PENTOSTATIN
Synonym(s):(8R)-3-(2-Deoxy-β-D-erythro-pentofuranosyl)-3,4,7,8-tetrahydroimidazo[4,5-d][1,3]diazepin-8-ol;2ʹ-Deoxycoformycin, (8R)-3-(2-deoxy-β-D-erythro- pentofuranosyl)-3,6,7,8-tetrahydroimidazo[4,5-d][1,3]diazepin-8-ol, Pentostatin, S. antibioticus;2′-dCF;DCF;Deoxycoformycin
- CAS NO.:53910-25-1
- Empirical Formula: C11H16N4O4
- Molecular Weight: 268.27
- MDL number: MFCD00078802
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-19 23:02:33
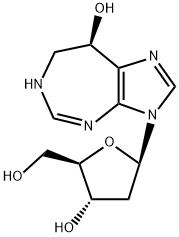
What is PENTOSTATIN?
Absorption
Not absorbed orally, crosses blood brain barrier.
Toxicity
LD50=128 mg/kg (mouse), side effects include lethargy, rash, fatigue, nausea and myelosuppression.
Description
Pentostatin, an adenosine deaminase inhibitor, is an orphan drug introduced for the treatment of hairy cell leukemia. The agent is considered a significant advance over alpha-interferon, the only other drug available for this indication. The majority of patients treated with pentostatin have been reported to remain in remission for at least four years. It is also under investigation for the treatment of other kinds of leukemia and in transplant rejection.
Description
Because of their antitumor activity via inhibition of DNA synthesis, purine nucleoside derivatives resistant to deamination have been developed for the treatment of various leukemias. Pentostatin is a purine nucleoside analog that irreversibly inhibits adenosine deaminase (Ki = 0.9 pM) and thus interrupts DNA synthesis in dividing cells. Pentostatin has been reported to display strong efficacy in the clinical treatment of hairy cell leukemia as well as relapsed chronic lymphocytic leukemia.
Chemical properties
White Solid
Originator
Warner-Lambert (Parke-Davis) (U.S.A.)
The Uses of PENTOSTATIN
Pentostatin is a potent antitumour antibiotic isolated from a Streptomyces species. Pentostatin is a potent inhibitor of adenine deaminase and has been used therapeutically as an antitumour agent.
The Uses of PENTOSTATIN
An adenosine deaminase inhibitor used as an anti-cancer therapeutic drug. Shown to be effective in the treatment of hairy cell leukemia as well as having use in the treatment of other types of cancer such as chronic lymphocytic leukemia.
The Uses of PENTOSTATIN
Pentostatin is a potent antitumor antibiotic isolated from a Streptomyces species. Pentostatin is a potent inhibitor of adenine deaminase and has been used therapeutically as an antitumor agent.
Background
A potent inhibitor of adenosine deaminase. The drug is effective in the treatment of many lymphoproliferative malignancies, particularly hairy-cell leukemia. It is also synergistic with some other antineoplastic agents and has immunosuppressive activity.
Indications
For the treatment of hairy cell leukaemia refractory to alpha interferon.
What are the applications of Application
Pentostatin is an adenosine deaminase inhibitor effective against cancer cell lines
Indications
Pentostatin (Nipent, deoxycoformycin) is a purine isolated
from fermentation cultures of the microbe
Streptomyces antibioticus. Its mechanism of action involves
inhibition of the enzyme adenosine deaminase,
which plays an important role in purine salvage pathways
and DNA synthesis.The resulting accumulation of
deoxyadenosine triphosphate (dATP) is highly toxic to
lymphocytes.
Pentostatin is effective in the therapy of hairy cell
leukemia, producing remissions in 80 to 90% of patients
and complete remissions in more than 50%. The major
toxic effects of the drug include myelosuppression, nausea,
and skin rashes.
brand name
Nipent (SuperGen), Coforin (Katetsuken).
