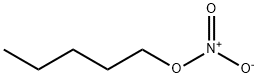
n-Propyl nitrate
- CAS NO.:627-13-4
- Empirical Formula: C3H7NO3
- Molecular Weight: 105.09
- MDL number: MFCD00044556
- EINECS: 210-985-0
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:08:57

What is n-Propyl nitrate?
Chemical properties
White to straw-colored liquid; ethereal odor. Insoluble in water; soluble in alcohol and ether.
Chemical properties
n-Propyl nitrate is a colorless to pale yellow liquid. Ethereal odor.
Physical properties
Colorless to light yellow, flammable liquid with an ether-like odor. Odor threshold concentration is 50 ppm (quoted, Amoore and Hautala, 1983).
The Uses of n-Propyl nitrate
Fuel ignition promoter, in rocket fuel formulations, as organic intermediate.
The Uses of n-Propyl nitrate
Fuel ignition promoter; rocket propellants; organic intermediate.
General Description
A white to straw-colored liquid with an ether-like odor. About the same density as water and insoluble in water. Flash point 70°F. Vapors heavier than air. Used as a fuel. Shock sensitive. The shock sensitivity is removed by addition of 1-2% of propane, butane, chloroform, ethyl ether, or methyl ether.
Air & Water Reactions
Highly flammable. Insoluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
Organonitrates, such as n-Propyl nitrate, range from slight to strong oxidizing agents. If mixed with reducing agents, including hydrides, sulfides and nitrides, they may begin a vigorous reaction that culminates in a detonation. Nitroalkanes are milder oxidizing agents, but still react violently with reducing agents at higher temperature and pressures. Nitroalkanes react with inorganic bases to form explosive salts. The presence of metal oxides increases the thermal sensitivity of nitroalkanes. Nitroalkanes with more than one nitro group are generally explosive. Contact with either strong oxidizers or with combustibles may cause fires and explosions.
Hazard
Flammable, severe fire and explosion risk, strong oxidizing material, explosive limits in air 2– 100%. Nausea and headache.
Health Hazard
Exposure can cause anoxia and cyanosis. Other effects are weakness, dizziness, and severe headaches.
Fire Hazard
Special Hazards of Combustion Products: Toxic gases and vapors, such as oxides of nitrogen and carbon monoxide, may be released in a fire.
Safety Profile
Poison by intravenous route. Inhalation can cause hypotension and methemoglobinemia. Dangerous fire hazard when exposed to heat, flame, or oxidizers. Explosive in the form of vapor when exposed to heat or flame. A shock-sensitive explosive. It can be desensitized by the addition of 1-2% propane, butane, chloroform, dunethyl ether, or dithyl ether. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of NOx. Used as a fuel ignition promoter, chemical intermediate, and in the manufacture of rocket fuels. See also NITRATES and ESTERS.
Potential Exposure
Propyl nitrate has been used as an intermediate as a rocket propellant and as an ignition improver in diesel fuels.
Shipping
UN1865 n-Propyl nitrate, Hazard Class: 3; Labels: 3-Flammable liquid.
Incompatibilities
Vapor may form explosive mixture with air. Reacts with reducing agents, combustible materials; may be violent. A shock-sensitive explosive. The shock sensitivity is removed by addition of 1%?2% of propane, butane, chloroform, ethyl ether, or methyl ether . May explode on heating. Forms explosive mixtures with com- bustible materials. This material is an organonitrate. They can range from slight to strong oxidizing agents. If mixed with reducing agents, including hydrides, sulfides, and nitrides, they may begin a vigorous reaction that culminates in a detonation. Nitroalkanes are milder oxidizing agents, but still react violently with reducing agents at higher tem- perature and pressures. Nitroalkanes react with inorganic bases to form explosive salts. The presence of metal oxides increases the thermal sensitivity of nitroalkanes. Nitroalkanes with more than one nitro group are generally explosive. Contact with either strong oxidizers or with combustibles may cause fires and explosions .
Waste Disposal
Incineration: large quantities of material may require nitrogen oxide removal by catalytic or scrubbing processes . An alternative route suggested involves pouring over soda ash, neutralizing with HCl and flushing to the drain with water.
Properties of n-Propyl nitrate
| Melting point: | -99.99°C |
| Boiling point: | bp762 110°; bp760 84.8° |
| Density | d420 1.0538 |
| vapor pressure | 18 at 20 °C (NIOSH, 1997) |
| refractive index | nD20 1.3979 |
| solubility | Soluble in ether (Weast, 1986) and many alcohols including methanol, ethanol, propanol, and
butanol. |
| form | Clear to yellow liquid |
| Henry's Law Constant | 9.09 at 25 °C (Kames and Schurath, 1992) |
| Exposure limits | NIOSH REL: TWA 25 ppm (109 mg/m3), STEL 40 ppm (170 mg/m3), IDLH
500 ppm; OSHA PEL: TWA 25 ppm; ACGIH TLV: TWA 25 ppm, STEL 40 ppm (adopted). |
| EPA Substance Registry System | n-Propyl nitrate (627-13-4) |
Safety information for n-Propyl nitrate
Computed Descriptors for n-Propyl nitrate
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran



![GLYCEROL DINITRATE, [2-14C]](https://img.chemicalbook.in/StructureFile/ChemBookStructure2/GIF/CB0356600.gif)

You may like
-
 627-13-4 N-propyl nitrate 98%View Details
627-13-4 N-propyl nitrate 98%View Details
627-13-4 -
 N-Propyl nitrate 95% CAS 627-13-4View Details
N-Propyl nitrate 95% CAS 627-13-4View Details
627-13-4 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1