Paliperidone
Synonym(s):3-[2-[4-(6-Fluoro-1,2-benzisoxazol-3-yl)-1-piperidinyl]ethyl]-6,7,8,9-tetrahydro-9-hydroxy-2-methyl-4H-pyrido[1,2-a]pyrimidin-4-one;9-Hydroxyrisperidone
- CAS NO.:144598-75-4
- Empirical Formula: C23H27FN4O3
- Molecular Weight: 426.48
- MDL number: MFCD00871802
- EINECS: 620-493-1
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-11 08:41:34
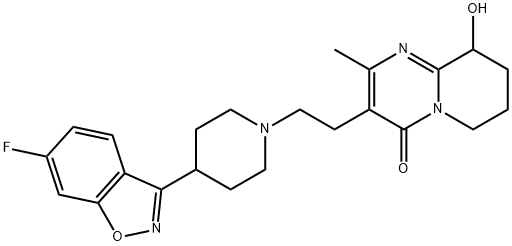
What is Paliperidone?
Absorption
The absolute oral bioavailability of paliperidone following paliperidone administration is 28%.
Toxicity
The possibility of obtundation, seizures, or dystonic reaction of the head and neck following overdose may create a risk of aspiration with induced emesis.
Description
Paliperidone, the
C-9 hydroxylated active metabolite of the antipsychotic agent risperidone, is the
newest atypical antipsychotic to join the market following the introductions
of olanzapine (ZyprexaTM), risperidone (RisperdalTM), quetiapine(SeroquelTM),
and ziprasidone (GeodonTM).
Compared to its parent, paliperidone has
improved PK properties and a reduced potential for drug interactions. In terms
of receptor affinity, the two drugs are equipotent.
Description
Paliperidone, or 9-hydroxyrisperidone, is an antipsychotic drug sold under the trade name Invega, an extended-release formulation. An “atypical”, or second-generation, antipsychotic, it is an active metabolite of the older drug risperidone. It was approved by the FDA in 2006 for treating schizophrenia and bipolar mania. An improved synthesis of paliperidone was described in the?May 2, 2011 edition of Patent Watch.
Chemical properties
Off White to Light Orange Coloured Solid
Originator
Johnson & Johnson (US)
The Uses of Paliperidone
Paliperidone(Invega) is an atypical antipsychotic. Chemically, paliperidone is the primary active metabolite of the older atypical antipsychotic risperidone. It is indicated for the acute and maintenance treatment of schizophrenia
The Uses of Paliperidone
A metabolite of Risperidone, a combined serotonin (5-HT2) and dopamine (D2) receptor antagonist
Background
Paliperidone is the primary active metabolite of risperidone. The mechanism of action is unknown but it is likely to act via a similar pathway to risperidone. It has been proposed that the drug's therapeutic activity in schizophrenia is mediated through a combination of central dopamine Type 2 (D2) and serotonin Type 2 (5HT2A) receptor antagonism. Paliperidone is also active as an antagonist at alpha 1 and alpha 2 adrenergic receptors and H1 histaminergic receptors, which may explain some of the other effects of the drug. Paliperidone was approved by the FDA for treatment of schizophrenia on December 20, 2006. It is available as an extended-release tablet, a once-monthly intramuscular injection, an every-three-month intramuscular injection, and a twice-yearly gluteal injection.
Indications
As an oral extended-release tablet and a once-monthly extended-release suspension for intramuscular injection, paliperidone is indicated for the treatment of adults and adolescents with schizophrenia and in the treatment of schizoaffective disorder in combination with antidepressants or mood stabilizers. Paliperidone is also available in both an every-three-month and twice-yearly extended-release suspension for intramuscular injection for the treatment of schizophrenia.
What are the applications of Application
Paliperidone is a serotonin (5-HT2) receptor antagonist and D2DR inhibitor
Definition
ChEBI: 3-{2-[4-(6-fluoro-1,2-benzoxazol-3-yl)piperidin-1-yl]ethyl}-9-hydroxy-2-methyl-6,7,8,9-tetrahydropyrido[1,2-a]pyrimidin-4-one is a member of the class of pyridopyrimidines that is 9-hydroxy-2-methyl-6,7,8,9-tetrahydropyrido[1,2-a]pyrimidin-4-one carrying an additional 2-[4-(6-fluoro-1,2-benzoxazol-3-yl)piperidin-1-yl]ethyl group at position 2. It is a member of 1,2-benzoxazoles, a heteroarylpiperidine, an organofluorine compound, a pyridopyrimidine and a secondary alcohol.