General Description
The drug is available in 10-mg vials for IV use. The drug isused to treat leukemias such as hairy cell leukemia, chroniclymphocytic leukemia, and lymphoblastic leukemia. Themechanism of action involves inhibition of the enzymeadenosine deaminase yielding increased cellular levels ofdeoxyadenosine and deoxyadenosine triphosphate (dATP).The increased levels of dATP are cytotoxic to lymphocytes.Pentostatin is a fermentation product of Streptomyces antibioticus.Resistance appears to involve decreased cellulartransport or increased expression of catabolic enzymes.Acid instability prevents oral administration, and the drug isonly administered by IV. The drug is distributed in totalbody water but does not enter the CNS. The majority of thedosage is excreted unchanged in the urine. Fatal pulmonary toxicity has occurred when pentostatin and fludarabine areused in combination. Toxicities include myelosuppression,immunosuppression, nausea, vomiting, headache, lethargy,and fatigue.
Biological Activity
Irreversible inhibitor of adenosine deaminase (K i = 2.5 pM). Anticancer agent.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Pentostatin/2′-deoxycoformycin is used to treat patients with Waldenstr?m′s macroglobulinemia.
Mechanism of action
Pentostatin is the most potent inhibitor of adenosine deaminase, an important and ubiquitous cellular enzyme. Inhibition of this enzyme leads to the accumulation of dATP, which inhibits ribonucleotide reductase and thus DNA synthesis.
Pharmacokinetics
Pentostatin is an antineoplastic anti-metabolite used in the treatment of several forms of leukemia including acute nonlymphocytic leukemia and hairy cell leukemia. Anti-metabolites masquerade as purine or pyrimidine - which become the building blocks of DNA. They prevent these substances becoming incorporated in to DNA during the "S" phase (of the cell cycle), stopping normal development and division. It is a 6-thiopurine analogue of the naturally occurring purine bases hypoxanthine and guanine. Intracellular activation results in incorporation into DNA as a false purine base. An additional cytotoxic effect is related to its incorporation into RNA. Cytotoxicity is cell cycle phase-specific (S-phase).
Clinical Use
Pentostatin is a ring-expanded purine ribonucleoside that inhibits adenosine deaminase and is used in the treatment of hairy cell leukemia. The elevated levels of deoxyadenosine triphosphate that result from inhibition of this degradative enzyme inhibit the action of ribonucleotide reductase (the enzyme that converts ribose diphosphate to deoxyribose diphosphate), thus halting DNA synthesis within the tumor cell.
Safety Profile
Poison by intravenous route. An experimental teratogen. Human mutation data reported. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of NOx.
Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Antipsychotics: avoid with clozapine (increased risk
of agranulocytosis).
Cytotoxics: increased risk of toxicity with high-dose
cyclophosphamide - avoid; increased pulmonary
toxicity with fludarabine (unacceptably high
incidence of fatalities).
Metabolism
Primarily hepatic, but only small amounts are metabolized.
Metabolism
Only a small amount is metabolised via the liver.
It is primarily excreted unchanged by the kidneys
(30-90% excreted by kidneys within 24 hours).
storage
Store at +4°C
Properties of PENTOSTATIN
| Melting point: | 154-157?C |
| alpha | D25 +76.4° (c = 1 in water); D23 +73.0° (c = 1, pH 7 buffer) |
| Boiling point: | 411.43°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 1.2576 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.6081 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | -20°C |
| solubility | H2O: soluble10mg/mL, clear |
| form | White solid |
| pka | 5.2(at 25℃) |
| color | white to beige |
| optical activity | [α]/D +70 to +80°, c = 1 in H2O |
Safety information for PENTOSTATIN
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H301:Acute toxicity,oral |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P301+P310:IF SWALLOWED: Immediately call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician. |
Computed Descriptors for PENTOSTATIN
PENTOSTATIN manufacturer
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 53910-25-1 Pentostatin 98%View Details
53910-25-1 Pentostatin 98%View Details
53910-25-1 -
 Adenosine Deaminase Inhibitor, DCF CAS 53910-25-1View Details
Adenosine Deaminase Inhibitor, DCF CAS 53910-25-1View Details
53910-25-1 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1