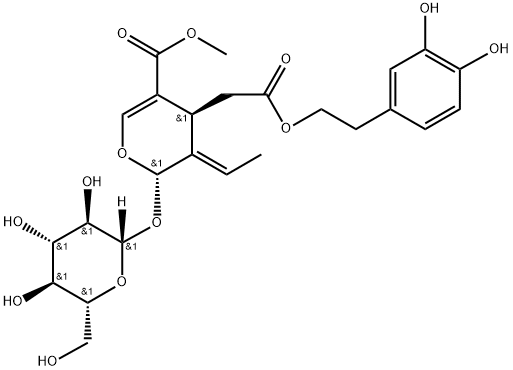
Oleuropein
Synonym(s):(2S,3E,4S)-3-Ethylidene-2-(β-D -glucopyranosyloxy)-3,4-dihydro-5-(methoxycarbonyl)-2H-pyran-4-acetic acid 2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)ethyl ester;Oleuropein
- CAS NO.:32619-42-4
- Empirical Formula: C25H32O13
- Molecular Weight: 540.52
- MDL number: MFCD16879008
- EINECS: 251-129-6
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-10 18:54:13
What is Oleuropein?
Description
Oleuropein is a phenolic compound extracted from olive (Canarium album (Lour.) Raeusch., Gan Lan) leaves mainly. The olive tree belongs to family Oleaceae Olea genus of evergreen trees, and it is the world famous fruit and woody species. There is highly edible value for cultivating trees. Affiliated to famous economic forest and subtropical fruit trees, they are rich in olive oil which is considered as high-quality edible oil .
Description
Oleuropein, found mainly in olive leaves, gives extra-virgin olive oil its pungent taste. Its powerful antioxidant activity makes olive oil among the healthiest plant-derived oils. Recently, oleuropein has also shown anti-inflammation properties. In one study, R. M. Giner and co-workers used it to?alleviate acute ulcerative colitis in mice.
Chemical properties
Brown Solid
Physical properties
Appearance: crystal in ethyl acetate. Solubility: very soluble in ethanol, acetone, glacial acetic acid, and 5% NaOH solution; soluble in water, butanol, ethyl acetate, and butyl acetate; insoluble in ether, petroleum ether, chloroform, and carbon tetrachloride. Melting point: 87–89 °C. Specific optical rotation: 147° in water/ethanol/ propane with a concentration of 1 mol/L; able to convert to 127° in water in 9 h.
History
The usage of olive ramification (including olive oil) in human health dates back to several centuries ago. For centuries, olive oil has been added to cosmetics and pharmacological agent. However, the unrefined mixture is applied primarily, and later studies have found that the main component of it which can be absorbed is olive polyphenols . Olive polyphenol, which gives a unique bitter taste, is mainly from the seeds, leaves, and immature bark of the olive (14% of dry weight). The content and purity are affected by fruit ripening stage, production, and extraction technology. In 1959, oleuropein was isolated, and the chemical structure was identified . In addition, oleuropein can be found in other kinds of plants, such as Lauraceae, Syringa, Ligustrum, Hibiscus and Jasminum. Up to now, the amount of Oleaceae containing oleuropein is 25 at least, including jasmine, cloves, lobular lilac, etc. Based on the molecular structure, pharmacological effects have been studied further. Clinical and experiment statistics demonstrated it is beneficial to human health. People gradually realized the function of its antioxidative, anti-inflammatory, and antitumor effects, atherosclerosis prevention, blood glucose hypoglycemia reduction, and nerve protection.
The Uses of Oleuropein
Oleuropein is a tyrosol ester derivative of elenolic acid and phenolic glycoside found in olive oil. Oleuropein shows antioxidant, anti-ischemic and hypolipidemic activity. Oleuropein has also been used as an immunomodulator .
The Uses of Oleuropein
olive leaf extract is astringent and anti-septic. It also has vasodialating capacities, as well as being perfuming and skin-conditioning. olive leaf extract has demonstrated some anti-oxidant and freeradical scavenger activities. olive leaves contain both bioflavonoids and polyphenols. The extract generally found in anti-aging products.
What are the applications of Application
Oleuropein is an antioxidant and immunomodulator in vitro that is a tyrosol ester derivative of elenolic acid (sc-497404) and phenolic glycoside found naturally olive oil
Definition
ChEBI: Oleuropein is a secoiridoid glycoside that is the methyl ester of 3,4-dihydro-2H-pyran-5-carboxylic acid which is substituted at positions 2, 3, and 4 by hydroxy, ethylidene, and carboxymethyl groups, respectively and in which the anomeric hydroxy group at position 2 has been converted into its beta-D-glucoside and the carboxylic acid moiety of the carboxymethyl substituent has been converted to the corresponding 3,4-dihydroxyphenethyl ester (the 2S,3E,4S stereoisomer). The most important phenolic compound present in olive cultivars. It has a role as a plant metabolite, a radical scavenger, an anti-inflammatory agent, an antineoplastic agent, an antihypertensive agent, a NF-kappaB inhibitor, an apoptosis inducer, an antioxidant and a nutraceutical. It is a secoiridoid glycoside, a beta-D-glucoside, a methyl ester, a member of catechols, a diester and a member of pyrans.
