Carbendazim
Synonym(s):Carbendazim;BCM;Methyl 2-benzimidazolecarbamate;Methyl benzimidazol-2-ylcarbamate;TNFRSF17
- CAS NO.:10605-21-7
- Empirical Formula: C9H9N3O2
- Molecular Weight: 191.19
- MDL number: MFCD00055390
- EINECS: 234-232-0
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:15:30
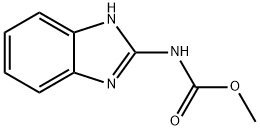
What is Carbendazim?
Description
Carbendazim is the degradation product and active ingredient of the carbamate fungicide benomyl. Carbendazim (100 μM) disrupts the growth of S. cerevisiae by inhibiting microtubule polymerization. It impairs meiosis and steroidogenesis in an ex vivo rat model of seminiferous tubules and increases prostate weight in rats when administered at a dose of 100 mg/kg but does not affect other testosterone-dependent or estrogen-dependent tissues.
Description
Carbendazim is a degradation product of the widely used fungicide benomyl and may be its active ingredient. Carbendazim itself is manufactured and marketed as a fungicide by several Chinese companies, but because it can disrupt hormone activity in animals, it is not approved for use in the United States and other countries. Recently,?carbendazim was detected?in orange juice imported from Brazil (where it is legal), and the FDA is testing the juice to determine whether it poses a health risk.
Chemical properties
Colorless crystalline solid or light-gray powder. Commercially supplied as dry concentrate that is mixed with water for spraying.
The Uses of Carbendazim
Carbendazim is the most widely used active ingredient in the benzimidazole class of fungicides. It is a systemic fungicide with both protective and curative activities against a wide range of fungal diseases, especially caused by most Ascomycetes spp. and some Basidiomycetes and Deuteromycetes spp. in a wide variety of crop and ornamental uses.
What are the applications of Application
Carbendazim is is a fungicide
Definition
ChEBI: A member of the class of benzimidazoles that is 2-aminobenzimidazole in which the primary amino group is substituted by a methoxycarbonyl group. A fungicide, carbendazim controls Ascomycetes, Fungi Imperfecti, and Basidiomy etes on a wide variety of crops, including bananas, cereals, cotton, fruits, grapes, mushrooms, ornamentals, peanuts, sugarbeet, soybeans, tobacco, and vegetables.
General Description
Light gray or beige powder.
Air & Water Reactions
Insoluble in water. Carbendazim slowly decomposes in alkaline solution. .
Reactivity Profile
Carbendazim is a carbamate ester-amine. Amines behave as chemical bases. Carbamates are chemically similar to, but more reactive than amides. Like amides they form polymers such as polyurethane resins. Carbamates are incompatible with strong acids and bases, and especially incompatible with strong reducing agents such as hydrides. Flammable gaseous hydrogen is produced by the combination of active metals or nitrides with carbamates. Strongly oxidizing acids, peroxides, and hydroperoxides are incompatible with carbamates.
Health Hazard
ACUTE/CHRONIC HAZARDS: When heated to decomposition Carbendazim emits toxic fumes of NOx.
Fire Hazard
Literature sources indicate that Carbendazim is probably nonflammable.
Agricultural Uses
Fungicide: Carbendazim is a systemic fungicide used as a drench to control a broad range of fungi in cereals, vegetables, oilseed rape, sugar beets, grapes, tomatoes, pome fruit and stone fruit. It is also used in post-harvest storage and as treatment in seed pre-planting, frequently in combination with other fungicides. In some areas, it has been used to combat Dutch elm disease.
Trade name
ABACOL®; AIMCOZIM; BAS® 3460; BAS® 67054; BATTAL®; BAVISTIN®; BENDAZIM®; CARBATE®; CARBENDAZIME®; CARBENDAZOL®; CARBENDAZOLE®; CARBENDAZYM®; CARBENDOR; CEKUDAZIM®; CORBEL; CTR® 6669; CUSTOS®; DEFENSOR®; DELSENE®; DEROSAL®; E-965®; DERROPRENE®; EQUITDAZIN®; FUNGISOL®; HOE 17411®; LIGNASAN®; IMISOL®; KEMDAZIN®; MERGAL®; PILLARSTIN®; POLYPHASE®; RODAZIM®; STEMPOR®; SUPERCARB, TRITICOL®; TRITICOL®; U-32.104®
Biochem/physiol Actions
B-cell maturation antigen (BCMA) or tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 17 (TNFRSF17) plays an important role in B cell development, function and regulation. BCMA also has the capability to activate nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB), janus kinase (JNK) and mitogen activated protein kinases (MAPKs). The protein is expressed in certain cancers like glioblastoma, chronic lymphocytic leukemia, Hodgkin lymphoma and multiple myeloma. It has a role in the maintenance of survival of long-lived plasma cells in bone marrow.
