somewhat controversial and due to unproven benefit in reducing mortality, increased expense associated with monitoring, and potential for serious effects (bleeding), many do not recommend its use.
Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
There are many significant interactions with warfarin.
Prescribe with care with regard to the following:
Anticoagulant effect enhanced by: alcohol,
amiodarone, anabolic steroids, aspirin, aztreonam,
bicalutamide, cephalosporins, chloramphenicol,
cimetidine, ciprofloxacin, clopidogrel, cranberry
juice, danazol, danshen, dipyridamole, dronedarone,
disulfiram, entacapone, esomeprazole, exenatide,
ezetimibe, fibrates, fluconazole, flutamide, fluvastatin,
glucosamine, grapefruit juice, itraconazole,
ketoconazole, levamisole, levofloxacin, macrolides,
methylphenidate, metronidazole, miconazole,
mirtazepine, nalidixic acid, neomycin, norfloxacin,
NSAIDs, ofloxacin, omeprazole, pantoprazole,
paracetamol, penicillins, proguanil, propafenone,
ritonavir, rosuvastatin, saquinavir, SSRIs, simvastatin,
sulfinpyrazone, sulphonamides, tamoxifen, tegafur,
testosterone, tetracyclines, thyroid hormones,
tigecycline, toremifene, tramadol, trimethoprim,
valproate, venlafaxine, vitamin E and voriconazole.
Anticoagulant effect decreased by: acitretin,
atorvastatin, azathioprine, barbiturates,
carbamazepine, enteral feeds, eslicarbazepine,
enzalutamide, fosphenytoin, ginseng, griseofulvin,
oral contraceptives, phenobarbital, phenytoin,
primidone, rifamycins, St John’s wort (avoid
concomitant use), sucralfate, vitamin K.
Anticoagulant effects enhanced / reduced by: anion
exchange resins, atazanavir, corticosteroids, dietary
changes, disopyramide, efavirenz, fosamprenavir,
nevirapine, ritonavir, telaprevir, tricyclics, trazodone.
Analgesics: increased risk of bleeding with IV
diclofenac and ketorolac - avoid concomitant use.
Anticoagulants: increased risk of haemorrhage with
apixaban, dabigatran, edoxaban and rivaroxaban -
avoid concomitant use.
Antidiabetic agents: enhanced hypoglycaemic
effect with sulphonylureas; also possible changes to
anticoagulant effect.
Camomile: enhanced anticoagulation.
Ciclosporin: there have been a few reports of altered
anticoagulant effect; decreased ciclosporin levels have
been seen rarely.
Cytotoxics: increased risk of bleeding with erlotinib,
imatinib and regorafenib; enhanced effect with
capecitabine, etoposide, fluorouracil, ifosfamide,
gefitinib, gemcitabine, sorafenib and vemurafenib;
reduced effect with mercaptopurine and mitotane.
Melatonin: possibly enhanced INR.
Metabolism
The R- and S-isomers are both metabolised in the liver. The
S-isomer is metabolised more rapidly than the R-isomer,
mainly by the cytochrome P450 isoenzyme CYP2C9, which
shows genetic polymorphism. Other isoenzymes are also
involved in the metabolism of the R-isomer.
The metabolites, which have negligible or no
anticoagulant activity, are excreted in the urine following
reabsorption from the bile.
Dose in renal impairment G
Properties of Warfarin sodium
| Melting point: | approximate 161℃ |
| alpha | ±0° |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | Very soluble in water and in ethanol (96 per cent), soluble in acetone, very slightly soluble in methylene chloride. |
| form | neat |
| color | White to Almost white |
| PH | pH (10g/l, 25℃) : 7.2~8.3 |
| Merck | 14,10038 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 129-06-6(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Sodium warfarin (129-06-6) |
Safety information for Warfarin sodium
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06  Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H300:Acute toxicity,oral H360:Reproductive toxicity H412:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P202:Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood. P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P270:Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P301+P310:IF SWALLOWED: Immediately call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician. |
Computed Descriptors for Warfarin sodium
Warfarin sodium manufacturer
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 Warfarin sodium 129-06-6 98%View Details
Warfarin sodium 129-06-6 98%View Details
129-06-6 -
 Warfarin sodium 129-06-6 98%View Details
Warfarin sodium 129-06-6 98%View Details
129-06-6 -
 129-06-6 Warfarin sodium 98%View Details
129-06-6 Warfarin sodium 98%View Details
129-06-6 -
 Warfarin sodium 98%View Details
Warfarin sodium 98%View Details
129-06-6 -
 129-06-6 98%View Details
129-06-6 98%View Details
129-06-6 -
 Warfarin sodium 129-06-6 99%View Details
Warfarin sodium 129-06-6 99%View Details
129-06-6 -
 Warfarin Sodium (contains Isopropyl Alcohol) CAS 129-06-6View Details
Warfarin Sodium (contains Isopropyl Alcohol) CAS 129-06-6View Details
129-06-6 -
 3-(α-Acetonylbenzyl)-4-hydroxycoumarin sodium salt CAS 129-06-6View Details
3-(α-Acetonylbenzyl)-4-hydroxycoumarin sodium salt CAS 129-06-6View Details
129-06-6