Pharmacology
According to the study, the pharmacological effects including antiviral, antitumor,
antioxidative, and antimicrobial and cardiovascular protection are investigated. In
cardiovascular system, olive leaf extract can reduce the discomfort caused by inadequate
arterial blood flow induced by angina and intermittent claudication. Oleuropein can decrease the degree of LDL oxidation and protect from coronary heart disease. The intensity of vascular smooth muscle can be decreased, and the ability of decreasing blood pressure can be achieved. Oleuropein regulates enzymes which participates in specific metabolism of protein, carbohydrate, and lipid and activates pepsin, trypsin, lipase, glycerol dehydrogenase, and GAPDH . The activity of other enzymes is also inhibited by oleuropein.
Oleuropein plays a role in resisting the virus; it can suppress VHSV and acts as a specific HIV inhibitor. It also shows significant activity against respiratory syncytial virus .
Oleuropein destroys the structure of actin filaments in cellular and noncellular detection and inhibits the proliferation and migration of tumor cells. The replication, movement, and invasion of tumor cells can be prevented. However, all of the above are reversible in normal cells .
Clinical Use
In the United States and other European countries, olive leaf extract serves as a dietary supplement, and its recommended dose is 50–100 mg as an immunomodulator. FDA also approves olive leaf extracts to be used as antioxidants in foods. In addition, 80% of oleuropein are used for skin care products mainly, and it can protect skin cells from UV. At the same time, it maintains soft and elastic skin effectively to protect skin. With light color and high content, oleuropein is very suitable for cosmetic formula design. In the cream and liquid formula, it is added at a concentration of 0.5–1%. The other pharmacological effects are still in preclinical study.
Properties of Oleuropein
| Melting point: | 89-90°C |
| Boiling point: | 772.9±60.0 °C(Predicted) |
| alpha | D20 -147° (H2O, alcohol, or acetone); D20 -127° |
| Density | 1.50±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | Inert atmosphere,2-8°C |
| solubility | DMSO (Slightly), Ethanol (Slightly, Sonicated), Methanol (Slightly) |
| form | neat |
| pka | 9.70±0.10(Predicted) |
| form | Solid |
| color | Light Beige to Dark Brown |
| Stability: | Hygroscopic, Light Sensitive |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 32619-42-4(CAS DataBase Reference) |
Safety information for Oleuropein
Computed Descriptors for Oleuropein
| InChIKey | RFWGABANNQMHMZ-JUVTZQQOSA-N |
| SMILES | C([C@@H]1C(=CO[C@@H](O[C@@]2([H])[C@@H]([C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@@H](CO)O2)O)/C/1=C/C)C(=O)OC)C(=O)OCCC1C=CC(O)=C(O)C=1 |&1:1,5,7,9,10,12,14,r| |
Oleuropein manufacturer
New Products
Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate (S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL N-octanoyl benzotriazole 4-Hydrazinobenzoic acid 3,4-Dibenzyloxybenzaldehyde 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) 4-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran



You may like
-
 Oleuropein, ≥98% CAS 32619-42-4View Details
Oleuropein, ≥98% CAS 32619-42-4View Details
32619-42-4 -
 Oleuropein 98% (HPLC) CAS 32619-42-4View Details
Oleuropein 98% (HPLC) CAS 32619-42-4View Details
32619-42-4 -
 Oleuropein CAS 32619-42-4View Details
Oleuropein CAS 32619-42-4View Details
32619-42-4 -
 55441-95-7 99%View Details
55441-95-7 99%View Details
55441-95-7 -
 N-Vinylformamide 99%View Details
N-Vinylformamide 99%View Details
13162-05-5 -
 Chloro Uracil 1820-81-1 99%View Details
Chloro Uracil 1820-81-1 99%View Details
1820-81-1 -
 2-ethyl-6-methyl-3-hydroxypyridine succinate 99%View Details
2-ethyl-6-methyl-3-hydroxypyridine succinate 99%View Details
127464-43-1 -
 2-ETHYLPYRIDINE 100-71-0 99%View Details
2-ETHYLPYRIDINE 100-71-0 99%View Details
100-71-0