Benzocaine
Synonym(s):4-Aminobenzoic acid ethyl ester;Benzocainum;Ethyl 4-aminobenzoate
- CAS NO.:94-09-7
- Empirical Formula: C9H11NO2
- Molecular Weight: 165.19
- MDL number: MFCD00007892
- EINECS: 202-303-5
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-11 08:41:34
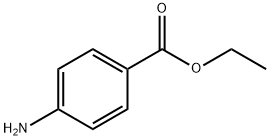
What is Benzocaine?
Toxicity
Patients experiencing an overdose may present with local anesthetic systemic toxicity syndrome, decreased cardiovascular function, decreased central nervous system function, cardiac arrest, bradycardia, hypotension, cardiac arrhythmias, syncope, and seizures. Patients should be treated with symptomatic and supportive measures which include airway maintenance, controlling seizures, and hemodynamic stabilization.
Description
Benzocaine (ethyl p-aminobenzoate) is used topically by itself or in combination with menthol or
phenol in nonprescription dosage forms such as gels, creams, ointments, lotions, aerosols, and
lozenges to relieve pain or irritation caused by such conditions as sunburn, insect bites,
toothache, teething, cold sores or canker sores in or around the mouth, and fever blisters.
Benzocaine is a lipophilic local anesthetic agent with a short duration of action.
Like most amino ester-type local anesthetics, it is easily hydrolyzed by plasma cholinesterase.
Because of its low pKa, however, it is un-ionized under most physiological conditions and, therefore, can only bind
to the lipid side of the local anesthetic receptor. It also can easily cross membranes
into systemic circulation to cause systemic toxicities. Furthermore, being a PABA derivative, it
has similar allergenic properties to procaine and is contraindicated with sulfonamide antibacterial
agents.
Description
Benzocaine, a common ingredient in sunburn remedies and first aid creams, is a topical anesthetic—it numbs the nerve endings near the surface of the skin where it is applied. This ethyl ester of?p-aminobenzoic acid (PABA, a common sunscreen ingredient) can react with compounds in sunscreens and hair dyes or produce an allergic reaction.
Chemical properties
Benzocaine is a white odourless needle-like crystal, slightly soluble in water and easily soluble in organic solvents. For example: ethanol, chloroform, ether, soluble in almond oil, olive oil.
The Uses of Benzocaine
Benzocaine is used as an anesthetic (Local and topical) that in products such as burn and sunburn remedies, hemorrhoidal creams, suppositories, creams for treatment of poison ivy, oral and gingival products, sore-throat sprays/lozenges, astringents, appetite suppressants, callus and wart remedies, athlete's-foot remedies, toothache- and denture-irritation products.
Background
Benzocaine is an ester local anesthetic that acts by preventing transmission of impulses along nerve fibers and at nerve endings. It is commonly used for local anesthesia in many over the counter products. Benzocaine was first used for local anesthesia in dentistry.
Indications
Benzocaine is indicated for local anesthesia in dentistry, minor trauma, and as preparation for infiltrative anesthesia. Benzocaine products are indicated for topical anesthesia in a wide variety of conditions including skin irritation, oral pain, and hemorrhoids.
What are the applications of Application
Benzocaine is a surface anesthetic
Definition
ChEBI: Benzocaine is a benzoate ester having 4-aminobenzoic acid as the acid component and ethanol as the alcohol component. A surface anaesthetic, it is used to suppress the gag reflex, and as a lubricant and topical anaesthetic on the larynx, mouth, nasal cavity, respiratory tract, oesophagus, rectum, urinary tract, and vagina. It has a role as a topical anaesthetic, an antipruritic drug, an allergen and a sensitiser. It is a benzoate ester and a substituted aniline.
brand name
Americaine (Fisons); Baby Anbesol (Whitehall-Robins).
Biological Functions
Benzocaine is a PABA derivative used primarily for topical application to skin and mucous membranes. Its low aqueous solubility allows it to stay at the site of application for long periods. Its minimal rate of absorption after topical administration is associated with a low incidence of systemic toxicity. Benzocaine is contraindicated in patients with known sensitivity to ester-linked anesthetics or PABA-containing compounds.
Synthesis Reference(s)
Journal of the American Chemical Society, 71, p. 4154, 1949 DOI: 10.1021/ja01180a513
Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin, 29, p. 1443, 1981 DOI: 10.1248/cpb.29.1443
General Description
Benzocaine is a unique local anesthetic because it does notcontain a tertiary amine. The pKa of the aromatic amine is 3.5ensuring that benzocaine is uncharged at physiological pH.Because it is uncharged, it is not water soluble but is ideal fortopical applications. The onset of action is within 30 secondsand the duration of drug action is 10 to 15 minutes.
Mechanism of action
Benzocaine inhibits sodium channels by reversibly binding to and inhibiting them on neuronal cell membranes. It enters the cell using a non-ionised form and crosses the cell membrane bilayer to an ionised form. The ionised form binds to the alpha subunit and inhibits voltage-gated sodium channels. This binding prevents cellular depolarisation, slows down signal transduction and reduces the ability to generate action potentials. Local anaesthetics such as benzocaine bind more readily to sodium channels in the open configuration. Benzocaine has a relatively low pKa value (2.6) compared to other local anaesthetics. The pKa values of local anaesthetics are useful in determining the onset of action. Benzocaine has a rapid rate of action and is pH independent.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Benzocaine is the ethyl ester of p-aminobenzoic acid (PABA). Benzocaine acts to inhibit the voltage-dependent sodium channels (VDSCs) on the nerve membrane, stopping the propagation of the action potential.
