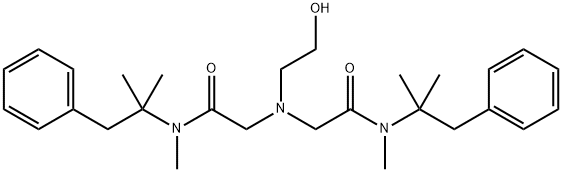
Oxethazaine
Synonym(s):2-Hydroxyethyliminobis(N-[α,α-dimethylphenethyl]-N-methylacetamide);Oxetacaine
- CAS NO.:126-27-2
- Empirical Formula: C28H41N3O3
- Molecular Weight: 467.64
- MDL number: MFCD00079202
- EINECS: 204-780-5
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-19 23:02:33
What is Oxethazaine?
Absorption
A peak plasma concentration of oxetacaine of approximately 20 ng/ml is attained about one hour after oral administration. LEss than 1/3 of the administered dose is absorbed as it undergoes extensive metabolism.
Toxicity
When orally administered, oxetacaine presents a good tolerance. However, following intravenous injection, oxetacaine toxicity is high and it is presented as a depression in myocardial contractility and impaired conduction.
Chemical properties
White Solid
Originator
Oxaine,Wyeth,US,1960
The Uses of Oxethazaine
A potent local anesthetic that is active even in acidic conditions. It is used (usually in combination with an antacid) for the relief of pain associated with peptic ulcer disease or esophagitis.
The Uses of Oxethazaine
antiviral, RT inhibitor
What are the applications of Application
Oxethazaine is used in combination with antacids for ulcer pain
Background
Oxetacaine, also called oxethazaince, is a potent surface analgesic with the molecular formula N, N-bis-(N-methyl-N-phenyl-t-butyl-acetamide)-beta-hydroxyethylamine that conserves its unionized form at low pH levels. Its actions have shown to relieve dysphagia, relieve pain due to reflux, chronic gastritis, and duodenal ulcer. Oxetacaine is approved by Health Canada since 1995 for its use as an antacid combination in over-the-counter preparations. It is also in the list of approved derivatives of herbal products by the EMA.
Indications
Oxetacaine is available as an over-the-counter antacid and it is used to alleviate pain associated with gastritis, peptic ulcer disease, heartburn, esophagitis, hiatus hernia, and anorexia.
Definition
ChEBI: Oxethazaine is an amino acid amide.
Manufacturing Process
Chlor-N-methyl-N-ω-phenyl-tert-butyl acetamide (23.95 g) (0.1 mol) is added to n-butanol (150.0 cc) containing anhydrous potassium carbonate (50.0 g). To the stirred refluxing solution is added dropwise freshly distilled ethanolamine (3.1 g) (0.05 mol). Stirring and refluxing is maintained for twenty hours. Upon cooling the solution is filtered; the residue is washed with n-butanol. The combined filtrates are washed with aqueous sodium carbonate solution then water and finally dried over anhydrous magnesium sulfate. The solvent is distilled under vacuum leaving a dry solid residue. The residue is dissolved in dry benzene to which is added n-hexane to crystallize the product melting at 104°C to 104.5°C. Yield 71-73%. Analysis-Carbon: calc. 71.9%; found 71.93%; hydrogen: calc. 8.8%; found 8.9%; nitrogen: calc. 9.0%; found 9.0%.
To make the hydrochloride salt, the bisacetamide or, by another name, 1,11diphenyl-2,2,3,9,10,10-hexamethyl-4,8-diketo-6-(β-hydroxyethyl)-3,6,9triazaundecane is dissolved in n-butanol. The solution is chilled and then dry hydrogen chloride gas is passed into the solution causing an oil to separate. To the heavy oil ether is added and then stirred causing crystallization to occur. MP 146°C to 147°C. Analysis for nitrogen: calc. 83%. found 8.2%.
To make the acetate salt, the bisacetamide (4.7 g) (0.01 mol) is dissolved in ethyl acetate to which is added glacial acetic acid (0.6 g) (0.01 mol). Ether is added to precipitate the acetate as a gum which is washed with hexane, and finally added to dry ether. Allow to stand for crystallization. MP 141°C. Analysis for nitrogen: calc. 8.0%; found 8.2%.
Other salts are: sulfate, MP 56°C; acid oxalate, MP 127°C; tartrate, MP 45°C; picrate, MP 151°C to 152°C.
Therapeutic Function
Local anesthetic
General Description
White powder.
Air & Water Reactions
Insoluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
A hydroxylated amide. Organic amides/imides react with azo and diazo compounds to generate toxic gases. Flammable gases are formed by the reaction of organic amides/imides with strong reducing agents. Amides are very weak bases (weaker than water). Imides are less basic yet and in fact react with strong bases to form salts. That is, they can react as acids. Mixing amides with dehydrating agents such as P2O5 or SOCl2 generates the corresponding nitrile. The combustion of these compounds generates mixed oxides of nitrogen (NOx).
Fire Hazard
Flash point data are not available for Oxethazaine, but Oxethazaine is probably combustible.
Pharmacokinetics
Oxetacaine improves common gastrointestinal symptoms. Oxetacaine is part of the anesthetic antacids which increase the gastric pH while providing relief from pain for a longer period of duration at a lower dosage. This property has been reported to relieve the symptoms of hyperacidity. Oxetacaine is reported to produce a reversible loss of sensation and to provide a prompt and prolonged relief of pain. In vitro, oxetacaine was showed to produce an antispasmodic action on the smooth muscle and block the action of serotonin.
The local efficacy of oxetacaine has been proven to be 2000 times more potent than lignocaine and 500 times more potent than cocaine. Its anesthetic action produces the loss of sensation which can be explained by its inhibitory activity against the nerve impulses and de decrease in permeability of the cell membrane.
Metabolism
Oxetacaine is rapidly and extensively metabolized hepatically. After metabolism, there is a formation of primary metabolites such as beta-hydroxy-mephentermine and beta-hydroxy-phentermine. The major metabolites are found in the plasma in insignificant amounts.
Properties of Oxethazaine
| Melting point: | 104-105°C |
| Boiling point: | 570.1°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 1.0974 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.7800 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | Refrigerator |
| solubility | Practically insoluble in water; freely soluble in methanol; soluble in ethyl acetate. |
| form | neat |
| pka | 14.62±0.10(Predicted) |
| form | Solid |
| color | White to Off-White |
| Water Solubility | <0.1 g/100 mL at 23 ºC |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 126-27-2(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Oxethazaine (126-27-2) |
Safety information for Oxethazaine
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral |
Computed Descriptors for Oxethazaine
Oxethazaine manufacturer
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 126-27-2 Oxethazaine 98%View Details
126-27-2 Oxethazaine 98%View Details
126-27-2 -
 126-27-2 99%View Details
126-27-2 99%View Details
126-27-2 -
 Oxethazaine 98%View Details
Oxethazaine 98%View Details
126-27-2 -
 Oxethazaine CAS 126-27-2View Details
Oxethazaine CAS 126-27-2View Details
126-27-2 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1