NOCODAZOLE
Synonym(s):[5-(2-Thienylcarbonyl)-1H-benzimidazol-2-yl]-carbamic acid methyl ester;Methyl [5-(2-thienylcarbonyl)-1H-benzimidazol-2-yl]carbamate;Methyl N-(5-thenoyl-2-benzimidazolyl)carbamate;Oncodazole;
- CAS NO.:31430-18-9
- Empirical Formula: C14H11N3O3S
- Molecular Weight: 301.32
- MDL number: MFCD00005588
- EINECS: 250-626-5
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-08-06 15:14:14
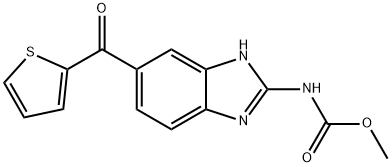
What is NOCODAZOLE?
Description
Nocodazole reversibly binds tubulin and alters tubulin-
Chemical properties
Amber Powder
The Uses of NOCODAZOLE
Nocodazole has been shown to enhance CRISPR genome editing efficiency. To see other small molecule CRISPR enhancers, visit sigma.com/CRISPR-enhancers.
The Uses of NOCODAZOLE
A synthetic chemotherapeutic agent with antineoplastic, antifungal and anthelmintic activities. Microtubule inhibitor; inhibits mitosis
The Uses of NOCODAZOLE
Antineoplastic;Microtubule poison
The Uses of NOCODAZOLE
A potent Tubulin production inhibitor and anti-neoplastic agent
What are the applications of Application
Nocodazole is a potent Tubulin production inhibitor, anti-neoplastic agent, and inhibitor of mitosis.
Definition
ChEBI: A member of the class of benzimidazoles that is benzimidalole which is substituted at position 2 by a (methoxycarbonyl)amino group and at position 5 by a 2-thienoyl group. It is an antineoplastic agent that exerts its effect by depolymerising microtubules.
General Description
White powder.
Air & Water Reactions
Insoluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
NOCODAZOLE may be sensitive to heat. .
Health Hazard
ACUTE/CHRONIC HAZARDS: When heated to decomposition NOCODAZOLE emits toxic fumes of sulfur oxides and nitrogen oxides.
Fire Hazard
Flash point data for NOCODAZOLE are not available; however, NOCODAZOLE is probably combustible.
Biological Activity
Microtubule inhibitor; inhibits mitosis.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Nocodazole is an anticancer drug that has been shown to interfere with the structure and function of microtubules in interphase and mitotic cells. Malignant cells may be more susceptible to the antimicrotubular effect of nocodazole than nonmalignant cells. Mammalian cells cultured in vitro can be treated with 0.04-10 μg/mL doses for cell synchronization experiments. Prolonged arrest of cells in mitosis due to nocodazole treatment typically results in cell death by apoptosis. Higher concentrations could not be used because of insolubility. High specificity of action may explain low toxicity to bone marrow cells and lack of neurotoxicity. Nocodazole is thought to bind directly to tubulin causing conformational changes resulting in increased exposure of some sulfhydryl and possibly tyrosine residues. Nocodazole′s apparent synergism with cytosine arabinofuranoside has been demonstrated on L1210 leukemic cells.
Safety Profile
Poison by intraperitoneal route.An experimental teratogen. Other experimentalreproductive effects. Human mutation data reported.When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes ofSOx and NOx. See also CARBAMATES
in vitro
nocodazolewas a high-affinity ligand for the cancer-related kinases including abl phosphorylated, c-kit, braf, and mek with the kd values of 0.091 μm, 1.6 μm, 1.8 μm and 1.6 μm, respectively. in addition, the kd for abl(e255k) phosphorylated, abl(t315i) phosphorylated, braf(v600e) and pi3kγ was 0.12 μm, 0.17 μm, 1.1 μm and 1.5 μm, respectively. in chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells, nocodazole induced apoptosis. in some human colon carcinoma cells, nocodazole decrease d apoptosis. also, nocodazole inhibited insulin-stimulated glucose transport. nocodazole impaired the morphology and directionality of migrating medial gan-glionic eminence cells [1]. at high concentrations, nocodazole rapidly depolymerized microtubules in cells, while low concentrations of nocodazole inhibited microtubule dynamic instability [2].in sh-sy5y cells, nocodazole disrupted microtubules by binding to β-tubulin, prevented the formation of one of the two interchain disulfide linkages and impaired the transport of vesicles. nocodazole significantly attenuated meth-induced cell death and lysosomal dysfunction [3]. nocodazole (≥ 50 nm) resulted in a rapid reduction in fibroblast locomotion to a new rate that was maintained for > 2 hours. nocodazole(100 nm) decreased the rate of locomotion by more than 60%; and 300 nm nocodazole completely stopped cell locomotion[4].
in vivo
in athymic mice bearing colo 205 tumor xenografts,after 6 wk of treatment with ketoconazole (50 mg/kg/three times per week)plus nocodazole (5 mg/kg/three times per week), the antitumor effects of nd were significantly potentiated by kt. the tumor volume and tumor weight of the mice are significantly reduced as compared with those treated with ketoconazole or nocodazole alone. nocodazole treatment in combination with ketoconazole strongly enhanced apoptosis of colo 205 tumor xenografts treated with ketoconazole or nocodazole alone [5].
Storage
+4°C
References
1) Jordan et al. (1992), Effects of vinblastine, podophyllotoxin and nocodazole on mitotic spindles. Implications for the role of microtubule dynamics in mitosis; J. Cell Science, 102 401 2) Storrie et al. (1998), Dynamics of the interphase mammalian Golgi complex as revealed through drugs producing reversible Golgi disassembly; Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1404 127 3) Mejillano et al. (1996), Studies on the nocodazole-induced GTPase activity of tubulin; Arch. Biochem. Biophys., 336 130 4) Wang et al. (1998), Microtubule-interfering agents activate c-Jun N-terminal kinase/stress-activated protein kinase through both Ras and apoptosis signal-regulating kinase pathways; J. Biol. Chem., 273 4928
Properties of NOCODAZOLE
| Melting point: | 300 °C (dec.) |
| Density | 1.490 |
| refractive index | 1.6740 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | -20°C |
| solubility | DMSO: 10 mg/mL, soluble |
| pka | 10.67±0.10(Predicted) |
| form | powder |
| color | white |
| BRN | 1085978 |
| Stability: | Stable for 2 years as supplied. Solutions in DMSO may be stored at -20° for up to 2 months. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 31430-18-9(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Nocodazole (31430-18-9) |
Safety information for NOCODAZOLE
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H341:Germ cell mutagenicity |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P201:Obtain special instructions before use. P202:Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P308+P313:IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention. P405:Store locked up. P501:Dispose of contents/container to..… |
Computed Descriptors for NOCODAZOLE
| InChIKey | KYRVNWMVYQXFEU-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 Nocodazole CAS 31430-18-9View Details
Nocodazole CAS 31430-18-9View Details
31430-18-9 -
 Nocodazole CAS 31430-18-9View Details
Nocodazole CAS 31430-18-9View Details
31430-18-9 -
 Nocodazole CAS 31430-18-9View Details
Nocodazole CAS 31430-18-9View Details
31430-18-9 -
 3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 -
 3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 -
 4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
5305-40-8
