Risperidone
Synonym(s):R 64,766;Risperidone
- CAS NO.:106266-06-2
- Empirical Formula: C23H27FN4O2
- Molecular Weight: 410.48
- MDL number: MFCD00274576
- EINECS: 600-733-1
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-23 21:30:31
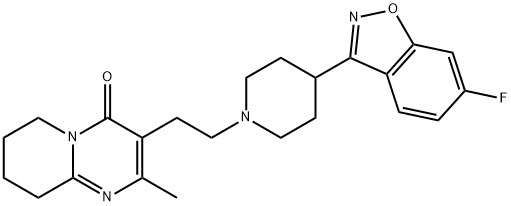
What is Risperidone?
Absorption
Well absorbed. The absolute oral bioavailability of risperidone is 70% (CV=25%). The relative oral bioavailability of risperidone from a tablet is 94% (CV=10%) when compared to a solution.
Toxicity
Symptoms of overdose include lethargy, dystonia/spasm, tachycardia, bradycardia, and seizures. LD50=57.7 mg/kg (rat, oral) and 34 mg/kg (rat, intravenous).
Description
Risperidone is a novel antipsychotic introduced for the treatment of acute and chronic schizophrenia. It has a balanced serotonin 5-HT2 and dopamine D2 receptor antagonist activity. While the anti-D2 activity may relate to the antipsychotic potency of neuroleptic agents, an antidepressive efficacy of substances with anti-5-HT2 activity has been suggested. Risperidone, therefore, has therapeutic action on both positive and negative symptoms of schizophrenia and produces significantly fewer side effects especially extrapyramidal symptoms compared with commonly used pure D2 antagonist antipsychotics. It also has potential for management of alcohol withdrawal and cocaine addiction.
Chemical properties
Crystalline Solid
Originator
Janssen (U.S.A.)
The Uses of Risperidone
Risperidone has been used:
- to study its effects on bone formation and differentiation
- to investigate the relationship between risperidone (RIS) dosages and RIS plasma levels in autism spectrum disorder (ASD) pediatric patients
- to reverse induced schizophrenia-like behavior in mice
The Uses of Risperidone
A combined serotonin (5-HT2) and dopamine (D2) receptor antagonist
The Uses of Risperidone
neuroprotectant, inhibitory neurotransmitter, GABA agonist
The Uses of Risperidone
For the treatment of schizophrenia in adults and in adolescents, ages 13 to 17, and for the short-term treatment of manic or mixed episodes of bipolar I disorder in children and adolescents ages 10 to 17. May also be used to manage symptoms of inappropria
Indications
Risperidone is indicated for the treatment of schizophrenia and irritability associated with autistic disorder. It is also indicated as monotherapy, or adjunctly with lithium or valproic acid, for the treatment of acute mania or mixed episodes associated with bipolar I disorder.
Risperidone is additionally indicated in Canada for the short-term symptomatic management of aggression or psychotic symptoms in patients with severe dementia of the Alzheimer type unresponsive to nonpharmacological approaches.
Risperidone is also used off-label for a number of conditions including as an adjunct to antidepressants in treatment-resistant depression.
Background
Risperidone is a second-generation antipsychotic (SGA) medication used in the treatment of a number of mood and mental health conditions including schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. It is one of the most widely used SGAs. Paliperidone, another commonly used SGA, is the primary active metabolite of risperidone (i.e. 9-hydroxyrisperidone).
Schizophrenia and various mood disorders are thought to be caused by an excess of dopaminergic D2 and serotonergic 5-HT2A activity, resulting in overactivity of central mesolimbic pathways and mesocortical pathways, respectively. Risperidone is thought to reduce this overactivity through inhibition of dopaminergic D2 receptors and serotonergic 5-HT2A receptors in the brain.
Risperidone binds with a very high affinity to 5-HT2A receptors, approximately 10-20 fold greater than the drug's binding affinity to D2 receptors, and carries lesser activity at several off-targets which may responsible for some of its undesirable effects.
