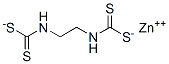NABAM
- CAS NO.:142-59-6
- Empirical Formula: C4H6N2Na2S4
- Molecular Weight: 256.34
- MDL number: MFCD00069382
- EINECS: 205-547-0
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:08:57
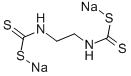
What is NABAM?
Chemical properties
Colorless crystals when pure. Easily sol-uble in water.
Chemical properties
Colorless crystalline solid (when pure). Light amber crystalline solid or 22% wettable powder solution. Slight odor of sulfide.
The Uses of NABAM
Nabam provides protection against fungal diseases of cotton, capsicums and onions when applied to soil.
The Uses of NABAM
Plant fungicide, starting material for derivativesthat are also pesticides.
Definition
ChEBI: A dithiocarbamate salt that is the disodium salt of ethylenebis(dithiocarbamic acid). A fungicide, algicide and bactericide used on various crops including on cotton, capsicums, onions and rice crops, it is considered to be a carcinogen, so is not licensed for use within the European Union. Mixing nabam with zinc sulfate affords the fungicide zineb.
General Description
Colorless to light amber solid with a a slight odor. Mixes with water.
Air & Water Reactions
Water soluble. Decomposes in boiling hot to give poisonous hydrogen sulfide and flammable carbon disulfide.
Reactivity Profile
NABAM is a dithiocarbamate. Flammable gases are generated by the combination of thiocarbamates and dithiocarbamates with aldehydes, nitrides, and hydrides. Thiocarbamates and dithiocarbamates are incompatible with acids, peroxides, and acid halides.
Hazard
Irritant to skin and mucous membranes, nar-cotic in high concentrations, use may be restricted.
Health Hazard
Contact with liquid irritates eyes and may cause mild to severe erythema of skin as well as sensitization reactions.
Fire Hazard
Behavior in Fire: If water solution boils, poisonous hydrogen sulfide and highly flammable carbon disulfide vapors form.
Agricultural Uses
Fungicide, Algaecide, Herbicide, Microbiocide: Nabam is a broad-spectrum fungicide/bactericide/ algaecide used to prevent crop damage by fungi, to protect harvested products from deterioration, and as an industrial microbiocide. As a result of the U.S. EPA review of nabam in 1989, all food uses were voluntarily canceled by the manufacturers except for one FDA-regulated food use on sugar mill grinding, crusher and/or diffuser systems, e.g., processing water systems. Registered only for nonfood application. Not approved for use in EU countries. Registered for use in the U.S. and Canada.
Trade name
AMA-30®, Kemira Chemical (Finland); CAMBELL’S® NABAM SOIL FUNGICIDE; CARBON D®; NALCO D-62C44®; CHEM-BAM®; DITHANE A-40®; DITHANE A-46®; DITHANE D-14®[C]; NAFUN-IPO®; NALCO® D-62C44; PARZATE®; SPRING-BAK®
Safety Profile
intraperitoneal route. Experimental teratogenic and reproductive effects. Mutation data reported. When heated to decomposition it emits very toxic fumes of NOx, Na2O, and SOx. See also CARBAMATES.
Potential Exposure
Nabam is a broad spectrum dithiocarbamate fungicide/bactericide/algaecide/herbicide/microbiocide used to prevent crop damage by fungi, to protect harvested products from deterioration, and as an industrial microbiocide. As a result of the United States Environmental Protection Agency review of nabam in 1989, all food uses were voluntarily canceled by the manufacturers except for one FDA-regulated food use on sugar mill grinding, crusher, and/or diffuser systems, e.g., processing water systems. All other uses of nabam are for the control of algae, slime-forming bacteria, and fungi in indoor nonfood environments, paper mills, water cooling systems, drilling mud and packer fluids, and secondary oil recovery water system. Registered in the United States only for nonfood application.
Metabolic pathway
Nabam and other alkylenebis(dithi0carbamate) fungicides are degraded and metabolised via a common pathway. Limited information is available to describe the fate of nabam in soil and animals. Based on information generated with structurally similar compounds (see maneb, zineb), the initial degradation reaction of nabam in water and plants involves the dissociation of the metal complex and decomposition to numerous degradation products including ethylenethiourea (ETU) and ethyleneurea (EU) as major products (Scheme 1).