Safety Profile
Moderately toxic by skin contact. Mildly toxic by ingestion. An experimental teratogen. Experimental reproductive effects. Human mutation data reported. An agricultural chemical and pesticide. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of NOx. See also CARBAMATES.
Potential Exposure
Carbendazim is a benzimidazole/carbamate systemic fungicide used as a drench to control a broad range of fungi in cereals, vegetables, oilseed rape, sugar beets, grapes, tomatoes, pome fruit, and stone fruit. It is also used in postharvest storage and as treatment in seed preplanting, frequently in combination with other fungicides. In some areas, it has been used to combat Dutch Elm disease.
Metabolic pathway
When the mites are exposed to 14C-carbendazim, the major carbendazim metabolite identified in the bulb mites is 5-hydroxy-2-aminobenzimidazole. Low levels of 2-aminobenzimidazole and 5-hydroxy-2- benzimidazole carbamate are also identified.
Shipping
UN3082 Environmentally hazardous substances, liquid, n.o.s., Hazard class: 9; Labels: 9-Miscellaneous hazardous material, Technical Name Required
Degradation
Carbendazim (MBC, 1) was stable in acidic and neutral solutions (pH 5-7,
DT50≥57 days at 22°C), but decomposed rapidly with a DT50 of 22
days (WHO, 1993b) to yield 2-aminobenzimidazole (2, Watluns, 1976;
Zbozinek, 1984) under alkaline conditions (pH 9). An increase in the
salinity of the water accelerated the degradation rate of MBC in water
(Deshpande and Patil, 1987).
Photolysis of MBC in natural sunlight is not a significant dissipation
mechanism in the environment. Significant degradation did not occur
either on leaf surfaces exposed to natural sunlight or in unamended dilute
aqueous solution. Degradation occurred in solution under natural sunlight
if photoinitiators such as riboflavin or acetone were present (Fleeker
and Lacy, 1977).
Incompatibilities
Carbamates are incompatible with reducing agents, strong acids, oxidizing acids, peroxides, and bases. Contact with active metals or nitrides cause the release of flammable, and potentially explosive, hydrogen gas.
Waste Disposal
Do not discharge into drains or sewers. Dispose of waste material as hazardous waste using a licensed disposal contractor to an approved landfill. Consult with environmental regulatory agencies for guidance on acceptable disposal practices. Incineration with effluent gas scrubbing is recommended. Containers must be disposed of properly by following package label directions or by contacting your local or federal environmental control agency, or by contacting your regional EPA office.
Properties of Carbendazim
| Melting point: | >300 °C (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 326.92°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 1.4500 |
| vapor pressure | 1.5 x 10-4 Pa (25 °C) |
| refractive index | 1.6500 (estimate) |
| Flash point: | 11 °C |
| storage temp. | -20°C |
| solubility | pyridine: soluble1%, clear, very faintly brownish-yellow |
| form | neat |
| pka | 4.48(at 25℃) |
| form | Solid |
| color | White to off-white |
| Water Solubility | <0.1 g/100 mL at 21 ºC |
| Merck | 13,1799 |
| BRN | 649044 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 10605-21-7(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Carbendazim (10605-21-7) |
Safety information for Carbendazim
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Health Hazard GHS08  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H340:Germ cell mutagenicity H410:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P202:Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P391:Collect spillage. Hazardous to the aquatic environment P308+P313:IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention. P405:Store locked up. |
Computed Descriptors for Carbendazim
| InChIKey | TWFZGCMQGLPBSX-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
Carbendazim manufacturer
Chemikos Laboratories Pvt Ltd
United Phosphorus Limited
Speciality Organics Pvt. Ltd.
Unique Farm Aid Pvt Ltd
Glyra Health Care Pvt Ltd
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 10605-21-7 99%View Details
10605-21-7 99%View Details
10605-21-7 -
 Fenbendazole impuity A 99%View Details
Fenbendazole impuity A 99%View Details
10605-21-7 -
 Carbendazim 10605-21-7 98%View Details
Carbendazim 10605-21-7 98%View Details
10605-21-7 -
 10605-21-7 98%View Details
10605-21-7 98%View Details
10605-21-7 -
 Carbendazim 98%View Details
Carbendazim 98%View Details
10605-21-7 -
 Carbendazim 98%View Details
Carbendazim 98%View Details -
 Methyl 2-benzimidazolecarbamate 98% (HPLC) CAS 10605-21-7View Details
Methyl 2-benzimidazolecarbamate 98% (HPLC) CAS 10605-21-7View Details
10605-21-7 -
 Fenbendazole Related Compound A CAS 10605-21-7View Details
Fenbendazole Related Compound A CAS 10605-21-7View Details
10605-21-7