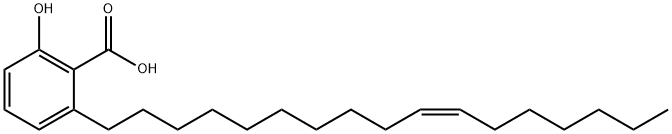
Ginkgo biloba extract
- CAS NO.:90045-36-6
- Molecular Weight: 0
- MDL number: MFCD00240717
- EINECS: 289-896-4
- Update Date: 2025-12-17 09:50:03
What is Ginkgo biloba extract?
The Uses of Ginkgo biloba extract
ginkgo biloba extract (ginkgo extract) is credited with anti-oxidant properties, it also appears to aid fibroblast cells in the production of collagen and elastin. This ability is attributed to a number of flavonoid fractions, including quercetin, kaempferol, and ginkgetin. Additionally, ginkgo is an anti-inflammatory and may help improve a couperose condition because of a protective effect on vascular walls. ginkgo was used in folkloric medicine as a blood vessel dilator because of its ability to increase blood flow and stimulate tissue oxygen consumption. It is considered a beneficial anti-aging ingredient. ginkgo’s key constituents include ginkgolide and bilobalide, catechin, tannin, quercetin, and luteolin.
Indications
Ginkgo, or maidenhair tree (Ginkgo biloba), is thought to be the most ancient of living tree species, and it is now also one of the top selling herbs in Europe and the United States because of its reputed ability to improve cognitive function. Ginkgo leaf extract is prepared from ginkgo leaf by a complex process that removes toxic ginkgolic acid. This reduces the risk of allergic reactions to the leaves if they are consumed directly. Ginkgo leaf extract contains 24% flavone glycosides (including the antioxidant rutin, which improves capillary fragility) and 6% terpene lactones.
Definition
ginkgo biloba extract (ginkgo extract)-credited with anti-oxidant properties, it also appears to aid fibroblast cells in the production of collagen and elastin. This ability is attributed to a number of flavonoid fractions, including quercetin, kaempferol, and ginkgetin. Additionally, ginkgo is an anti-inflammatory and may help improve a couperose condition because of a protective effect on vascular walls. Ginkgo was used in folkloric medicine as a blood vessel dilator because of its ability to increase blood flow and stimulate tissue oxygen consumption. It is considered a beneficial anti-aging ingredient. Ginkgo’s key constituents include ginkgolide and bilobalide, catechin, tannin, quercetin, and luteolin.
brand name
Tanakan.
General Description
Ginkgo is extracted by an extremely complex multistep process that concentrates the active constituents and removes the toxic ginkgolic acid. The ginkgo extract is a complex mixture of both polar and nonpolar components . The more polar fractions contain flavonol and flavone glycosides. The more nonpolar fractions contain some diterpene lactones, known as ginkgetin, ginkgolic acid, and isoginkgetin, and some interesting caged diterpenes known as ginkgolide A, B, C, J, and M. There is also a 15-carbon sesquiterpene (bilobalide) and other minor components.
G. biloba extract is prepared by picking the leaves, drying them, and constituting them into an acetone-water extract that is standardized to contain 24% flavone glycosides and 6% terpenes. G. biloba produces vasodilating effects on both the arterial and venous circulation. The result is increased tissue perfusion (i.e., in the peripheral circulation) and cerebral blood flow. The extract produces arterial vasodilatation (rodent models), dampens arterial spasticity, and decreases capillary permeability, capillary fragility, erythrocyte aggregation, and blood viscosity. There are several possible explanations for these effects. One possibility is that the compounds in G. biloba extract inhibit prostaglandin and thromboxane biosynthesis. It has also been speculated that G. biloba extract has an indirect regulatory effect on catecholamines. Ginkgolide B is reportedly a potent inhibitor of PAF.
Hazard
Lowtoxicity by ingestion. Human systemic effects.
Mechanism of action
Ginkgo leaf extract appears to act primarily as a mild cerebral vasodilator that increases cerebral blood flow and reduces blood viscosity. Ginkgolides inhibit platelet activating factor, and this may improve microcirculatory blood flow in atherosclerotic disease with slightly increased risk of bleeding. There appears to be an antioxidant effect that may be neuroprotective.Although some studies suggested a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) effect, this is considered to have questionable clinical relevance.
Clinical Use
Ginkgo leaf extract is most popular for cognitive disorders,
including memory loss, dementia, and cerebrovascular
insufficiency. A number of well-designed clinical
trials have shown modest benefit in Alzheimer’s disease,
with ginkgo extract appearing as effective as second-
generation cholinesterase inhibitors. At least one
large (214 patient) study, however, failed to show a
memory improvement in dementia patients. Studies are
now under way to see whether ginkgo use will protect
against development of Alzheimer’s disease.
Intermittent claudication appears to benefit from
ginkgo therapy: many studies demonstrate improved
walking distance and decreased pain. One meta-analysis
of eight studies documented statistically significant improvement
but questioned its clinical relevance. In some
studies, the high doses (240 mg) appeared more effective.
Vertigo and tinnitus are difficult to treat conditions
for which ginkgo is frequently recommended. At least
two trials support the use of gingko extract for vertigo,
but the evidence for tinnitus remains inconclusive.
Other suggested uses include sexual dysfunction
secondary to selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors
(SSRIs), macular degeneration, premenstrual syndrome,
and the prevention of acute mountain sickness
at high altitude. Some of these uses are supported only
by a single study.
Side Effects
Allergic reactions are a significant concern with unprocessed
ginkgo leaf (ginkgolic acid) but are much less
likely to occur with the leaf extract. The malodorous
ginkgo fruit cross-reacts with poison ivy (urushiol) and
may cause an identical contact dermatitis.
Children eating large numbers (>50) of the uncooked
ginkgo kernels have had seizures, and consequently
there is some concern about using high doses of
ginkgo in seizure patients. However, most patients tolerate
gingko extract very well, with only occasional GI
upset or headache being reported, and the product is
considered safe for healthy nonpregnant adults.
Bleeding complications are an infrequent but serious
concern, with subdural hematomas, subarachnoid
hemorrhages, hyphema (bleeding of the iris), and surgical
bleeding occasionally reported. Stopping ginkgo administration
prior to surgery and the avoidance of its
use with anticoagulant drugs and perhaps with aspirin is
recommended. Use of ginkgo extract should be avoided
in pregnant women and children, since at least one study
showed in a ginkgo preparation small amounts of
colchicine, a compound that can block cellular division
and cause abortion; however, it is unclear whether this
is a problem in all ginkgo preparations.
Ginkgo may reduce the effectiveness of thiazide diuretics
for blood pressure control and at least theoretically
should be avoided with MAOIs. There is also a
suggestion that ginkgo may decrease male and female
fertility, and it should be avoided in those trying to conceive.
Properties of Ginkgo biloba extract
| Odor | Characteristic |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 90045-36-6(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| IARC | 2B (Vol. 108) 2016 |
Safety information for Ginkgo biloba extract
Computed Descriptors for Ginkgo biloba extract
Ginkgo biloba extract manufacturer
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran



You may like
-
 90045-36-6 98%View Details
90045-36-6 98%View Details
90045-36-6 -
 Ginkgo biloba Extract 99%View Details
Ginkgo biloba Extract 99%View Details -
 Powder Ginkgo Biloba ExtractView Details
Powder Ginkgo Biloba ExtractView Details
90045-36-6 -
 3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 -
 3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 -
 4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
5305-40-8