What are the applications of Application
Risperidone is an inhibitor of SR-2A and D2DR
Definition
ChEBI: A member of the class of pyridopyrimidines that is 2-methyl-6,7,8,9-tetrahydropyrido[1,2-a]pyrimidin-4-one carrying an additional 2-[4-(6-fluoro-1,2-benzoxazol-3-yl)piperidin-1-yl]ethyl group at position 2.
brand name
Risperdal (Janssen).
General Description
Risperidone (Risperdal, a benzisoxazole)has the structural features of a hybrid molecule between abutyrophenone antipsychotic and a trazodone-like antidepressant.Its superior side effects profile (compared withhaloperidol) at dosage of 6 mg/d or less and the lower riskof tardive dyskinesia have contributed to its very widespreaduse. It benefited refractory psychotic patients, withparkinsonism controlled at one tenth the dose of antiparkinsoniandrugs used with haloperidol.Coexisting anxietyand depressive syndromes were also lessened. It is reportedto decrease the negative (e.g., withdrawal, apathy) as well asthe positive (e.g., delusions, hallucinations) symptoms ofschizophrenia. This is reportedly a consequence of the compound’scombination 5-HT2–D2 receptor antagonistic properties.Overall, the reasons for the decreased EPS and effectiveness against negative symptom are still under investigation.It is an important atypical antipsychotic.Risperidone is metabolized in the liver by CYP2D6 to anactive metabolite, 9-hydroxyrisperidone. Because thismetabolite and risperidone are nearly equipotent, the clinicalefficacy of the drug reflects both compounds.
General Description
Risperidone, 3-[2-[4-(6-fluoro-1,2-benzisoxazol-3-yl)-1-piperidinyl]ethyl-6,7,8,9-tetrahydro-2-methyl-4H-pyrido[1,2]pyrimidin-4-one (Risperdal), is awhite to slightly beige powder that is essentially insoluble inwater. Risperidone is also available as a 1-mg/mL oral solutionand as orally disintegrating tablets (Risperdal M-Tab).Risperidone is well absorbed, and peak levels occur about 1hour after administration. The absorption of risperidone is notaffected by food. Risperidone is about 90% bound to albuminand 1-acid glycoprotein, whereas its metabolite 9-hydroxyrisperidoneis bound about 77%. Risperidone is primarilymetabolized in humans to the active metabolite 9-hydroxyrisperidone..The major side effects associated with risperidonetherapy are orthostatic hypotension, dose-related hyperprolactinemia,mild weight gain, EPS, and insomnia.Athigher doses (6 mg/day), risperidone is the atypical antipsychoticthat most closely resembles conventional agents. APET study in a group of individuals with schizophreniashowed that D2 receptor occupancy was dose dependent. Ifthe dose was increased such that D2 receptor occupancy was79% to 85%, the majority of patients developed EPS.Risperidone is associated with increased mortality in elderlypatients with dementia-related psychosis and is not recommendedfor these individuals.23 Risperidone binds with highaffinity at 5-HT2A, 5-HT7, D2, 1, 2, and H1 receptors. Theantipsychotic action of risperidone has been proposed tobe the result of D2 and 5-HT2A antagonism.
Biological Activity
Atypical antipsychotic agent that displays 5-HT 2A receptor antagonism. Also displays high affinity at D 2 receptors (K i values are 0.4 and 3.13 nM for 5-HT 2A and D 2 receptors respectively).
Biochem/physiol Actions
Risperidone is an antipsychotic; serotonin-dopamine antagonist.
Pharmacokinetics
The primary action of risperidone is to decrease dopaminergic and serotonergic pathway activity in the brain, therefore decreasing symptoms of schizophrenia and mood disorders.
Risperidone has a high binding affinity for serotonergic 5-HT2A receptors when compared to dopaminergic D2 receptors in the brain. Risperidone binds to D2 receptors with a lower affinity than first-generation antipsychotic drugs, which bind with very high affinity. A reduction in extrapyramidal symptoms with risperidone, when compared to its predecessors, is likely a result of its moderate affinity for dopaminergic D2 receptors.