brand name
Invega
General Description
Paliperidone, (±)-3-[2-[4-(6-fluoro-1,2-benzisoxazol-3-yl)-1-piperidinyl]ethyl]-6,7,8,9-tetrahydro-9-hydroxy-2-methyl-4H-pyrido[1,2-a]pyrimidin-4-one(Invega), is essentially insoluble in water and is available asextended-release tablets. Paliperidone is delivered at a constantrate using an osmotic drug release device (OsmoticRelease Oral Systems [OROS]). The absolute bioavailabilityof paliperidone is 28%, and studies in healthy subjects on ahigh-fat, high-calorie meal showed an increase in AUC.Paliperidone is 74% bound to plasma proteins. After a single,1-mg dose of C-paliperidone, 59% of the dose was excretedin the urine as unchanged drug, and 32% of the dose was recoveredas metabolites. Most of the drug (80%) is excreted bythe kidneys. Paliperidone is metabolized by dealkylation, hydroxylation,dehydrogenation, and scission of the benzoxazolering. None of these metabolic pathways account for morethan 10% of the dose. The terminal elimination half-life ofpaliperidone is 23 hours.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Paliperidone is an atypical antipsychotic; active metabolite of risperidone.
Pharmacokinetics
Paliperidone is an atypical antipsychotic developed by Janssen Pharmaceutica. Chemically, paliperidone is primary active metabolite of the older antipsychotic risperidone (paliperidone is 9-hydroxyrisperidone). The mechanism of action is unknown but it is likely to act via a similar pathway to risperidone.
Side Effects
The most common adverse events included tachycardia, QTc prolongation, headache, anxiety, dizziness, tremors, and insomnia along with the dose-related events of somnolence, orthostatic hypotension, salivary hypersecretion, and extrapyrimidal disorder. Weight gain was also observed in 6–9% of patients which may be attributable to paliperidone’s lower affinity for H1-histaminergic and a1- and a2-adrenergic receptors. Patients with renal impairment require dose adjustments since elimination of paliperidone is altered. Paliperidone is contraindicated in patients with a hypersensitivity to risperidone. Concomitant use of class III antiarrhythmic agents should be avoided since this may result in additive QT interval prolongation. Also, loss of levodopa efficacy is expected with this D2 antagonist.
Synthesis
The synthesis of paliperidone involves the reaction of 2-acetyl-g-butyrolactone with 2-amino-3-benzyloxypyridine in the presence of phosphoryl chloride. The benzyl protecting group of the intermediate 9-benzyloxy- 3-(2-chloroethyl)-2-methylpyrido[1,2-a]pyrimidin-4-one is then removed by hydrogenolysis over Pd/C followed by the nucleophilic displacement of the chlorine with 6-fluoro-3-(4-piperidinyl)-1,2-benzisoxazole to provide racemic paliperidone. While paliperidone can be resolved, both enantiomers are equipotent and interconvert in vivo obviating the need for separation.
Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Anaesthetics: enhanced hypotensive effect.
Analgesics: increased risk of convulsions with
tramadol; enhanced hypotensive and sedative
effects with opioids; increased risk of ventricular
arrhythmias with methadone.
Anti-arrhythmics: increased risk of ventricular
arrhythmias when given with anti-arrhythmics that
prolong the QT interval.
Antidepressants: increases concentration of tricyclics
(possibly increased risk of ventricular arrhythmias).
Antiepileptics: antagonise anticonvulsant effect
(convulsive threshold lowered); concentration
reduced by carbamazepine.
Antimalarials: avoidance of antipsychotics advised by
manufacturer of artemether/lumefantrine.
Antipsychotics: possible increased risk of ventricular
arrhythmias with risperidone.
Antivirals: concentration possibly increased by ritonavir.
Atomoxetine: increased risk of ventricular
arrhythmias with atomoxetine.
Cytotoxics: increased risk of ventricular arrhythmias
with arsenic trioxide.
Metabolism
Although in vitro studies suggested a role for CYP2D6 and CYP3A4 in the metabolism of paliperidone, in vivo results indicate that these isozymes play a limited role in the overall elimination of paliperidone. Four primary metabolic pathways have been identified in vivo, none of which could be shown to account for more than 10% of the dose: dealkylation, hydroxylation, dehydrogenation, and benzisoxazole scission. Paliperidone does not undergo extensive metabolism and a significant portion of its metabolism occurs in the kidneys.
Metabolism
Paliperidone is the active metabolite of risperidone.
Four metabolic pathways have been identified in vivo,
none of which accounted for more than 6.5% of the
dose: dealkylation, hydroxylation, dehydrogenation,
and benzisoxazole scission.
Following administration
of [14C]-paliperidone, 59% of the dose was excreted
unchanged into urine, indicating that paliperidone is not
extensively metabolised in the liver. Approximately 80% of
the administered radioactivity was recovered in urine and
11% in the faeces.
