N,N-Dimethyltryptamine
Synonym(s):Dimethyltryptamine;DMT;N,N-Dimethyl-1H-indole-3-ethanamine
- CAS NO.:61-50-7
- Empirical Formula: C12H16N2
- Molecular Weight: 188.27
- MDL number: MFCD00055989
- EINECS: 200-508-4
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2023-05-29 13:57:48
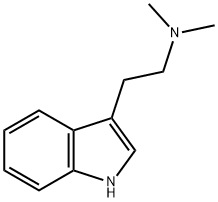
What is N,N-Dimethyltryptamine?
Description
N,N-Dimethyltryptamine (DMT) is a plant-based hallucinogen that is outlawed in most countries. DMT was isolated from many species in the 1950s, notably by Pfizer chemists F. A. Hochstein and Anita M. Paradies, who discovered it in the leaves of Prestonia amazonica (aka Haemadictyon amazonicum), which is called “yagé” by inhabitants of the Peruvian Amazon basin.
Hungarian chemist/psychologist Stephen Szará synthesized DMT in 1956 and studied its psychotropic effects in volunteers during that decade. DMT is sometimes called the “spirit molecule”; it produces psychedelic results when it is swallowed, inhaled, injected, or “vaped”. The DMT structure with a hydroxyl group on the benzene ring is the “feel-good” molecule serotonin.
DMT is currently an outlaw, but chemist David Olson and his research team at the University of California, Davis, may have found a legitimate pharmaceutical use for it and other hallucinogens. In an effort to find alternatives to the side effect–prone anesthetic ketamine* for treating depression, the investigators showed that DMT, LSD, and other psychotropics increase the number of synapses in the brain areas of lab animals that regulate emotion and mood.
As with ketamine, the effects are long-lasting and involve a similar signaling pathway. These results are promising, but any commercial drug to arise from them is a long way off.
*Recently reported research indicates that ketamine may require signaling through opioid receptors.
Chemical properties
Tan Solid
The Uses of N,N-Dimethyltryptamine
It is an endogenous Sigma-1 receptor regulator.
The Uses of N,N-Dimethyltryptamine
A labelled endogenous Sigma-1 receptor regulator.
Definition
ChEBI: A tryptamine derivative having two N-methyl substituents on the side-chain.
Synthesis Reference(s)
The Journal of Organic Chemistry, 59, p. 3738, 1994 DOI: 10.1021/jo00092a046
General Description
Dimethyltryptamine is a very weak hallucinogen, activeonly by inhalation or injection, with a short duration of action.It possesses pronounced sympathomimetic (NE) sideeffects.
Biological Activity
Endogenous σ 1 receptor ligand and psychoactive plant compound (K i = 14.8 μ M). Binding to σ 1 inhibits voltage-gated Na + channels and is responsible for the behavioral effects of DMT. Also a 5-HT 2A receptor agonist and inhibitor of 5-HT uptake at plasma membrane serotonin transporters (SERT) (K i = 4.0 μ M).
Properties of N,N-Dimethyltryptamine
| Melting point: | 42-44°C |
| Boiling point: | bp 60-80° |
| Density | 1.0580 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.5430 (estimate) |
| Flash point: | 9℃ |
| storage temp. | Store at -20°C |
| solubility | DMSO: soluble15mg/mL, clear |
| form | powder |
| appearance | clear or white crystals |
| pka | 8.68 (ethanol-water) |
| color | white to beige |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | N,N-Dimethyltryptamine(61-50-7) |
Safety information for N,N-Dimethyltryptamine
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H336:Specific target organ toxicity,single exposure; Narcotic effects |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P271:Use only outdoors or in a well-ventilated area. P405:Store locked up. P403+P233:Store in a well-ventilated place. Keep container tightly closed. P501:Dispose of contents/container to..… |
Computed Descriptors for N,N-Dimethyltryptamine
New Products
Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate (S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL N-octanoyl benzotriazole 3,4-Dibenzyloxybenzaldehyde 4-Hydrazinobenzoic acid 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 4-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 4-(3-chloropropyl)morpholine phenylhydrazine hydrochloride (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran



You may like
-
 (9H-fluoren-9-yl)methyl (2,5-dioxopyrrolidin-1-yl) carbonate 82911-69-1 98.0%View Details
(9H-fluoren-9-yl)methyl (2,5-dioxopyrrolidin-1-yl) carbonate 82911-69-1 98.0%View Details
82911-69-1 -
 13057-17-5 95.0%View Details
13057-17-5 95.0%View Details
13057-17-5 -
![2-Nitro-8,9-dihydro-5H-benzo [7] annulen-7(6H)-one 98.0%](https://img.chemicalbook.in//Content/image/CP5.jpg) 2-Nitro-8,9-dihydro-5H-benzo [7] annulen-7(6H)-one 98.0%View Details
2-Nitro-8,9-dihydro-5H-benzo [7] annulen-7(6H)-one 98.0%View Details
740842-50-6 -
 4-bromoaniline 106-40-1 99.0%View Details
4-bromoaniline 106-40-1 99.0%View Details
106-40-1 -
 1421517-99-8 99.0%View Details
1421517-99-8 99.0%View Details
1421517-99-8 -
 5-bromo-2-chlorobenzoic acid 99.0%View Details
5-bromo-2-chlorobenzoic acid 99.0%View Details
21739-92-4 -
 2-methyl-5-nitrophenol 98.0%View Details
2-methyl-5-nitrophenol 98.0%View Details
5428-54-6 -
 15761-38-3 97.0%View Details
15761-38-3 97.0%View Details
15761-38-3