Pharmacokinetics
Benzocaine is indicated for use as a topical anesthetic. It has a duration of action of approximately 10 minutes and a wide therapeutic window. Patients should be counselled regarding the risks of methemoglobinemia.
Clinical Use
Benzocaine is used for endoscopy, bronchoscopy, and topicalanesthesia. Benzocaine is available as a 20% solution topicalspray, in a 1% gel for mucous membrane application, and a14% glycerin suspension for topical use in the outer ear.Toxicity to benzocaine can occur when the topical doseexceeds 200 to 300 mg resulting in methemoglobinemia.Infants and children are more susceptible to this and methemoglobinemiahas been reported after benzocaine lubricationof endotracheal tubes and after topical administration to treata painful diaper rash.
Safety Profile
Poison by ingestion and intraperitoneal routes. Human systemic effects by rectal route: methemoglobinemia/carboxyhemoglobinem ia in infants. A skin irritant and a mild sensitizer. Local contact may cause contact dermatitis. Used as a topical anesthetic and as a sun-screening agent. When heated to decomposition it emits highly toxic fumes of NOx. See also ETHYL ALCOHOL and ESTERS
Synthesis
Benzocaine is the ethyl ester of 4-aminobenzoic acid (2.3.1). The classic, optimal way of benzocaine synthesis is the reduction of the nitro group of the ethyl ester of 4-nitrobenzoic acid to benzocaine by hydrogen, which generates directly in the reaction medium by the reaction of iron filings with dilute acids [24¨C26].

Side Effects
A common adverse reaction to Benzocaine is methemoglobinemia, which manifests as cyanosis, hypoxia, and dyspnea, with no improvement in symptoms with oxygen. Other adverse reactions include hypotension, bradycardia, cardiac arrest, convulsions, somnolence, dizziness, oedema and allergic reactions. Contact your doctor if any of these or other serious adverse reactions occur during use.
Metabolism
Benzocaine undergoes ester hydrolysis to form 4-aminobenzoic acid, acetylation to form acetylbenzocaine, or N-hydroxylation to form benzocaine hydroxide. 4-aminobenzoic acid can be acetylated or acetylbenzocaine can undergo ester hydrolysis to form 4-acetaminobenzoic acid.
Purification Methods
Crystallise Benzocaine from EtOH/H2O or EtOH (m 93-94o), and dry it in air. [Beilstein 14 H 422, 14 IV 1129.]
Structure and conformation
Ethyl aminobenzoate, a para-aminobenzoate derivative (PABA)
Properties of Benzocaine
| Melting point: | 88-90 °C |
| Boiling point: | 172 °C (12.7517 mmHg) |
| Density | 1.17 |
| refractive index | 1.5600 (estimate) |
| Flash point: | 172°C/13mm |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | alcohol: soluble1 gm in 5 ml |
| form | Crystalline Powder |
| pka | 2.5(at 25℃) |
| color | White |
| Odor | odorless |
| Water Solubility | Soluble in ethanol, chloroform, ethyl ether and dilute acids. Sparingly soluble in water |
| Merck | 14,1086 |
| BRN | 638434 |
| Stability: | Stable. Combustible. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 94-09-7(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Benzoic acid, 4-amino-, ethyl ester(94-09-7) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Benzocaine (94-09-7) |
Safety information for Benzocaine
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H317:Sensitisation, Skin |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P272:Contaminated work clothing should not be allowed out of the workplace. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P302+P352:IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of soap and water. P333+P313:IF SKIN irritation or rash occurs: Get medical advice/attention. |
Computed Descriptors for Benzocaine
| InChIKey | BLFLLBZGZJTVJG-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
Benzocaine manufacturer
Shreeji Pharma International
New Products
Boc-N-Me-Val-OH tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin Gabapentin EP Impurity B Ethyl N-(2- cyanoacetyl)carbamate Magnessium Ascorbate 1-Chloro-4-Methyl-2-Nitrobenzene 1,3-Diethyl-1,3-Diphenylurea 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile Benzethonium Chloride Trenbolone Enanthate Prednisolone acetate Cisplatin Chlorodehydromethyl testosterone Ketoconazole 1,3-Di Iodo Benzene Methyl 2-oxo-2,3-dihydrobenzo[d]oxazole-7-carboxylate 3-Hydroxy-4-nitrobromobenzene 4-(2-Aminoethyl)-7-hydroxy-2H-chromoen-2-one 2-Ethyl-1,4-diaminobenzene 2-Ethylhexyl 4-aminobenzoateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran



You may like
-
 Benzocaine 98%View Details
Benzocaine 98%View Details -
 Benzocaine 99%View Details
Benzocaine 99%View Details -
 Benzocaine 95% CAS 94-09-7View Details
Benzocaine 95% CAS 94-09-7View Details
94-09-7 -
 Benzocaine A P IView Details
Benzocaine A P IView Details
94-09-7 -
 benzocaine ip bp usp, Packaging Size: DrumView Details
benzocaine ip bp usp, Packaging Size: DrumView Details
94-09-7 -
 Benzocaine api, Grade Standard: EP, Packaging Size: DrumView Details
Benzocaine api, Grade Standard: EP, Packaging Size: DrumView Details
94-09-7 -
 Benzocaine Powder api, Grade Standard: USP, Packaging Size: DrumView Details
Benzocaine Powder api, Grade Standard: USP, Packaging Size: DrumView Details
94-09-7 -
 Benzocaine Powder, Grade Standard: IP, Packaging Size: DrumView Details
Benzocaine Powder, Grade Standard: IP, Packaging Size: DrumView Details
94-09-7