Storage
+4°C
References
1) Beijsterveldt?et al.?(1994),?Regional brain distribution of risperidone and its active metabolite 9-hydroxy-risperidone in the rat; Psychopharmacology,?114?53 DOI:10.1007/BF02245444
2) Leysen?et al. (1994),?Risperidone: a novel antipsychotic with balanced serotonin-dopamine antagonism, receptor occupancy profile, and pharmacologic activity; J. Clin. Psychiatry,?55?suppl: 5 PMID: 7520908
3) Schotte?et al.?(1996),?Risperidone compared with new and reference antipsychotic drugs: in vitro and in vivo receptor binding; Psychopharmacology (Berl.),?124?57 DOI:10.1007/BF02245606
Properties of Paliperidone
| Melting point: | 158-160°C |
| Boiling point: | 612.3±65.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.45±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| Flash point: | 9℃ |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | DMSO: soluble2mg/mL, clear (warmed) |
| pka | 13.00±0.60(Predicted) |
| form | powder |
| color | white to brown |
| Stability: | Stable for 2 years from date of purchase as supplied. Solutions in DMSO may be stored at -20° for up to 2 months. |
| InChI | InChI=1S/C23H27FN4O3/c1-14-17(23(30)28-9-2-3-19(29)22(28)25-14)8-12-27-10-6-15(7-11-27)21-18-5-4-16(24)13-20(18)31-26-21/h4-5,13,15,19,29H,2-3,6-12H2,1H3 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 144598-75-4(CAS DataBase Reference) |
Safety information for Paliperidone
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H301:Acute toxicity,oral |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P301+P310:IF SWALLOWED: Immediately call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician. |
Computed Descriptors for Paliperidone
| InChIKey | PMXMIIMHBWHSKN-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | C12C(O)CCCN1C(=O)C(CCN1CCC(C3C4=C(ON=3)C=C(F)C=C4)CC1)=C(C)N=2 |
Paliperidone manufacturer
New Products
Boc-N-Me-Val-OH tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin Gabapentin EP Impurity B Ethyl N-(2- cyanoacetyl)carbamate Magnessium Ascorbate 1-Chloro-4-Methyl-2-Nitrobenzene 1,3-Diethyl-1,3-Diphenylurea 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile Benzethonium Chloride Trenbolone Enanthate Prednisolone acetate Cisplatin Chlorodehydromethyl testosterone Ketoconazole 1,3-Di Iodo Benzene Methyl 2-oxo-2,3-dihydrobenzo[d]oxazole-7-carboxylate 3-Hydroxy-4-nitrobromobenzene 4-(2-Aminoethyl)-7-hydroxy-2H-chromoen-2-one 2-Ethyl-1,4-diaminobenzene 2-Ethylhexyl 4-aminobenzoateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

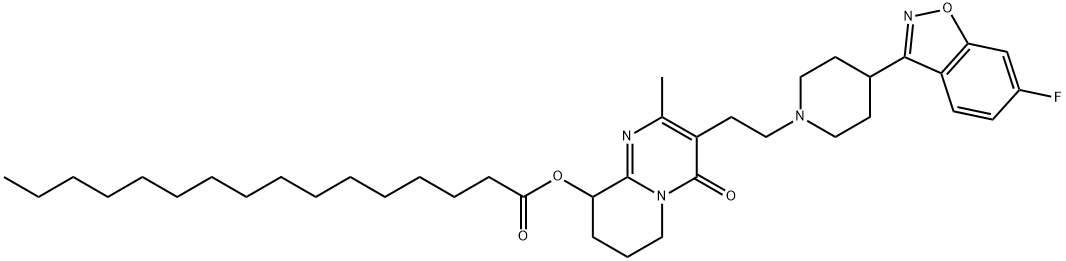

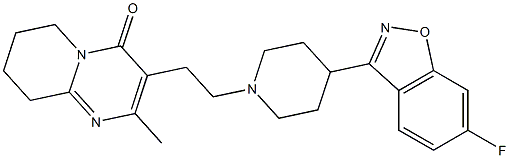
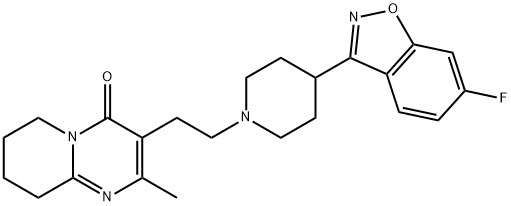
You may like
-
 144598-75-4 Paliperidone 98%View Details
144598-75-4 Paliperidone 98%View Details
144598-75-4 -
 Paliperidone 98%View Details
Paliperidone 98%View Details -
 144598-75-4 98%View Details
144598-75-4 98%View Details
144598-75-4 -
 Paliperidone 144598-75-4 99%View Details
Paliperidone 144598-75-4 99%View Details
144598-75-4 -
 Paliperidone CAS 144598-75-4View Details
Paliperidone CAS 144598-75-4View Details
144598-75-4 -
 Paliperidone 98% (HPLC) CAS 144598-75-4View Details
Paliperidone 98% (HPLC) CAS 144598-75-4View Details
144598-75-4 -
 Paliperidone 95% CAS 144598-75-4View Details
Paliperidone 95% CAS 144598-75-4View Details
144598-75-4 -
 Paliperidone CAS 144598-75-4View Details
Paliperidone CAS 144598-75-4View Details
144598-75-4