Shipping
UN3077 Environmentally hazardous substances, solid, n.o.s., Hazard Class: 9; Labels: 9-Miscellaneous hazardous material, Technical Name Required.
Purification Methods
It crystallises (as hexahydrate) from aqueous ethanol. It is a skin irritant. [Beilstein 4 III 149, 4 IV 234.]
Degradation
In aqueous solution, ethylenebis( thiocarbamate) compounds (eg. maneb,
zineb) decompose to yield ethylenetl.uourea (ETU, 2) and 5,6-dihydro-
3H-imidazo[2,l-c]-1,2,4-dithiazole-3-thione(3) (kaars Sijpestijn and Vonk,
1974). Nabam (1) decomposed to a complex pattern of degradation
products when exposed to aqueous solution at 90 °C (Marshall, 1977). A
possible degradation pathway involves the oxidation of nabam to
ethylenethiuram disulfide (4) which is further degraded to ETU (2) and
compound 3. Other decomposition products included carbon disulfide,
hydrogen sulfide, ethylene diisothiocyanate (5), β-aminoethy 1 isothiocyanate
(6), β-aminoethyl dithiocarbamate (7) and ethylenediamine (8).
The primary hydrolytic and thermal degradation pathways of nabam are
presented in Scheme 1
ETU in aqueous solution was ultimately converted into 2-imidazoline
(9) and EU (10) (kaars Sijpesteijn and Vonk, 1974).
Incompatibilities
Combustible material. Dust may form explosive mixture in air, water, acid, oxidizing materials. Heat or contact with moisture or acids causes rapid decomposition and the generation of toxic and flammable hydrogen sulfide and carbon disulfide. Dithiocarbamate esters are combustible. They react violently with powerful oxidizers such as calcium hypochlorite. Poisonous gases are generated by the thermal decomposition of dithiocarbamate compounds, including carbon disulfide, oxides of sulfur, oxides of nitrogen, hydrogen sulfide, ammonia, and methylamine. Thio and dithiocarbamates slowly decompose in aqueous solution to form carbon disulfide and methylamine or other amines. Such decompositions are accelerated by acids. Flammable gases are generated by the combination of dithiocarbamate with aldehydes, nitrides, and hydrides. Dithiocarbamate are incompatible with acids, peroxides, and acid halides. Corrosive to iron, copper, brass, and zinc metals, especially in the presence of moisture. Heat alkalies (lime), moisture can cause decomposition. Decomposes on prolonged storage; by moisture, light, and heat. Degradation produces ethylene thiourea.
Waste Disposal
Do not discharge into drains or sewers. Dispose of waste material as hazardous waste using a licensed disposal contractor to an approved landfill. Consult with environmental regulatory agencies for guidance on acceptable disposal practices. Generators of waste containing this contaminant (≥100 kg/mo) must conform with EPA regulations governing storage, transportation, treatment, and waste disposal. A potential candidate for liquid injection incineration at a temperature range of 650 1600℃ and a residence time 0.1-2 seconds. Also, a potential candidate for rotary kiln incineration at a temperature range of 820 1600℃ and residence times of seconds for liquids and gases, and hours for solids.
Properties of NABAM
| Melting point: | 76-80 °C |
| vapor pressure | Negligible |
| storage temp. | 0-6°C |
| solubility | Methanol (Slightly), Water (Slightly) |
| Water Solubility | ca. 200 g l-1 (room temperature) |
| form | Solid |
| color | Off-White to Pale Yellow |
| Merck | 13,6367 |
| Stability: | Extremely Hygroscopic |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Nabam (142-59-6) |
Safety information for NABAM
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H317:Sensitisation, Skin H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation H410:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P501:Dispose of contents/container to..… |
Computed Descriptors for NABAM
NABAM manufacturer
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 142-59-6 98%View Details
142-59-6 98%View Details
142-59-6 -
 Nabam 99%View Details
Nabam 99%View Details
142-59-6 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1