Clinical Use
Schizophrenia
Psychoses
Mania
Persistent aggression in Alzheimer’s dementia
Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Anaesthetics: enhanced hypotensive effect.
Analgesics: increased risk of convulsions with
tramadol; enhanced hypotensive and sedative
effects with opioids; increased risk of ventricular
arrhythmias with methadone - avoid.
Antidepressants: concentration increased by
fluoxetine and possibly paroxetine; concentration of
tricyclics possibly increased.
Antiepileptics: antagonism, convulsive threshold
may be lowered; metabolism accelerated by
carbamazepine.
Antimalarials: avoid with artemether with
lumefantrine; possible increased risk of ventricular
arrhythmias with mefloquine and quinine.
Antipsychotics: possible increased risk of ventricular
arrhythmias with other antipsychotics that prolong
the QT interval; avoid concomitant use of depot
formulations with clozapine (cannot be withdrawn
quickly if neutropenia occurs).
Antivirals: ritonavir may increase concentration of
risperidone.
Anxiolytics and hypnotics: enhanced sedative effects.
Atomoxetine: increased risk of ventricular
arrhythmias.
Beta blockers: possible increased risk of ventricular
arrhythmias with sotalol.
Cytotoxics: increased risk of ventricular arrhythmias
with arsenic trioxide.
Lithium: increased risk of extra-pyramidal side
effects and possible neurotoxicity.
Metabolism
Extensively metabolized by hepatic cytochrome P450 2D6 isozyme to 9-hydroxyrisperidone (i.e. paliperidone), which has approximately the same receptor binding affinity as risperidone. Hydroxylation is dependent on debrisoquine 4-hydroxylase and metabolism is sensitive to genetic polymorphisms in debrisoquine 4-hydroxylase. Risperidone also undergoes N-dealkylation to a lesser extent.
Metabolism
Risperidone is metabolised in the liver by CYP 2D6
to its main active metabolite, 9-hydroxy-risperidone
(paliperidone), which has a similar pharmacological
activity as risperidone. This hydroxylation is subject to
genetic polymorphism. Oxidative N-dealkylation is a
minor metabolic pathway.
Excretion is mainly in the urine and, to a lesser extent, in
the faeces.
Storage
+4°C
Properties of Risperidone
| Melting point: | 170°C |
| Boiling point: | 572.4±60.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.38±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| Flash point: | 9℃ |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | DMSO: ≥5mg/mL |
| form | powder |
| pka | pKa 8.3 (Uncertain) |
| color | white to off-white |
| Water Solubility | 44.74mg/L(25 ºC) |
| Merck | 14,8233 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 106266-06-2(CAS DataBase Reference) |
Safety information for Risperidone
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H301:Acute toxicity,oral |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P301+P310:IF SWALLOWED: Immediately call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician. |
Computed Descriptors for Risperidone
Risperidone manufacturer
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 Risperidone 99%View Details
Risperidone 99%View Details -
 Risperidone 99%View Details
Risperidone 99%View Details -
 Risperidone 98%View Details
Risperidone 98%View Details -
 Risperidone 99% (HPLC) CAS 106266-06-2View Details
Risperidone 99% (HPLC) CAS 106266-06-2View Details
106266-06-2 -
 Risperidone 95.00% CAS 106266-06-2View Details
Risperidone 95.00% CAS 106266-06-2View Details
106266-06-2 -
 Risperidone Powder API MANUFACTURER INDIA, 50kgView Details
Risperidone Powder API MANUFACTURER INDIA, 50kgView Details
106266-06-2 -
 Risperidone API IP/BP/USP, 5kgView Details
Risperidone API IP/BP/USP, 5kgView Details
106266-06-2 -
 Risperidone Powder for LaboratoryView Details
Risperidone Powder for LaboratoryView Details
106266-06-2
